Snowflake vs Oracle - Table of Content
- What is Snowflake?
- What is Oracle?
- Oracle Architecture
- Snowflake Architecture
- Comparing Snowflake with Oracle
- Pro and Cons of Snowflake and Oracle
- Conclusion
What is Snowflake?
Snowflake is a cloud-based Software-as-a-service(SAAS) solution which allows data storage, preprocessing and analysis. It provides an all-in-one software package to support data collection from a variety of sources as well as storage, processing and analysis solutions. Snowflake does not employ any past or existing database technology. Still, its architecture, as well as query engines, are designed from the beginning, specifically to fit the public cloud infrastructure behind it.
All the data of Snowflake is stored on Amazon S3 using a central repository that can be accessible to all the computation instances; it is similar to the shared disk architecture. For its analytical computations, Snowflake uses virtual compute instances where massive parallel compute clusters process user clusters and handle user queries that, in turn, is the same as the share-nothing architecture. Snowflake, therefore, brings together the best of the two approaches to offer speed, flexibility, scalability, and adaptability.
Become a Snowflake Certified professional by learning this HKR Snowflake Training !
What is Oracle?
Oracle is a slightly more traditional database management system that began with relational RDBMS technologies and was improvised with object-relational and multi-model databases. From the past few years, Oracle has shifted its offerings to the Cloud to leverage the benefits of cloud technology. It also presented some of the modern SAAS offerings such as ERPs/CRMs/SCMs/IoT on the Cloud.
Become a Oracle CRM Certified professional by learning this HKR Oracle CRM Training !
Now let us go through the architectural difference between Oracle and Snowflake:
Oracle Architecture:
Oracle has been a leading databasd for running online transaction processing and analytical databases across the industry for more than 40 years. There are three main structures of the Oracle data server. They are Storage structure, process structure and memory structure. The objective of the storage structure is just to keep the data in the databases, and it has a more complex storage architecture. The process is divided into oracle database processes (for main compute), client processes (for user execution) and Oracle Demons, as well as application processes (for the background). The memory stores the shared data as well as the program code, and in the backend engine, there are System Global Areas(SGA) and Program Global Areas (PGA). Basically, PGA is a client-specific memory allocation space dedicated to the users, and SGA is a shared memory pool space connected to all the users.

