Snowflake Architecture - Table of Content
- Features of snowflake data warehouse
- Snowflake Architecture
- Snowflake Architecture: Hybrid model
- Conclusion
Snowflake data warehouse:
Snowflake seems to be a SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) cloud-based Data Warehouse solution that supports ANSI SQL and also has a distinctive architecture that allows users to simply create tables and begin querying data with very little administration or DBA activities required.
Become a Snowflake Certified professional by learning this HKR Snowflake Training !
Features of snowflake data warehouse:
Let's go over some of the key features of the Snowflake data warehouse:
- Snowflake data warehouse provides enlarged authentication through Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), federal authentication, Single Sign-on (SSO), and OAuth. TLS secures all interaction between the customer and the server.
- Standard and Extended SQL Support: Snowflake data warehouse supports the majority of SQL DDL and DML commands. Advanced DML, transactions, lateral views, stored procedures, and other features are also supported.
- Snowflake data warehouse covers a wide variety of client connectors and drivers, including Python connectors, Spark connectors, Node.js drivers,.NET drivers, and so on.
- Data Sharing: Users could indeed share your information with other Snowflake accounts in a secure manner.

Snowflake Training
- Master Your Craft
- Lifetime LMS & Faculty Access
- 24/7 online expert support
- Real-world & Project Based Learning
Snowflake Architecture:
Snowflake architecture integrates traditional shared-disk and shared-nothing architectures to provide the perfect combination. Let's take a look at these architectures then see how Snowflake manages to combine them to create a new hybrid architecture.
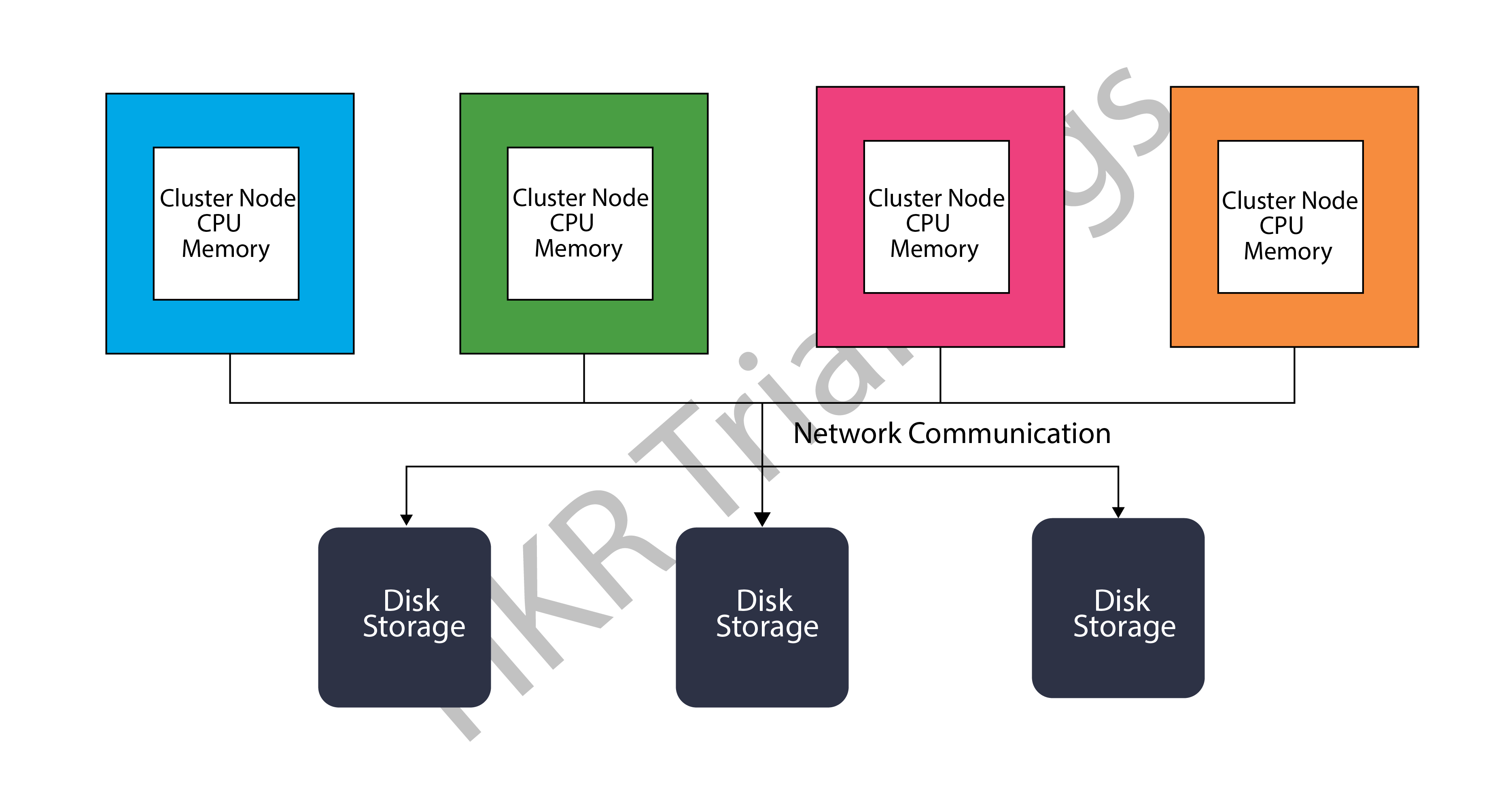
Shared disk architecture:
Shared-disk architecture, that is used in traditional databases, has a single storage layer that is available to all cluster nodes. Multiple cluster nodes with CPU and memory but no disc storage interact with the central storage layer to obtain and process data.
