Powerapps variables
In the world of PowerApps, variables play a pivotal role as temporary storage elements, essential for dynamic app development. PowerApps offers three distinct types of variables, each with unique features and use cases
Become a PowerApps Certified professional by learning this HKR PowerApps Training !
Global Variables:
Global variables are akin to universally accessible containers in PowerApps, holding various data types like text, numbers, tables, records, or booleans. These variables are accessible across all screens within a PowerApps app. For instance, creating a global variable is simple:
Set(global_variable, “Example”)
In this example, global_variable represents the variable name, and "Example" is its assigned value.
Key Points to Remember
- Global variables can save multiple data types.
- Their scope is across the App.
- Creating a global variable requires the Set() function.
- Use the Blank() function to reset a global variable.
How to Create a Global Variable in PowerApps?
- To begin, initiate a new Canvas App project by selecting the "Canvas App from blank" option in PowerApps.
- Name your app "GlobalVariable" and opt for the Tablet layout.
- Navigate to the insert menu and incorporate a label, a text input field, and a button into your canvas.
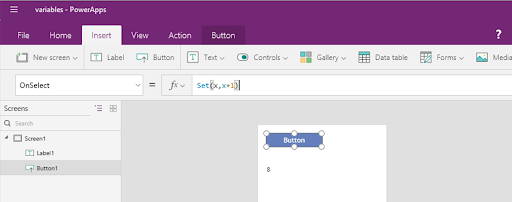
- Focus on the button and alter its OnSelect formula to:
- Set(Global_Variable, FirstInput.Text)
- Next, target the label and adjust its text formula to simply:
- Global_Variable
- To get an overview of the global variables, you can access the file menu and choose the variables. This section displays all global variables present in your App. Clicking on a variable will reveal its definition points and usage instances throughout the App.
- This App is specifically built to update and restore the variable's value. It is based on the input within the text field, showing this value in the label.
Become a Power Automate Certified professional by learning this HKR Power Automate Training

PowerApps Training
- Master Your Craft
- Lifetime LMS & Faculty Access
- 24/7 online expert support
- Real-world & Project Based Learning
Context Variables:
Context variables in PowerApps are similar to method parameters in traditional programming. The scope of these variables is limited to the screen as they are defined. To declare a context variable, use:
UpdateContext({context_variable: ”Example”})
Context_variable is the variable name; the value is shown by "Example." These variables are defined within curly braces and support various data types.
How to Create a Context Variable in PowerApps?
- Choose "Canvas App from blank" in PowerApps.
- Enter "ContextVariable" as the app name and select the Tablet layout.
- Add a label, text input, and a button from the insert menu.
- Please select the button and adjust its OnSelect formula to UpdateContext({context_variable: FirstInput.Text}).
- Alter the text formula within the label field to context_variable.
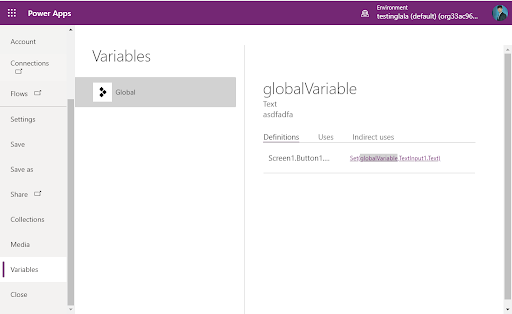
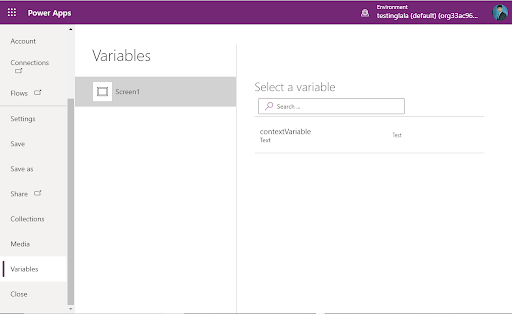
- To view all Context variables, go to the file menu, then select variables. It shows all screens in the application.
- Select a screen to view all the context variables associated with it, including where they are defined and used.
- The application will update and display the variable's value in the label as per the input in the text field.

Subscribe to our YouTube channel to get new updates..!
Collections:
Collections are akin to tables or arrays in PowerApps, capable of storing multiple rows of data. They are application-wide variables. Moreover, collections are created using:
Collect(collect_variable, “Example”)
collect_variable here is the collection's name, and "Example" is its initial value.
Building Collections in PowerApps
- Choose 'Canvas App from blank' to start your PowerApps project.
- Name your App (e.g., CollectionVariable) and select a layout.
- Add a data table, text inputs, and buttons to your canvas.
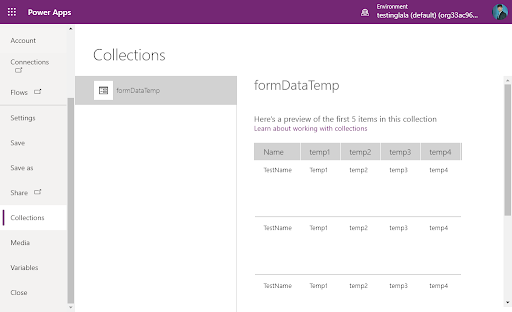
- Set up a collection using the Collect function in a button's OnSelect property.
- Use a data table to display the contents of the collection.
Top 30 frequently asked PowerApps Interview Questions !
Conclusion:
This exploration of PowerApps variables has delved into creating and managing global variables, context variables, and collections. These elements are the foundation for building robust and dynamic apps in PowerApps. Stay tuned to HKR Trainings for more insights like these into PowerApps and other technologies.
Related Articles:
About Author
As a content writer at HKR trainings, I deliver content on various technologies. I hold my graduation degree in Information technology. I am passionate about helping people understand technology-related content through my easily digestible content. My writings include Data Science, Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence, Python, Salesforce, Servicenow and etc.
Upcoming PowerApps Training Online classes
| Batch starts on 18th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 22nd Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 26th Mar 2026 |
|