- Introduction to SAP MDG (master data governance)
- SAP master data governance Architecture
- Key capabilities of the SAP master data governance
- Process flow Overview of Master data governance
- Applications of master data governance
- Final words
Introduction to SAP MDG (master data governance):
SAP master data governance (MDG) is considered a state-of-the-art data management solution. The master data governance provides the out-of-the-box and domain defined master data management to create, distribute, and modify the data across the complete enterprise system landscape.
The SAP MDG guarantees data integrity across both the SAP R/3 system as well as non SAP systems. SAP MDG is also known for its integrated foundation for the optimized business process that leads to higher productivity, is cost effective, and is also time-consuming.
Become a SAP MDG Certified professional by learning this HKR SAP MDG Online Training !
Benefits of using SAP master data governance:
The following are the major business benefits of using SAP master data governance:
- The SAP MDG ensures data centralization, compliance, transparency, master data creation, integrated staging, central auditing, and data approval.
- SAP MDG helps in the delivery of consistent data, authorization, and replication of the master data key representatives.
- Helps to eliminate the error-prone manual maintenance process for the master data across multiple systems.
- Enables organizations to create centralized data to define the key records and mapping between the duplicates.
- Defines the master data quality, consistent data usage across all data entry points monitors the data quality, and analysis.
- Helps organizations to observe and investigate the master data management quality to enable data optimization.
- Offers native integration and openness to integrate with 3rd-party services.
- Reusing SAP data models, business logic, and data validation configurations.
- It acts as an open application to manage master data, and also check for the flexibility of the non-SAP environments.
Acquire SAP MM certification by enrolling in the HKR SAP MM Training in Marathahalli!

SAP MDG Training
- Master Your Craft
- Lifetime LMS & Faculty Access
- 24/7 online expert support
- Real-world & Project Based Learning
SAP Master data governance Architecture:
The SAP MDG architecture enables users to know about the workflow and processes that are involved in the process.
The following diagram illustrates the overall SAP MDG architecture:
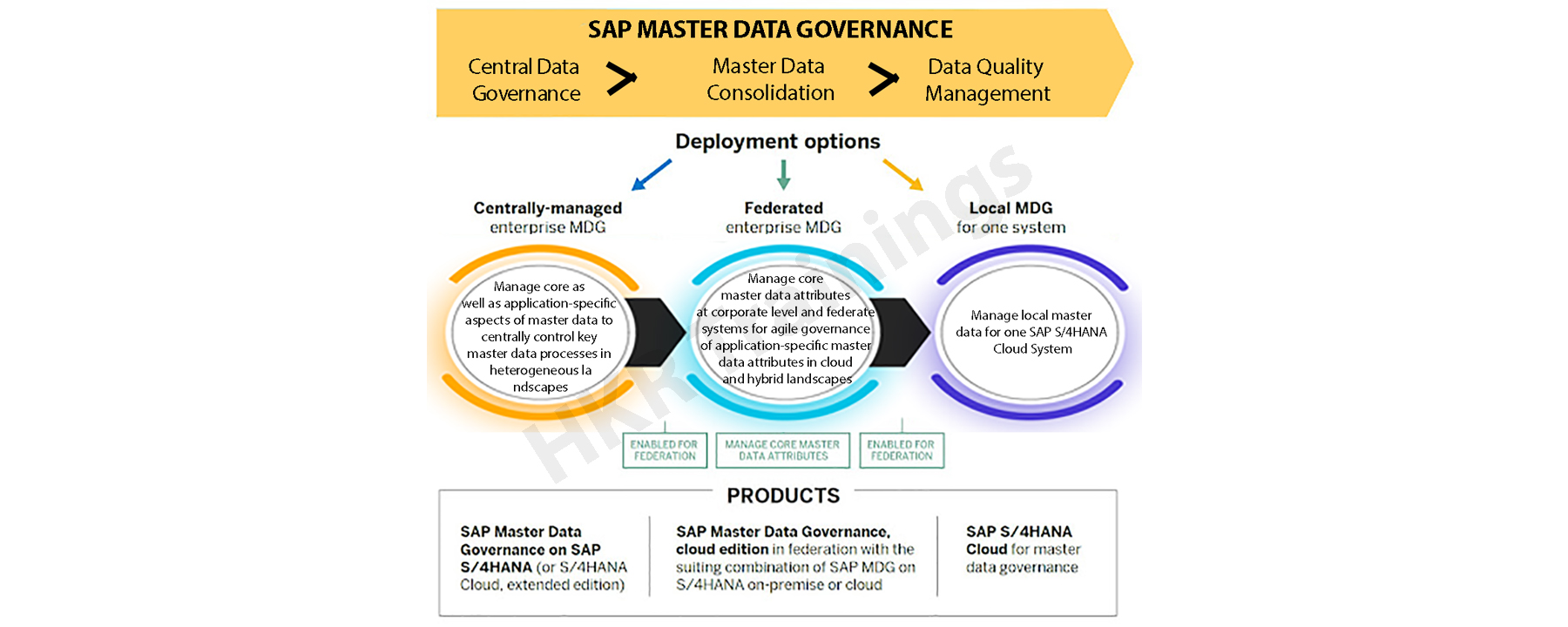
The process is as follows;
- SAP MDG can be used as a “one -enterprise-wide-hub” and centralized data core attributes that are based on the SAP R/3 HANA data models, suppliers, products, financial assets, and retail master data usage.