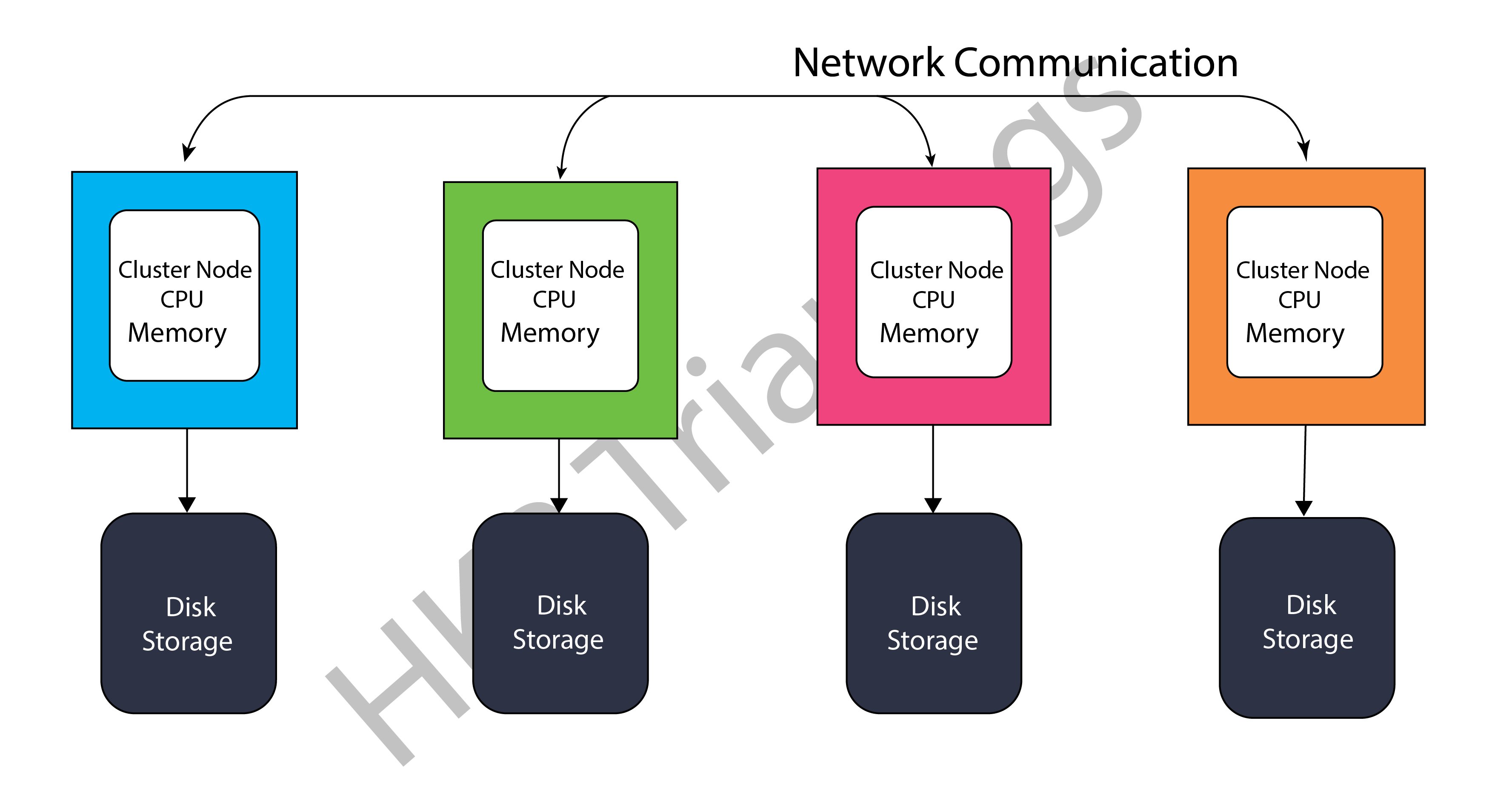
Shared Nothing Architecture:
Shared-Nothing architecture, in contrast to Shared-Disk architecture, has distributed cluster nodes with disc storage, their own CPU, and Memory. Because each cluster node has its own disc storage, data can be partitioned and stored across these cluster nodes.
