Overview of the SAP PM Module
SAP PM (plant maintenance) is also an important functional module that helps the organization to maintain its business activities. The key functionalities of the SAP PM module include are;
- Inspection
- Notifications
- Corrective
- Preventive maintenance
- Repairs
- Other measures are used to maintain the technical system.
The SAP plant maintenance application components offer the organization several tools, with the help of these tools maintenance activities can be performed. All the SAP plant maintenance module activities are interconnected, and hence they closely integrate with other functional modules like Production planning, Material management (MM), and sales and distribution (SD). The SAP PM module also allows users to record problems in the SAP system, labor planning, material activities, and settling the costs.
To perform all the above-mentioned activities, the Plant maintenance module contains the following sub-modules.
- Managing the technical objects and equipment master record.
- Planning of the task manager.
- The workflow notification management and work order management.
Become a SAP PM Certified professional by learning this HKR SAP PM Training !
The key functions of the SAP PM module
The following are the main functions of the SAP plant maintenance module. Let us explain one by one;
Inspection:
Inspection is an integral part of any product development process, and it will check for the condition of the technical systems.
Preventive maintenance:
Preventive maintenance sometimes plays a crucial role while checking for high-level technical systems.
Repair:
Repairing is a process where all the necessary measures can be taken to restore the performance under ideal conditions. This repair process can be done at many stages they are;
- Work scheduling
- Resource planning
- Initial costing
The repair process also enables users to respond immediately concerning the damage event that caused the production to shut down. One more thing, with the help of the repair process users, can also create a purchase requisition and also processes the work order to reduce the labor working time.

SAP PM Training
- Master Your Craft
- Lifetime LMS & Faculty Access
- 24/7 online expert support
- Real-world & Project Based Learning
Integration of SAP PM with other SAP modules
As I mentioned before the SAP PM module integrates with other SAP modules, are product planning, material management, controlling, personnel management, sales, and distribution. These modules are closely interconnected with the SAP PM module to keep the current data as per the requirements, and automatically initiate to maintain the current data systems.
The following diagram explains the work process/workflow of the SAP PM module;
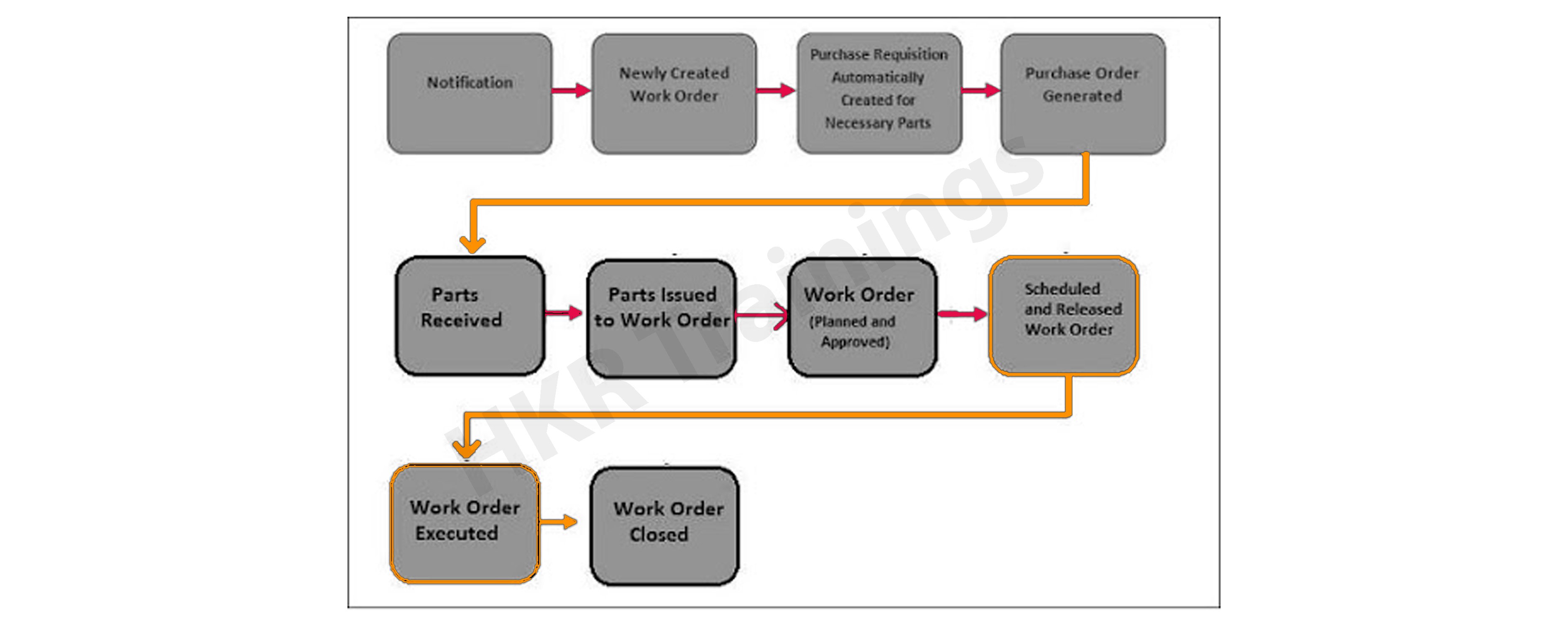
The key steps involved in the SAP PM are;
- Notification
- Newly created work order
- Creation of the purchase request for work orders
- Purchase order created and parts received.
