Arithmetic operators
To perform calculations like addition, subtraction, division, etc. between two operands, we can use the arithmetic operators.The below table gives an explanation of all the arithmetic operators.
Become a python Certified professional by learning this HKR Python Training !
Here is a small program that performs all the arithmetic operations on two variables. Let’s take two operands as an example, and see what the results are going to be when we use different operators on them.
a = 10
b = 4
print(‘a+b = ’, a+b)
print(‘a-b = ’, a-b)
print(‘a*b = ’, a*b)
print(‘a/b = ’, a/b)
print(‘a%b = ’, a%b)
print(‘a//b = ’, a//b)
print(‘a**b = ’, a**b)
Here is the output for the above program,
a+b = 14
a-b = 6
a*b = 40
a/b = 2.5
a%b = 0.4
a//b = 2
a**b = 10000
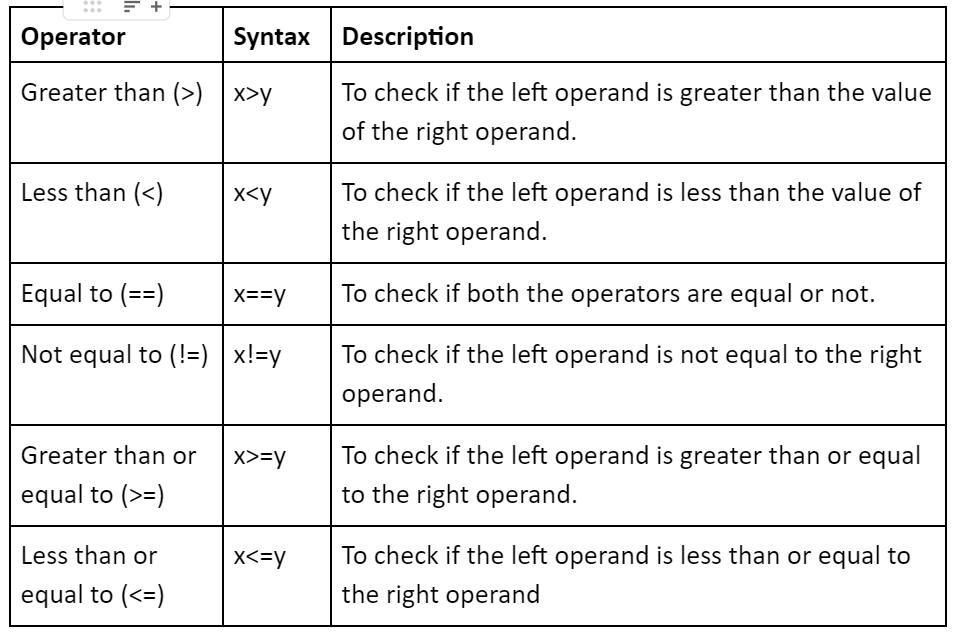
Comparison operators
To compare the values of two operands,we can use the comparison operators.The result of these operators is either true or false i.e. a boolean value.Let’s take look at all the available comparison operators.
Here is a program that contains all the comparison operators.
a = 10;
b = 4;
print('a>b is ', a>b)
print('a
print('a==b is ', a==b)
print('a!=b is ', a!=b)
print('a>=b is ', a>=b)
print('a
The output for the above program will be as follows.
a> b is True
a
a==b is False
a!=b is True
a>=b is True
a

