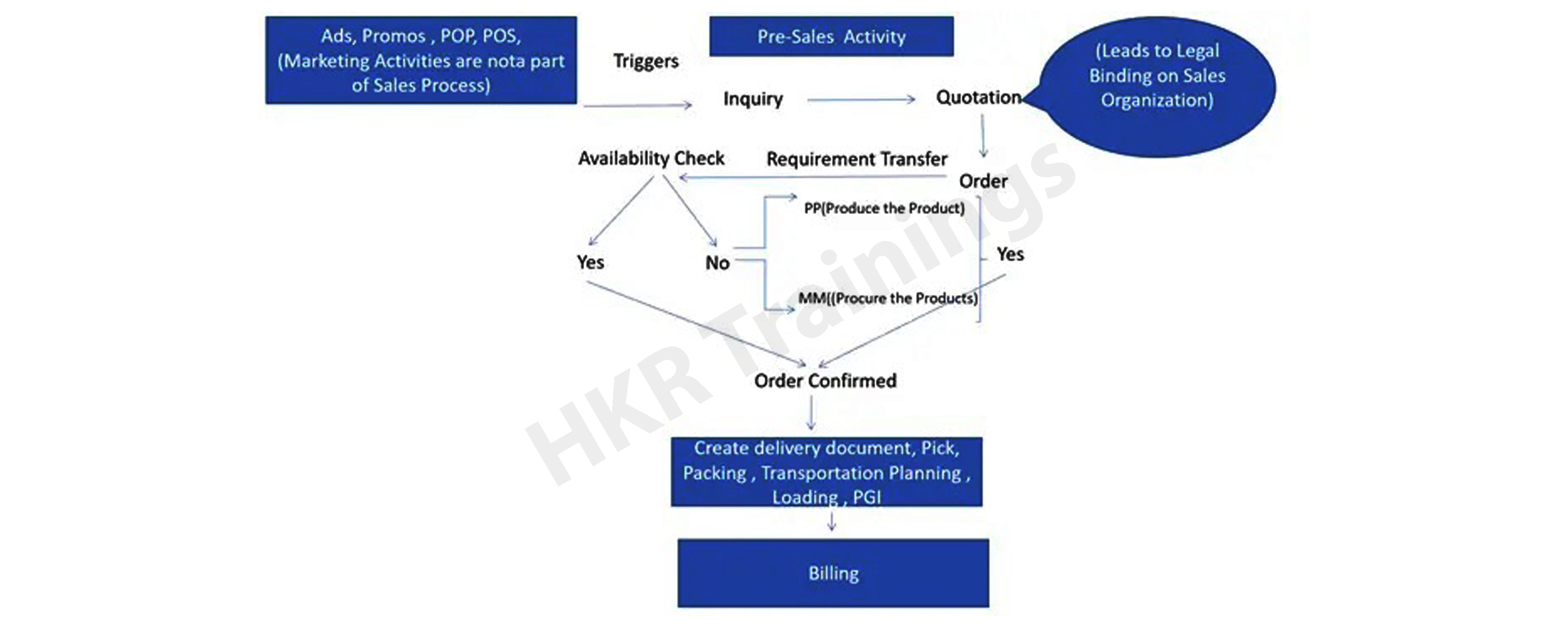
The SAP SD process flow steps are as follows:
Introduction to SAP Sales and Distribution
SAP Sales and Distribution (SAP SD) is crucial in managing the entire order-to-cash sequence. It includes various stages, including customer inquiry, sales order creation, delivery of products to the customer’s chosen location, and handling billing and payment collection. SAP SD is complexly linked with logistics execution modules like shipping, packing, and picking.
This system is set up to streamline daily business sales and distribution activities. It facilitates numerous functions like sales order reception, availability checks, and integrating sales forecasts into supply chain needs. This integration extends to production planning, scheduling, and purchasing, eventually leading to distribution processes such as shipping, transportation planning, and yard management, supported by warehousing and inventory management.
Become a SAP SD Certified professional by learning this HKR SAP SD Training !
What is the Process of Sales and Distribution (SD)?
SAP ERP Sales and Distribution (SAP ERP SD) collaborates seamlessly with other modules like SAP ERP MM and SAP ERP Logistics Execution, offering a complete order-to-cash process. This module captures many business activities and provides customizable solutions to bridge gaps between standard capabilities and specific business needs. Its functionality, covering most common business tasks, is universally applicable across various industries.