Get ahead in your career with our Snowflake Tutorial !
Snowflake Architecture: Hybrid model
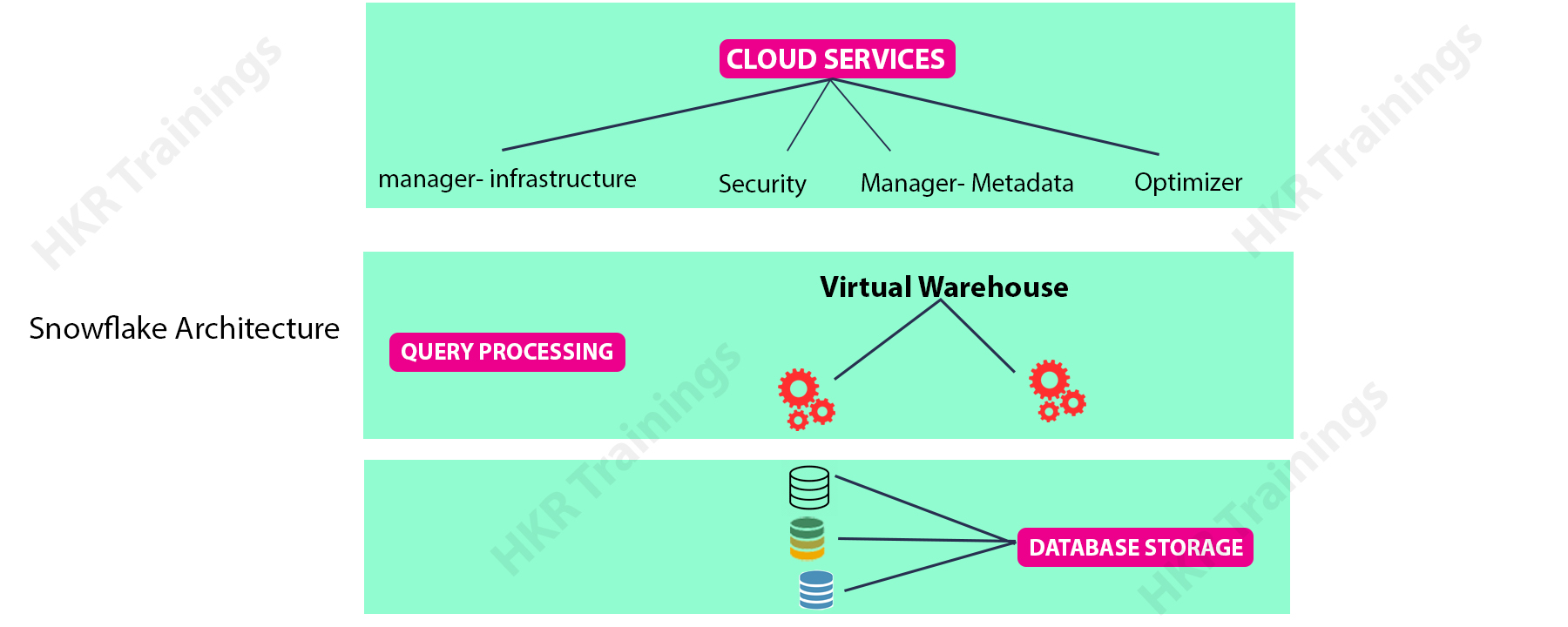
As shown in the diagram below, Snowflake supports a high-level architecture. The layers of a snowflake are as follows:

The storage layer, the compute layer, and the cloud services layer are all interconnected.