- SAP MDG module is open for custom-defined objects, that are available for both SAP S/4 HANA on-premises as well as for the cloud edition.
- SAP MDG also serves as an “open for federation”, it can be used as an application for specific SAP S/4 HANA master data MDG deployments.
- SAP MDG master data cloud edition provides core attribute governance for the customers and suppliers based on the SAP model data.
- Master data governance also offers SAAS subscription solutions to the public cloud.
- The cornerstone for the federation also enables orchestrating master data as well other specific applications.
Want to know more about SAP MDG,visit here SAP MDG Tutorial !
SAP master data Governance Business values:
The main function of using Master data governance in any enterprise is to improve the quality of business and product data.
Few important points about business values:
- Master data governance in any business ensures data quality by offering transparent technical implementations, business aspects, usage, consistent data quality, and monitoring.
- Both business partners and product data are covered as package data, applications, and platforms for custom defined data objects.
- Collaboratively defines the catalog and technical implementation for the data quality evaluations.
- Schedules the quality evaluation, analyzes the data evaluation results, and also error-free data.
- Helps to get an overview of the current data quality.
- Allows users to perform drill down analysis for the data quality checkings along with the multiple dimensions to encounter error free data.

Subscribe to our YouTube channel to get new updates..!
Key capabilities of the SAP master data governance:
The following are the key capabilities of the SAP master data governance:
- Defines the data quality: with the help of MDG, the requirements will be defined that are based on the company’s business process. The business priorities will be set according to the values, and quality evolutions. And also the business experts collaborated to check for the quality and required checks.
- Ensures the quality: Master data governance ensures the data quality at each entry point and also offers rules-based checks in all the SAP MDG business end-points.
- Monitoring the business quality: this step can be differentiated into three categories they are;
- Data Operational motivation: helps in the detection of all issues before processing them for the next level of operations.
- Tactical: helps to ensure the progress and the performance of the current activities.
- Business strategies: this step enables users to achieve the goals, and also defines the new initiatives.
It is very easy to consume data monitoring and trend reporting.
- Improve the quality: MDG corrects the data and also drives the correlation process. Evolves the data quality definitions, and also fixes the data entry processes. It also offers various tools to fix the data and also check for the data entry processes.
Process flow Overview of Master data governance:
Below are the few process flow overview of Master data governance; we can also refer to it as data quality management;
The process flow adds up the efficiency and also manages the data quality. Here we would like to mention a few of the process flow methods;
Data load:
The functionalities that come under data load are;
Smart data integration, Non - SAP S/4 HANA ETL (Extract, Transform, and load) mechanism, and data import from the file.
Enables initial check:
This process flow allows users to view loaded data, and check for the data quality based on customization.
Standardize the data quality:
This step consists of three major aspects;
- Validation and enriching the data addressability.
- Possibility to connect through the 3rd-party vendors for the standardization and data enrichments.
- Usage of BRF (it’s a tool that is used to define both technical and functional rule sets).
Data matching:
It helps users to find duplicate data based on the customer specifications and also review the data matches.
Calculates the best record:
- Initially, it creates the best records on the basis of approved match groups.
- The BRF can be used for customer-specific best record calculations.
- The final step includes the reviewing of the results.
Data validation:
- Helps in the validation of the best records against the backend customizations to check whether the records are activated or not.
- Data validation can also be done against control governance checks (for example, BADI (business adds in), and BRF).
Activate:
- Offers the consolidated master data for analytical and operational usage.
- Options to activate the triggering posting directly or indirectly using central governance.
Applications of master data governance:
Till now we have seen the architecture overview, benefits, and key abilities of the Master data governance. Now it’s time for us to know what are all the various industries that make use of MDG to boost up the data quality and management.
- SAP master data governance for financial business:
For example; financial/ accounting data consolidations, profit, and cost centers. - SAP master data governance for the supplier data:
For example; corporate, companies, partner functions, and purchasing related data. - SAP MDG for the customer data:
For example; sales related data, and partner functions. - SAP MDG for the material data:
For example; corporate industries, sales organizations, storage, plants, warehouse, and costing data. - SAP MDG for enterprise assets management data:
For example; equipment, billing, and functional locational data. - SAP MDG for fashion and retail management:
For example; hierarchies, single and generic billings, listings, and characteristics variants. - SAP MDG can also be used in data models, user interfaces, and governance for the master-related data.
Top 30 frequently asked SAP MDG Interview Questions !
Final words:
It’s very important to maintain data quality to achieve the overall performance of any business application. In this SAP Master data governance article, we have explained the architectural overview, key abilities, business functionalities, and applications of SAP MDG in various enterprises. Learning this article may help you to explore more about SAP master data governance which ensures the high-level data quality management system.
About Author
Kavya works for HKR Trainings institute as a technical writer with diverse experience in many kinds of technology-related content development. She holds a graduate education in the Computer science and Engineering stream. She has cultivated strong technical skills from reading tech blogs and also doing a lot of research related to content. She manages to write great content in many fields like Programming & Frameworks, Enterprise Integration, Web Development, SAP, and Business Process Management (BPM). Connect her on LinkedIn and Twitter.
Upcoming SAP MDG Training Online classes
| Batch starts on 12th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 16th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 20th Mar 2026 |
|