Activity of Pre-sales
Before initiating transactions, businesses must gather essential data and create master records for potential or existing customers. This phase involves documenting inquiries or quotations in SAP ERP SD and detailing vital sales-related information for analysis and marketing efforts, leading to sales order conversion.
Processing of Sales Orders
Sales order processing starts with recording the actual order, which can be done by back office staff, the sales team, or directly by customers through various means. These orders enclose complete customer and partner information, product details, pricing, and delivery specifics. The material availability check is crucial at this stage, which influences procurement requests.
Processing of Deliveries
On the shipping due date, delivery documents are prepared, routes are selected, and warehouse management activities like picking and packing commence. Delivery preparation includes engaging with freight service providers, initiating the tendering process, and preparing shipping cost documents. The process culminates in updating inventory and financial records upon product issue posting.
Invoicing and Revenue Identification, Reporting
The billing phase involves creating invoices and sending them to the customer. This step incorporates data from previous documents and involves account determination and financial postings in SAP General Ledger accounts. All transactions in SAP SD are documented and used for analysis in the Sales Information System or SAP BW.
Steps of SAP SD Flow:
1) Sales Inquiry
A sales inquiry is a document that records customer questions about product availability, pricing, and potential delivery dates. It serves as a communication channel between the customer and the sales team used to request product information.
Become an SAP Basis Certified professional by learning this HKR SAP Basis Training
Creating a SAP Inquiry
Step 1: Access the SAP SD interface by entering transaction code VA11 in the SD Master Data Screen.
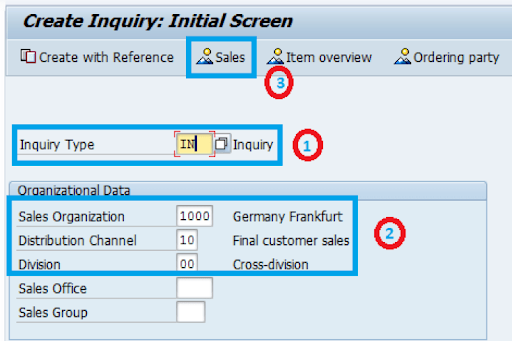
Step 2: Input Organizational Information
- Select 'IN' for the Inquiry type.
- Input details like Sales organization, Distribution channel, and Division, then proceed to Sales.
- Example: Sales organization - 1000, Distribution channel - 10, Division - 00.
Step 3: Provide Customer and Material Details
- Enter the addresses for both sold-to-party and ship-to-party.
- Input the queried material number (e.g., R-1140) and quantity (e.g., 10).
- Save the inquiry. A confirmation message, such as "Inquiry 10000004 saved," will display.
Want to know more about SAP SD,visit here SAP SD Tutorial !
2) Quotation
The quotation follows the inquiry, offering product or service details at a specified price and terms. This document lays out delivery conditions for a set quantity of a product at a stated price, valid for a defined period.
Creating a SAP Quotation
Step 1: Access the SAP SD screen using the transaction code VA21.
Step 2: Input Organizational Data and Quotation Type
- Enter 'QT' for the quotation type.
- Provide details like Sales organization, Distribution channel, and Division, then click 'Create with reference'.
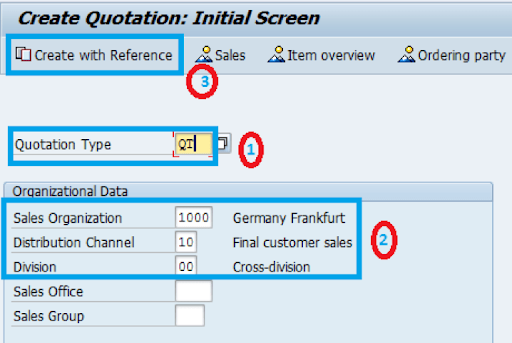
Step 3: Reference the Inquiry
- Enter the inquiry number you're quoting against and select 'Copy'.
