Snowflake Data sharing - Table of Content
- Data Sharing in Snowflake
- Data sharing with non-Snowflake users
- Snowflake data share
- Performing data sharing using the web UI
- Data sharing using SQL Commands
- Conclusion
Data Sharing in Snowflake:
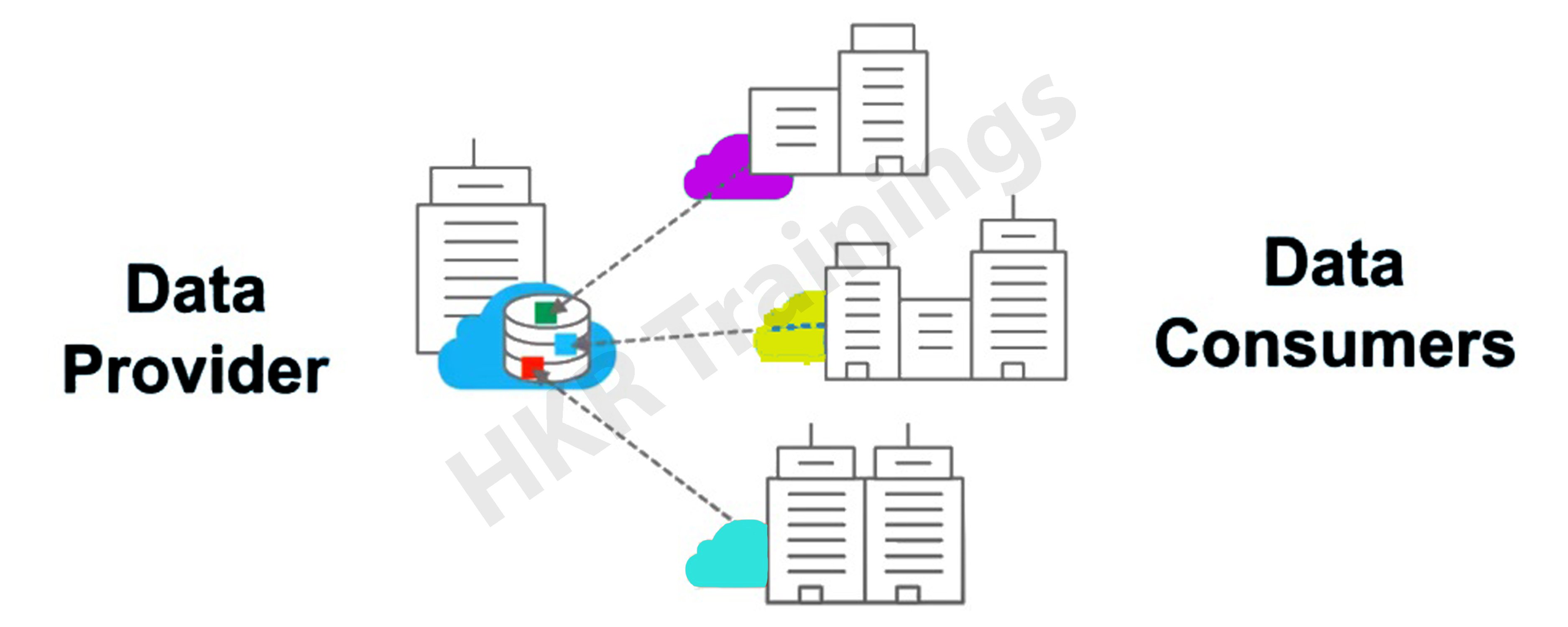
Snowflake utilises data sharing to distribute the latest details to all Snowflake accounts:
- Dataset and
- Data on account usage
The term "secure data sharing" refers to the fact that no relevant figures are copied or converted between accounts. Because all communication is done through Snowflake's distinctive services layer as well as metadata store, shared data doesn't really take up any data storage in a consumer account and thus does not make a contribution to the consumer's quarterly data storage charges.