Want to know more about Oracle Project Accounting, visit here Oracle Project Accounting Training.

- Master Your Craft
- Lifetime LMS & Faculty Access
- 24/7 online expert support
- Real-world & Project Based Learning
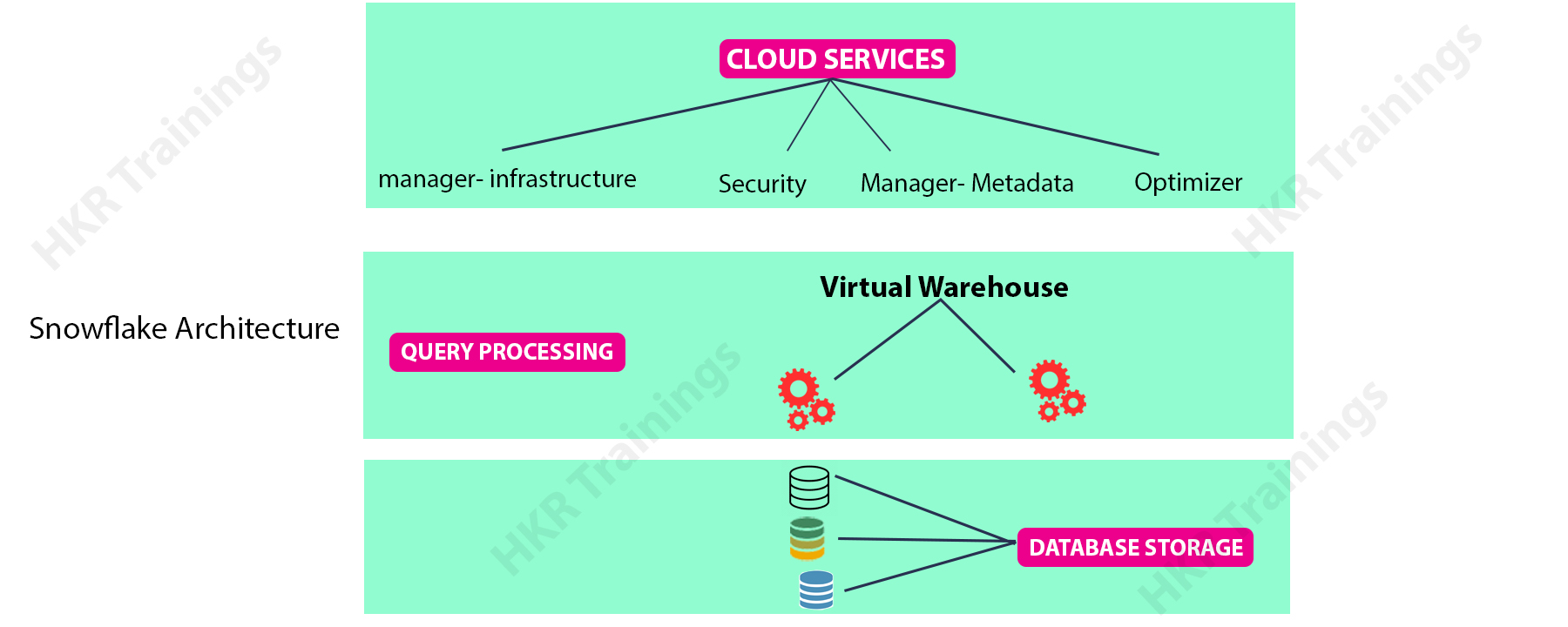
Snowflake Architecture:
Snowflake is a database technology newly brought into the Cloud. The basic design of Snowflake consists of three main components: Services, storage, and compute. Snowflake storage is the same as Oracle storage in which it stores data, which includes relational as well as semi-structured data, in databases. All data is stored in a single layer, so updates are made only once. Compute is the design component which runs the query computations. The dynamic computing infrastructure of Snowflake makes it possible for users to submit a large number of queries that Snowflake assigns automatically to the virtual warehouses, which are capable of accessing storage space without any restraint. The Services will coordinate the execution of all processes in Snowflake, including user verification and security, metadata handling and maintenance of optimized performance. The ability of Snowflake to manage a wide variety of usage scenarios with high performance offers the flexibility and availability needed for the increasing variety of data.
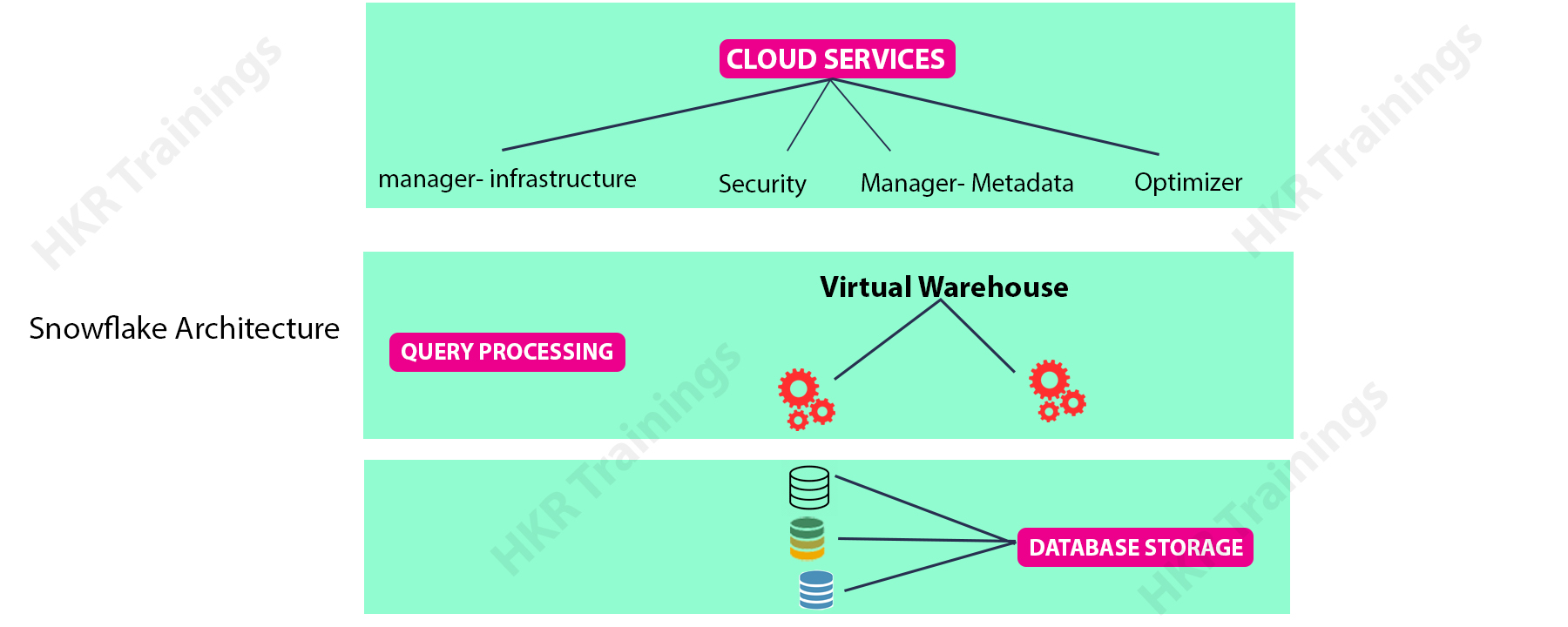
Architectural difference between Snowflake and Oracle:
When we compare Oracle and Snowflake architecture, Oracle data servers have three main structures: Storage structure(to store the data), process structure(divided into oracle database processes for main compute, client processes and Oracle Demons and application processes) and memory structure(to store the shared data and program code). It also consists of a client-specific memory allocation space (PGA) and a shared memory pool space(SGA) connected to all the users. While Snowflake architecture includes the components Services, storage, and compute. Snowflake storage is the same as Oracle storage in which it stores data, Compute is to run the computations and services are to coordinate the execution of all processes.
Oracle Core Storage Units are referred to as data blocks which store persistent pieces of data which will be connected with each other. While the storage of Snowflake is arranged in micro-partitions rooted in a columnar format. Using this structure, the systems that run Snowflake do not need to read useless data but can identify which columns or rows are required by micro partitioning. By default, Oracle needs processing exponential amounts of unwanted data because it must read through complete rows. Many times, users are required to access information only in some column that Snowflake can retrieve easily because of its columnar format, whereas Oracle does not manage to do this effectively because it has to read a whole row before finding that column.