Python Training Certification
- Master Your Craft
- Lifetime LMS & Faculty Access
- 24/7 online expert support
- Real-world & Project Based Learning
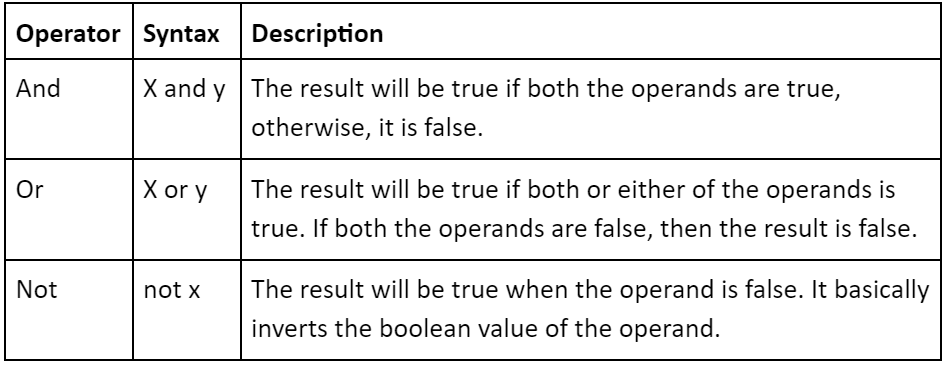
Logical operators
To check if the operands satisfy a specific condition, we can use logical operators.It is mainly used for decision making.The following table explains the logical operators.
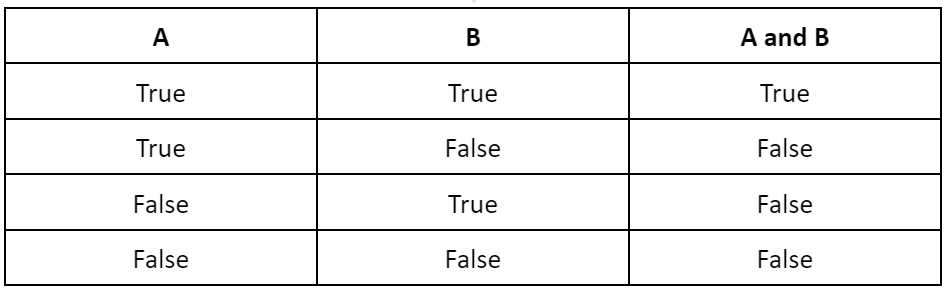
Here is the truth table for the ‘and’ operator.
Here is the truth table for the ‘or’ operator.
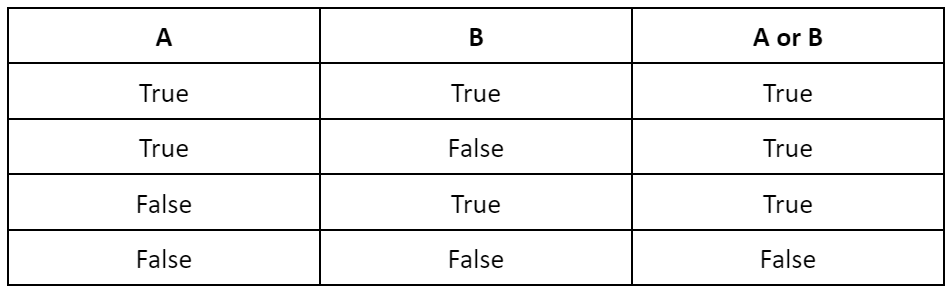
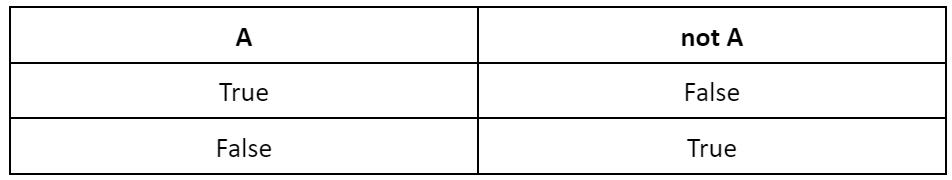
Here is the truth table for the ‘not’ operator.
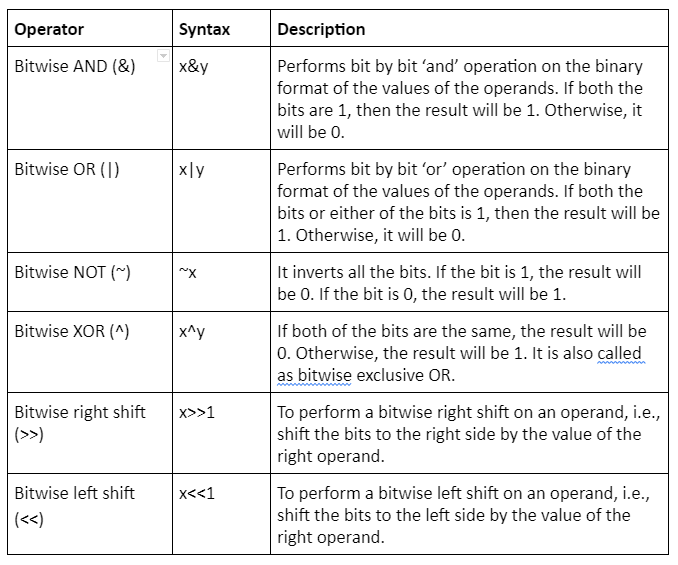
Bitwise operators
We can use bitwise operators to compare the numbers in binary format.They operate bit by bit on the binary format of the numbers.
Let’s consider a = 10 (0000 1010) and b = 5 (0000 1011) in binary formats as example.
a = 10
b = 5
Print('a&b = ', a&b)
Print('a|b = ', a|b
Print('~a = ', ~a)
Print('a^b = ', a^b)
Print('a>>1 = ', a>>1)
Print('a
The output for the above program will be as follows. Let me add the binary format for the output values for a better understanding.
a&b = 10 (0000 1010)
a|b = 13 (0000 1011)
~a = 5 (0000 0101)
a^b = 1 (0000 0001)
a >> 1 = 5 (0000 0101)
a
Assignment operators
We can use assignment operators to assign values to variables. We can use the assignment operator along with an arithmetic operator. In this case, the arithmetic operation will be performed first, and then the value will be assigned to the variable.

The below program shows the usage of the assignment operators.