Become a Snowflake Certified professional by learning this HKR Snowflake Training !
When designers generate the shares and give them a catchy name. First-class Snowflake objects which contain all of the data necessitate the sharing of a database.
Each share includes the following components:
- The privileges that allow access to the database and the schema containing the shared objects.
- The permissions that allow access to specific objects (tables, secure views, and secure UDFs).
- The consumer accounts that have access to the database and its objects.
- Shares are secure, configurable, and completely controlled by the provider account (the account that is sharing the dataset)
New objects added to a share are immediately available to all consumers, allowing them to access shared data in real time.Access to a share (or any of its contents) can be revoked at any time.
Data sharing with non-Snowflake users:
Hardly data sharing among Snowflake accounts is endorsed. As a database server, you might just want to share information with an end user who still does not have a Snowflake account and/or has not yet been ready to get to be a licenced Snowflake customer. Snowflake claims to support suppliers in creating audience account balances in facilitating information exchange with these consumers. Reader account holders (previously known as "read-only accounts") offer a quick, simple, and cost-effective way to share data without requiring the consumer to become a Snowflake customer. Users with a reader account can query information which has been communicated with them, but they cannot perform any DML tasks that really are available to full account users (data loading, insert, update, etc.).

Snowflake Training
- Master Your Craft
- Lifetime LMS & Faculty Access
- 24/7 online expert support
- Real-world & Project Based Learning
Snowflake data share:
Snowflake data sharing actually does work because of its multi-cluster shared information architecture, which allows any snowflake customer (data consumer) who wishes to communicate information with someone to grant other organisations live access to data via a secured network. Instead of being physically transferred to the customer, the data is kept in the provider's account and is accessible and visible to the consumer via SQL.
Get ahead in your career with our Snowflake Tutorial !

Subscribe to our YouTube channel to get new updates..!
Performing data sharing using the web UI:
Step1: Creating the share account
We must first create the person account with whom we will share the account. In Snowflake, we can create user accounts or readers accounts as needed:
For example, in this example, we will see how to create a Readers account.
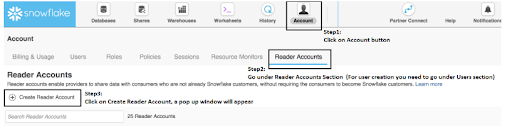
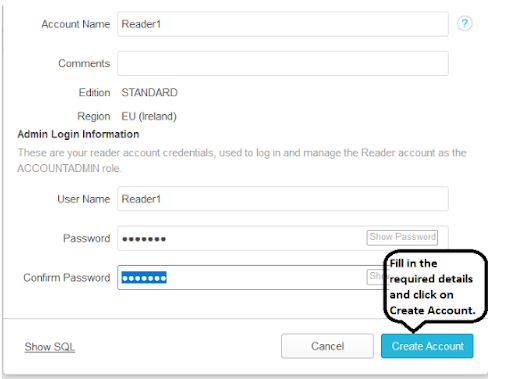
Now the reader account is created, next you need to create the snowflake user account.
Step2: creating the share
If you have the ACCOUNT ADMIN role (or a role that has been granted the CREATE SHARES privilege), you can perform most tasks related to creating and managing shares by clicking the Shares button on the menu list in the Snowflake web interface.
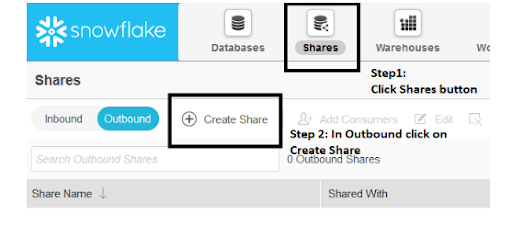
Next click on the create share option, a window will be opened , fill in all the details.