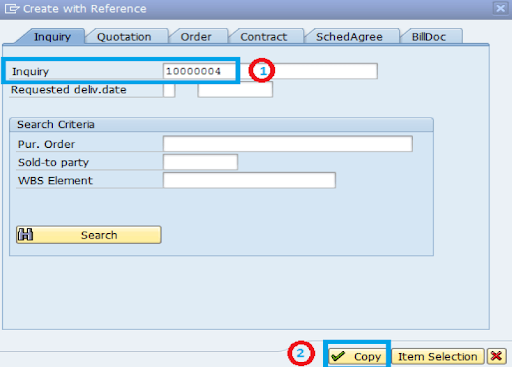
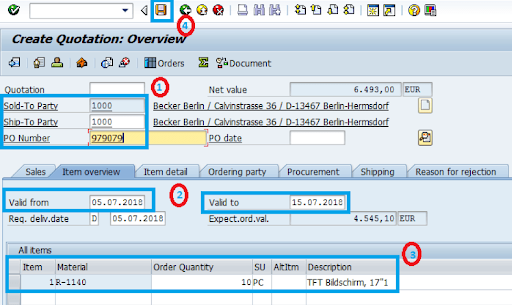
Step 4: Enter Customer and Product Details
- Input details like sold-to-party, ship-to-party, and PO number.
- Set the quotation's validity period.
- Input the material and quantities offered.
- A message such as "Quotation 20000066 saved" will appear upon saving.
Become an SAP Basis Certified professional by learning this HKR SAP Basis Training In Hyderabad

Subscribe to our YouTube channel to get new updates..!
3) Sales order
The sales order is a formal agreement between a customer and the sales organization for providing specified goods/services within a set timeframe.
Creating a Sales Order
Step 1: Enter T-code VA01 in the command field.
- Choose 'OR' for the Standard order type.
- Input details in the Organizational Data section and click 'Create with Reference'.
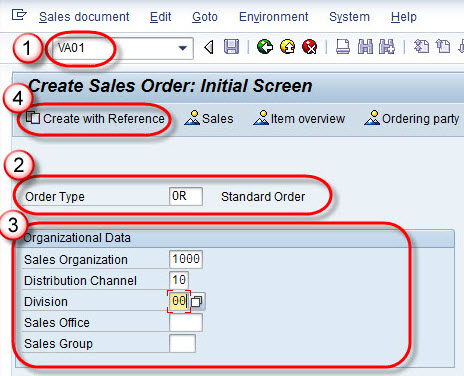
Top 30 frequently asked SAP SD Interview Questions !
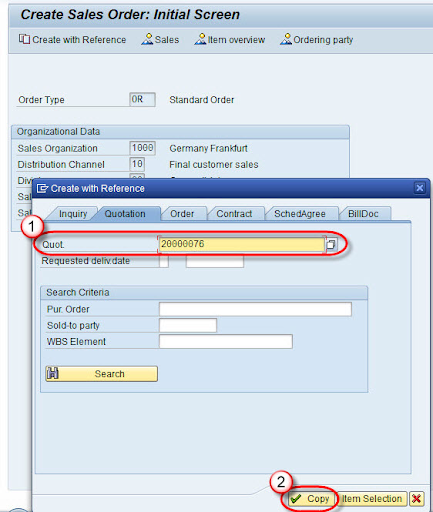
Step 2: Reference the Quotation
- Input the quotation number and select 'Copy'.
Step 3: Finalize Order Details
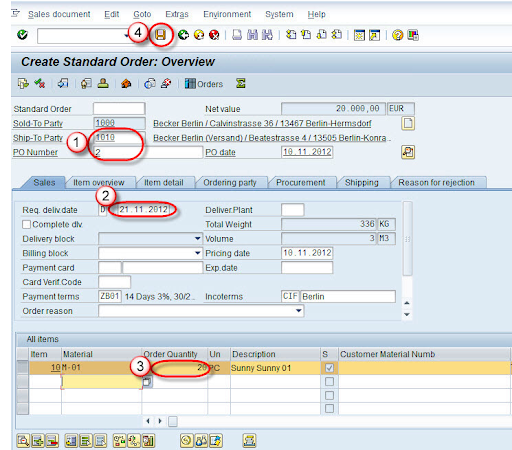
- Enter Ship-To-Party, PO number, PO date, and required delivery date.
- Modify the order quantity if needed and save.
- A confirmation like "Standard Order 2000958 saved" will be displayed.