Comparing Snowflake with Oracle:
Now let us compare how Oracle and Snowflake differ technically and in terms of features, performance, and more.
- Workload: Workload in Oracle is Transactional or Analytical, while in Snowflake, the workload is Analytical.
- Deployment: When it comes to Oracle, deployment can be done on-premise or on Oracle cloud, while for Snowflake, deployment can be done in public Cloud that includes AWS Microsoft(Azure) and Google.
- Cost: Oracle costs fixed prices for every user, CPU core, and support options. While Snowflake offers flexible charges, it provides you with the feature pay per usage. It follows per-second billing.
- Databases: Database types supported by Oracle are Transactional, Relational, OLTP, but for Snowflake, the Database type supported is OLAP.
- Availability and Recoverability: Oracle requires manual intervention and high technical experience to develop a plan in terms of availability and disaster recoverability. But in Snowflake, it is automatically done as it is on the Cloud.
- Upgrades, patches and fixes: For Oracle, a database administrator is required for the frequent updates, While for Snowflake, they are automatically done for the users by the company.
- Scaling, Indexing, partitioning: In the Oracle database management system, Managing tasks like Indexing, Scaling, partitioning, etc., are to be done manually by the database administrator. For scaling up, additional costs are applied, but downscaling will not decrease the costs. However, in Snowflake, all these activities will be managed by Snowflake itself automatically. When we downscale, the costs will be reduced.
- Solution Strategy: Oracle was originally developed when the computer applications and usage were well-structured and of limited scope. Relational databases were adequate to meet the computer needs of that time. There was no expectation that the programs would be flexible or smart enough to accommodate certain expected input/output changes. In brief, computers have been used in a limited number of areas such as payroll, statistics, science, programming, etc. On the other hand, computers are everywhere these days, from the microwave to the cars, from telephones to the Cloud. Companies have many unstructured data streamed, which comes from disparate sources. They have heavy and different computing needs. The greater part of the human population is computer-related in one way or another. Snowflake is the modern software that can manage many types of data and carries out powerful analytics to provide you with valuable information about your business processes.