- Parts issues to work order.
- Approval and planning of the work order.
- Scheduling and releasing work orders.
- Work order execution.
- Closing a work order.
SAP PM - technical objects
To manage SAP activities effectively in the organization, users need to divide the existing maintenance activities into technical objects. The main purpose to use technical objects is to define the machine types objects that exist in the organization.
Most importantly, to define the technical objects in the organization, it is mandatory to know the maintenance planning and the structure.
Let us know the technical objects one by one;
Maintenance plant:
a maintenance plant is a technical object, simply we call it a plant. The maintenance plant enables users to manage all the activities. Here we have listed a few activities of the maintenance plant, they are;
- Helps in defining the task lists as per the maintenance plan.
- Performs material planning as per the BOM lists.
- Helps to manage and schedule the maintenance plan.
- Creates and executes all the maintenance orders.
Maintenance planning:
maintenance planning can be performed as per the structure of an organization.
The following are the important types of maintenance planning:
- Centralized maintenance planning
- Decentralized maintenance planning
- Partially centralized maintenance planning.
Now it’s time to know them in brief;
Centralized maintenance planning:
- The following are the structures that are performed under the centralized maintenance planning;
a. There is only one plant available for all the technical objects that are the maintenance planning plant/maintenance plant.
b. In rare scenarios, where organizations need multiple plants, but these can be used according to the maintenance plant.
Important t-codes used in the maintenance plant;
Plants -> 001, 002
Maintenance plants -> 001, 002
Maintenance planning plant -> 002
Plants assigned to maintenance planning plant -> 001
- Decentralized maintenance planning: in some scenarios, some organizations consist of multiple plants and they act as a maintenance planning plant.
The following are the important t-codes used;
Plants -> 001, 002
Maintenance plants -> 001, 002
Maintenance planning plants -> 001, 002
- Partially centralized maintenance planning: the plants which are not responsible for maintenance planning, they consider as Partially centralized maintenance planning.
The following are the important t-codes used;
Plants -> 001, 002, 003, 004
Maintenance plants -> 001, 002, 003, 004
Maintenance planning plants -> 001, 004
Plants assigned to maintenance planning plant 001 -> 001, 002
Plants assigned to maintenance planning plant 004 -> 003, 004
Get ahead in your career with our SAP PM Tutorial !

Subscribe to our YouTube channel to get new updates..!
Structure of technical objects
There are various kinds of structures used to define technical objects. They are;
Functional structuring:
this type of structure helps to divide the technical system that depends on the functional locations. Not only is a technical object considered a functional location, but the product line also comes under the functional location group.
Object-related structuring:
in this type of structuring, the technical system can be divided into different pieces known as “Pieces of equipment”. The users can also consider equipment as an individual object, later which are placed in the technical system or a part of the technical object.
Functional and object-oriented structuring:
this is a combination of both the object-oriented and functional structures they make use of types of equipment, and they are further divided into functional locations.
Note: The functional structuring can also be used to manage the technical objects in an organization. For example, the technical objects can be of functional areas, process, or spatial criteria.
The following are the few tasks, which are performed by the functional structuring;
- Functional area example: pumping station
- Process related criteria: modeling
- Spatial criteria example: storeroom
Top most frequently asked SAP PM Interview Questions & Answers for freshers & experienced professionals
How to create a functional location?
In this section, we are going to explain how can we create a functional location in the organization.
A step by step guide;
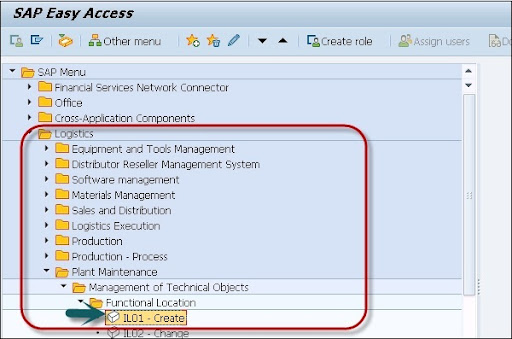
1. The navigation to create the functional location; Go to SAP Access Menu -> select Logistics -> Plant maintenance -> management of technical object -> functional location -> create as shown in the below image.
2. A new window will pop up-> then select the structure indicator -> click continue.
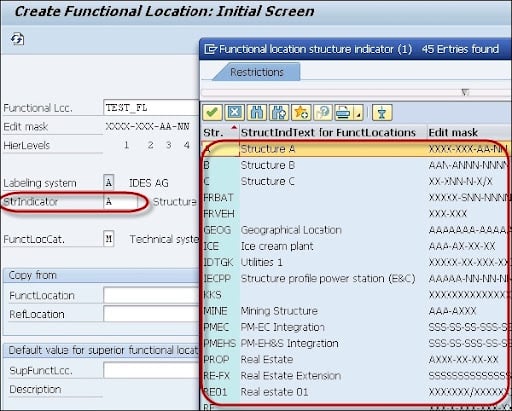
In this image, you can see that the system displays the edit mask for the functional location label as well as the hierarchy level.