4) Delivery/Shipping
The SAP System manages the creation and processing of delivery orders based on customer specifications.
Process Flow
- Outline agreements, like a specific scheduling agreement, guide delivery order processing.
- Customer data sent via pick-up sheets are converted into IDocs and stored in the SAP system.
- This data determines the corresponding scheduling agreement and generates appropriate schedule lines.
- Regular deliveries are created for each unloading point.
- Upon the customer's agent picking up the supplies, an invoice referencing the pick-up sheet number is produced for payment.
5) Billing/Invoice
5) Billing/Invoice
Billing represents the culmination of the SAP SD module's transaction process.
Components of Billing
- Credit/debit memos for returned goods.
- Invoices for deliveries and services.
- Cancellation of billing transactions.
- Pricing functions, including discounts and rebates.
- Transfer of billing data to Financial Accounting (FI).
Key Billing Functions
Various Billing Types.
- Match codes.
- Number Range.
- Blocking Reasons.
- Displaying billing lists and duelists.
Document Types for Billing
In SAP, billing documents are produced for various transactions, including credit and debit memos, invoices, and cancelled deals. Each billing document consists of two main parts:
Header: This section contains general information about the billing document, such as:
- Billing Date
- Payer Identification Number
- Total Billing Value
- Currency Used
- Partner Identification Numbers (e.g., ship-to-party, sold-to-party)
Item List: The detailed part of the document lists:
- Material Number
- Quantity of Goods
- Volume and Weight of Each Item
- Individual Item Value
- Pricing Details for Each Item
Creation and Modification of Billing Documents
Billing documents are not static; they can be created, altered, or deleted as part of regular billing operations. This flexibility allows them to adapt to various stages of the sales and delivery process, such as:
- Aligning with a sales order
- Corresponding to a delivery
- Matching external transactions
Billing documents can encompass complete documents, specific items within them, or portions of items.
-
Methods to Generate Billing Documents
There are several ways to create billing documents in SAP:
- Automatically, through system-run background operations that process billing duelists.
- Manually, by using a worklist for individual processing.
- Explicit creation of a billing document as needed.
Billing Document Creation
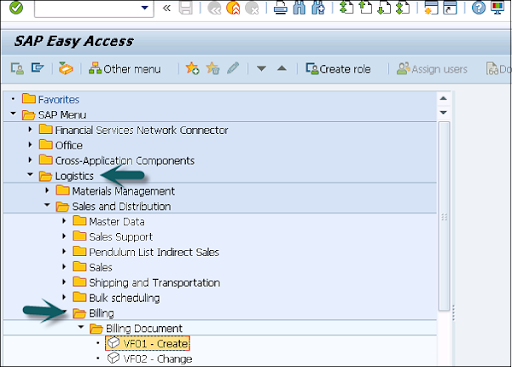
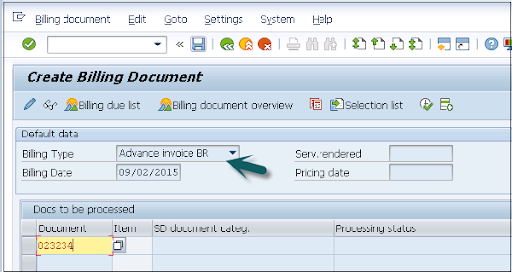
- Use T-Code: VF01 to navigate to Billing Document creation in the SAP system.
- Input the Billing Type, Date, and Document Number, then save the file.
Other relevant T-Codes:
- VF02 (Change Billing Document),
- VF03 (Display Billing Document),
- VF11 (Cancel Billing Document),
- VF05 (List Billing Document).
Conclusion:
In this blog, we have successfully learned the implementation steps required for processing the SAP SD flow.
About Author
Kavya works for HKR Trainings institute as a technical writer with diverse experience in many kinds of technology-related content development. She holds a graduate education in the Computer science and Engineering stream. She has cultivated strong technical skills from reading tech blogs and also doing a lot of research related to content. She manages to write great content in many fields like Programming & Frameworks, Enterprise Integration, Web Development, SAP, and Business Process Management (BPM). Connect her on LinkedIn and Twitter.
Upcoming SAP SD Training Online classes
| Batch starts on 7th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 11th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 15th Mar 2026 |
|