- Time Era ad Paradigm: Oracle was brought into an era where memory was a highly expensive and rare resource. Most developed commercial programs have used most of their code to handle memory and less code by effectively delivering the useful work that they claimed to complete successfully. While Snowflake has been introduced into an era in which the memory is a million times less expensive, resources and computing hardware are very, very powerful. The majority of commercial programs that are developed today use cloud computing to meet complex computing requirements and provide scalability, availability, collaborative efficiency and reliability. So, Oracle looks more like an on-premise offering, while Snowflake is like a scalable cloud-based offering

Pro and Cons of Snowflake and Oracle
Pros of Snowflake:
Following are some of the benefits of Snowflake:
- Scalability: Users can create an unlimited number of virtual warehouses practically, each running its workloads based on its database data. Users can easily resize the number of nodes in every cluster for best performance.
- Automatic Performance tuning: Snowflake features an integrated automatic query performance optimization through a query optimization engine, without the need for the users to modify the settings manually.
- Strong data security: Snowflake features a great variety of leading data security features across the industry along with IP enable and block lists, automatic 256-bit AES encryption and multi-factor authentication. Snowflake complies with the data security standards like PCI DSS, HIPAA, and SOC 1 & SOC 2.
Cons of Snowflake:
Following are some of the drawbacks of Snowflake:
- Lack of synergy: Snowflake may run in the Google, Amazon, and Microsoft public clouds; this is not a native offering. Public clouds like Amazon Redshift, Microsoft Azure SQL Data Warehouse, Google Bigdata, etc., provide their own cloud data warehouse solution. This indicates that users may miss the advantages of a more closely integrated cloud ecosystem.
- Higher cost: According to the use case, Snowflake may be higher priced than competitors like Amazon Redshift.
Become a Snowflake Certified professional by learning this HKR Snowflake Training in Bangalore!
Pros of Oracle:
Following are some of the benefits of Oracle:
- Oracle will support huge databases, data type numbers, and characters, as well as give data in support of object-oriented database storage.
- It can manage more than one database using a two-phase commit protocol.
- Oracle supports cursors, making it easier to program.
- It also carries out every transaction individually, and each transaction result is invisible to the other transactions till it is finished, that increases the data security.
Cons of Oracle:
Following are some of the drawbacks of Oracle:
- The complexity of the Oracle database is a significant drawback.
- Oracle usage is not ideal when users do not have the technical capabilities and expertise to work with the Oracle databases. Nor is it for individuals seeking an easy-to-use database with core functionality.
- Oracle is useful when there is a need for a large database. It is inappropriate for small and medium companies where small databases are enough.
Top 30 frequently asked Snowflake Interview Questions !
Weekday / Weekend Batches
Which is Better?
In comparing Oracle with Snowflake, both are Scalable, and the best results are observed with the right size of the hardware. There are also higher costs associated with assigning more hardware on both platforms in terms of pricing. But it's also very tough to compare prices directly. Oracle charges the prices by OCPU and disk space, while Snowflake costs for operating warehouses, according to size. Since these warehouses are normally suspended when queries are not running, the calculation of the price is different from an Oracle ADW. But when the question "Which among Oracle and Snowflake databases is better?" then the answer will be "It depends on the needs of the organization".
Conclusion:
In this blog, we have seen what Oracle and Snowflake are, their architecture, compared their features, and learned their pros and cons. We hope now you have enough knowledge of Snowflake and Oracle databases and their differences. For more blogs like this, Stay tuned to HKR Trainings.
Related Articles:
About Author
As a senior Technical Content Writer for HKR Trainings, Gayathri has a good comprehension of the present technical innovations, which incorporates perspectives like Business Intelligence and Analytics. She conveys advanced technical ideas precisely and vividly, as conceivable to the target group, guaranteeing that the content is available to clients. She writes qualitative content in the field of Data Warehousing & ETL, Big Data Analytics, and ERP Tools. Connect me on LinkedIn.
Upcoming Snowflake Training Online classes
| Batch starts on 26th Feb 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 2nd Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 6th Mar 2026 |
|