1.Storage Layer:
Snowflake data is divided into various micro partitions that are optimised and pressed institutionally. It stores data in a columnar format. Data is stored in the cloud and operates as a shared-disk model, making data management simple. In the shared-nothing model, this ensures that users do not have to worry about data distribution across multiple nodes.
To extract data for query processing, compute nodes communicate with the storage layer. Because the storage layer is self-contained, we only pay for the monthly average storage usage. Because Snowflake is hosted in the cloud, storage is elastic and charged monthly based on usage per TB.

Subscribe to our YouTube channel to get new updates..!
2.Compute Layer:
For query execution, Snowflake employs the "Virtual Warehouse" (explained further below). Snowflake is the layer that separates the query processing layer from the disc storage. Queries in this layer run on data from the storage layer.
Virtual Warehouses are MPP compute clusters made up of multiple nodes with CPU and Memory provided by Snowflake on the cloud. Snowflake allows the creation of multiple Virtual Warehouses for a variety of requirements based on workloads. So every virtual warehouse only needs a single storage layer. A virtual warehouse, in overall, does have its own impartial high - performance computing cluster and does not communicate with the other virtual warehouses.
The advantages of the virtual warehouses are:
- Virtual Warehouses can indeed be initiated or ended at any time, and they can also be expanded without affecting running queries.
- Individuals could also be set to auto-suspend or auto-resume, which means that warehouses are delayed after a certain period of inactivity and then resumed when a query is submitted.
- Those could also be set to auto-scale with such a min and max cluster size, so for example, we can set a minimal level of 1 and a max value of 3 so that Snowflake could indeed set up around 1 and 3 multi-cluster warehouses relying on the load.
Top 30 frequently asked snowflake interview questions & answers for freshers & experienced professionals
3.Cloud Service layer:
This layer seems to be where all of the activities taking place across Snowflake, such as identity verification, safety, data management of the loaded data, and query optimization method, take place.
Services handled by this layer include:
- When a login request is made, it must pass through this layer.
- Snowflake queries are sent to the optimizer in this layer and then forwarded to the Compute Layer for query processing.
- This layer stores the metadata required to optimise a query or filter data
Snowflake charges for storage as well as virtual warehouse separately, and these three layers scale independently. The services layer is managed within resourced high computational nodes and thus is not charged.
The Snowflake architecture has the benefit of allowing us to scale any one layer autonomously of the others. For example, you could indeed elastically scale the storage layer and also be billed separately for storage. Once additional funds are required for quicker making progress and solutions that would help, virtual machines warehouses could be procured and expanded.
Conclusion:
This blog has taught you about the Snowflake data warehouse, the Snowflake architecture, or how it stores and organizes information. In Snowflake architecture, users learned about various layers of the hybrid model.However if you had any doubts please drop them in the comments section to get them clarified.
Related Articles:
About Author
As a senior Technical Content Writer for HKR Trainings, Gayathri has a good comprehension of the present technical innovations, which incorporates perspectives like Business Intelligence and Analytics. She conveys advanced technical ideas precisely and vividly, as conceivable to the target group, guaranteeing that the content is available to clients. She writes qualitative content in the field of Data Warehousing & ETL, Big Data Analytics, and ERP Tools. Connect me on LinkedIn.
Upcoming Snowflake Training Online classes
| Batch starts on 15th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 19th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 23rd Mar 2026 |
|
FAQ's
Snowflake architecture is a hybrid model combining a shared disk and a shared-nothing structure. Further, it consists of a central repository that helps to store data safely for the future to make informed decisions. Also, this data can be accessed from the different compute nodes within the platform.
Snowflake is a popular data warehouse built on Microsoft Azure’s cloud structure. It is a pure cloud data warehouse that allows data to be stored securely to scale separately.
The following are the three crucial layers of Snowflake architecture-
Database Storage
Cloud Services
Query Processing
In Snowflake, a cloud services layer controls the security services. It consists of services like security, metadata, access control system, etc. However, the Snowflake system is managed by these services.
The Snowflake architecture consists of many layers, among which the cloud services layer is called the brain. These cloud services manage many things, such as client sessions, metadata, query planning, security, etc.