3. Now select the functional location label and a technical location as a reference -> then click on the “Continue” button.
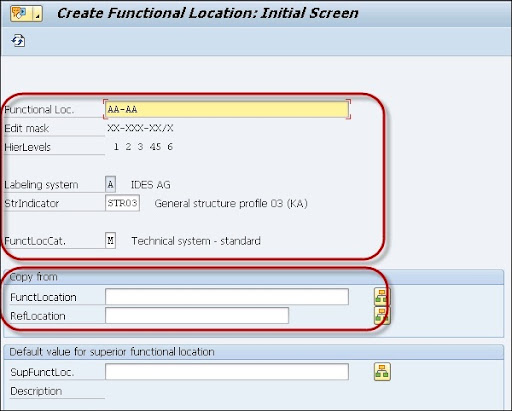
4. A new window will pop up -> now create the master data for the functional location -> if you want to create the classification -> click on the “Classification” button
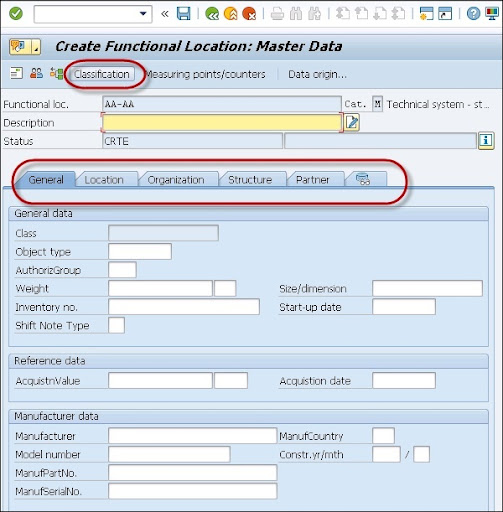
5. Once you click on the classification -> it will create the functional location classification window as shown below;
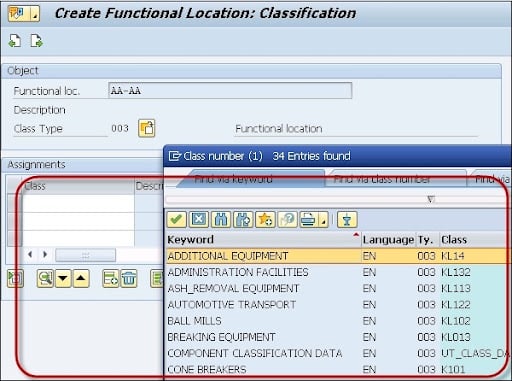
6. Now enter the classes to assign the functional location in the column classes.
7. Now select the class to decide on which is the standard class -> choose the functional location standard class.
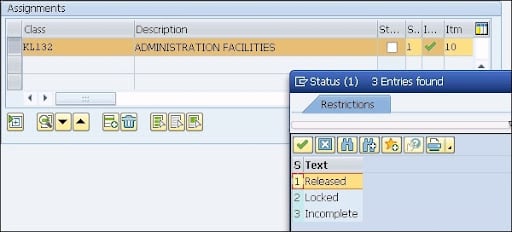
8. To specify the value entries for the classes assigned, position the cursor on the class name where you want to create the class entries.
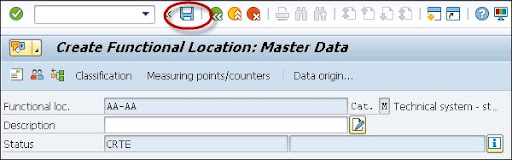
9. Now select the status for the functional location as shown below;
10. Once you specify all the fields for the master record -> then go to the main screen by using arrow buttons -> then click on the “save” button to save all the entries.
Final words
In our previous articles, we explained the important things which are related to the Sales and distribution functional module. As per our audience demand, then we thought why not begin with a new SAP module, then what comes to our mind is the SAP PM module. This SAP PM module article is the best example of an easier and simple version to gain more knowledge concerning the topic. This article helps you to get some basic idea about the SAP PM module, in future articles you will be learning core concepts of the PM module. If you need any assistance regarding articles, please visit our website to learn more.
Related Articles:
About Author
Kavya works for HKR Trainings institute as a technical writer with diverse experience in many kinds of technology-related content development. She holds a graduate education in the Computer science and Engineering stream. She has cultivated strong technical skills from reading tech blogs and also doing a lot of research related to content. She manages to write great content in many fields like Programming & Frameworks, Enterprise Integration, Web Development, SAP, and Business Process Management (BPM). Connect her on LinkedIn and Twitter.
Upcoming SAP PM Training Online classes
| Batch starts on 9th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 13th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 17th Mar 2026 |
|