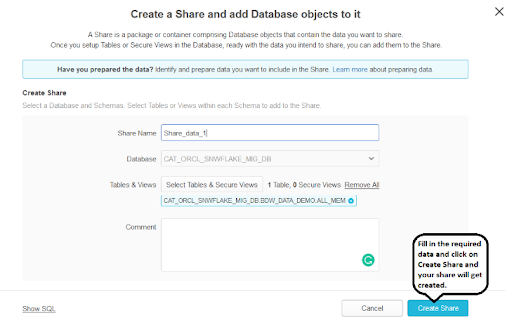
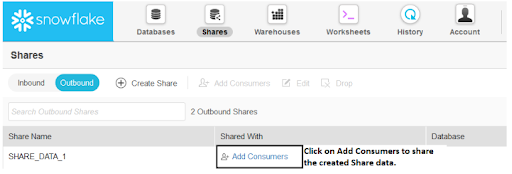
Once a share has already been invented in the UI, the consumer can be added. br />A pop-up window appears, allowing you to select the accounts with which you want to share the data.

Top 30 frequently asked snowflake interview questions & answers for freshers & experienced professionals
Data sharing using SQL Commands:
The same steps can be performed in worksheets using SQL commands.
Step 1: Make a Share.
You can follow these steps in worksheets once the accounts for the clients with whom we need to share the data have been created.
To make a share, use CREATE SHARE. At this point, the share is merely a container awaiting the addition of objects and accounts.
Step 2: Grant Privileges to Add Objects to the Share
GRANT privilege>... TO SHARE to grant the share the following object privileges:
- ON THE DATABASE YOU WISH TO SHARE, YOU MUST HAVE THE USAGE PERMISSION.
- You must have the USAGE privilege on each database schema that contains the objects you want to share.
- In each shared schema, use the SELECT privilege to share specific objects (tables, secure views, and secure UDFs).
- SHOW GRANTS can be used to view the share's object grants.
Step3:Add an Account or Accounts to the Share
ALTER SHARE can be used to add one or more accounts to the share. SHOW GRANTS can be used to view the accounts that have been added to the share.
It is critical that the person sharing the DB has the DB owner rights, or else the issue will be granted insufficient permission.
That's all! The share has become suitable for consumption by the designated accounts.
Example:
The following illustration depicts the entire provider process as described above.
It should be noted that the following assumptions are made in this example:
There is a database called sales db, which has a schema called aggregates eula and a table called aggregate 1.
Two accounts, xy12345 and yz23456, will have access to the database, schema, and table.
USE ROLE account admin;
CREATE SHARE sales_s;
GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE sales_db TO SHARE sales_s;
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA sales_db.aggregates_eula TO SHARE sales_s;
GRANT SELECT ON TABLE sales_db.aggregates_eula.aggregate_1 TO SHARE sales_s;
SHOW GRANTS TO SHARE sales_s;
ALTER SHARE sales_s ADD ACCOUNTS=xy12345, yz23456;
SHOW GRANTS OF SHARE sales_s;
Restrictions for the shared databases:
Consumers face some serious limitations when using shared databases:
- Databases that are decided to share are read-only. Users with a consumer account can view and query data but cannot insert, update, or create objects in the database.
- The actions listed below are not permitted:
- Time travel for a shared database or indeed any schemas/tables within the database.
- I'm working on modifying the commentary for a shared database.
- Shared databases as well as all database objects cannot be forwarded.
Conclusion:
In the above blog post we had discussed the snowflake data sharing and steps to create the shared accounts in a detailed way. If you have any doubts please drop them in the comments section to get them resolved.
Related Articles:
About Author
As a senior Technical Content Writer for HKR Trainings, Gayathri has a good comprehension of the present technical innovations, which incorporates perspectives like Business Intelligence and Analytics. She conveys advanced technical ideas precisely and vividly, as conceivable to the target group, guaranteeing that the content is available to clients. She writes qualitative content in the field of Data Warehousing & ETL, Big Data Analytics, and ERP Tools. Connect me on LinkedIn.
Upcoming Snowflake Training Online classes
| Batch starts on 11th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 15th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 19th Mar 2026 |
|