Subscribe to our YouTube channel to get new updates..!
a = 5
print("a = 5 is ", a)
a += 20
print("a += 20 is ", a)
a -= 5
print("a -= 5 is ", a)
a *= 6
print("a *= 6 is ", a)
a /= 2
print("a /= 2 is ", a)
a %= 4
print("a %= 4 is ", a)
The output for the above program will be as follows.
a = 5 is 5
a += 20 is 25
a -= 5 is 20
a *= 6 is 120
a /= 2 is 60.0
a %= 4 is 0.0
Top 50 frequently asked Python interview Question and answers !
Identity operators
To check if two operands share the same memory location or not, we can use the identity operators.It doesn't mean that the two variables are the same, but they are of the same object.These come under the special operators’ category in python.

Here is a program that explains the identity operators.
a = ["hello", "hi"]
b = ["hello", "hi"]
c = a
print("a is c = ", a is c)
print("a is b = ", a is b)
a = [1, 2]
b = [1, 2]
c = b
print("a is not c = ", a is not c)
print("b is not c = ", b is not c)
The following is the output for the above program.
a is c = True
a is b = False
a is not c = True
b is not c = False
Membership operators
To check if a value or variable is found in a sequence or not, we can use membership operators.These come under the special operators’ category in python.

Here is a sample program that explains the usage of the membership operators.
a = ["hello", "welcome"]
b = "hello"
print("b in a = ", b in a)
print("welcome in a =", "welcome" in a)
a = [1, 2]
b = 3
print("b not in a = ", b not in a)
print("2 not in a = ", 2 not in a)
The output of the above program is as follows.
b in a = True
welcome in a = True
b not in a = True
2 not in a = False
Order of precedence of python operators
An expression might have more than one operator. An order of precedence guides the order in which the operations should get executed. In an expression, the operator with the highest precedence will get executed first, and then the lowest precedence operator will get executed. It is very important to learn the order of precedence of python operators. The following table lists the order of precedence of operators from highest to lowest.
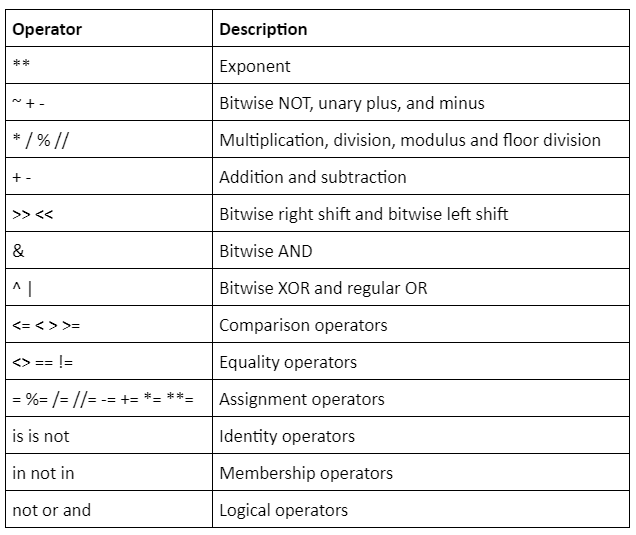
Let’s take a look at an example with a simple program.
a = 8
b = 7
c = 4
d = 11
e = a + b * d / c
f = d - a * b + c / a
print(“The value of a + b * d / c is”, e)
print(“The value of d - a * b + c / a is”, f)
The output for the above program is,
The value of a + b * d / c is 27.25
The value of d - a * b + c / a is -44.5
Parenthesis plays an important role in changing the precedence. If you want a certain operation to be performed first in your expression, wrap it in parenthesis. Let’s take the same program mentioned above and see how the output changes when parenthesis is used in the expressions.
a = 8
b = 7
c = 4
d = 11
e = (a + b) * d / c
f = (d - a) * b + (c / a)
print('The value of (a + b) * d / c is', e)
print('The value of (d - a) * b + (c / a) is', f)
The output for the above program will be as follows.
The value of a + b * d / c is 41.25
The value of (d - a) * b + (c / a) is 21.5
Conclusion
Python operators are the core fundamental concept.It is popular for a variety of operators that it provides.That is the reason python is the most preferable language by most of the developers. In this blog,we have discussed in detail about each of the python operators.
Now that you know about operators,you can start writing programs in python for your applications.Play around with the operators,use them in conditions.Create compound expressions with a combination of operators to master them.Remember the order of precedence and parenthesis to set priority for your calculations.Have fun with python coding!
Related Articles:
5. Python Pop
About Author
As a senior Technical Content Writer for HKR Trainings, Gayathri has a good comprehension of the present technical innovations, which incorporates perspectives like Business Intelligence and Analytics. She conveys advanced technical ideas precisely and vividly, as conceivable to the target group, guaranteeing that the content is available to clients. She writes qualitative content in the field of Data Warehousing & ETL, Big Data Analytics, and ERP Tools. Connect me on LinkedIn.
Upcoming Python Training Certification Online classes
| Batch starts on 6th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 10th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 14th Mar 2026 |
|

