Maven Interview Questions
Last updated on Jun 12, 2024
Maven is a project management tool that provides the developer with a complete build lifecycle framework. Usually, a typical Maven project is conceived by an Apache Software Foundation where you will see that it was previously a component of the Jakarta project. Several reasons contribute to the popularity quotient. These factors are seamless dependency management, complete environment support (plugins, etc.), and the much-needed build life cycle support. DevOps comprise many phases and Maven is a tool that helps in the build phase of the DevOps lifecycle.
We have developed a list of Maven interview questions and answers for our readers. This list of interview questions and answers is surely going to give you a good head start for your Maven interview.
Most Frequently Asked Maven Interview Questions
- Explain POM
- Explain some striking features of Maven
- Explain about a Build Profile
- Why should one utilize optional dependency
- What is Mojo
- Why do you use Maven Plugins
- What do you mean by Maven
- What is the use of Maven's external dependency
- List out the various Build Profile types
- Name the different Clean LIfecycle stages in Maven?
Explain POM
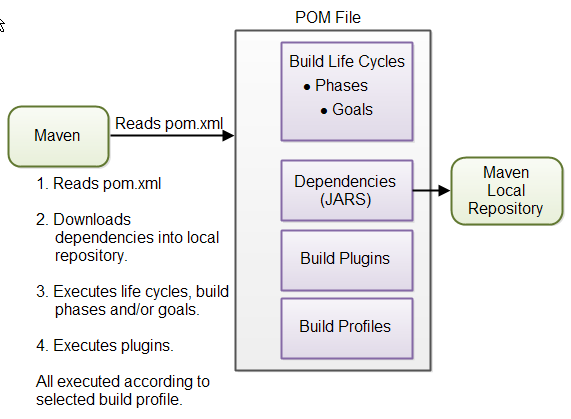
Ans: POM is the acronym that is used for Project Object Model. A POM is the important unit of the Work module in Maven. POM is an XML file that is always located in the base directory of the given project. It can be found with the extension of pom.xml. It contains the complete information that is available about the project along with the various configuration details used by Maven to build the project(s).
Become a master of Maven by going through this HKR Maven Certification Training!
Explain an Artifact in Maven.
Ans: A Maven artifact is a file that is generally like a JAR that directly gets organized on to a repository of Maven. The usual build in Maven generates one or more artifacts at one given time.
Every Maven artifact comes with a unique group ID, the artifacts' ID, and a version string. These three components collectively form the unique ID that is used to identify the Maven artifact.
What are the 3 kinds of build phase lifecycle in Maven?
Ans: There are three kinds of build phase lifecycles in Maven, they are −
clean: cleans up the Maven artifacts that were created by the previous builds.
default (or build): This lifecycle is generally used to build the given application.
site: helps to generate site documentation that is needed for the project.
Describe the various phases that comprise a Maven Build Lifecycle.
Ans: The different phases that comprise a Maven Build lifecycle are−
- validate − approve the task is right and all essential data is accessible.
- compile − aggregate the source code of the task.
- test − test the aggregated source code utilizing an appropriate unit testing system. These tests ought not to require the code to be bundled or sent
- package − take the aggregated code and bundle it in its distributable organization, for example, a JAR.
- integration-test − process and send the bundle if important into a situation where coordination tests can be run.
- verify − run any checks to confirm the bundle is substantial and meets quality criteria.
- install − introduce the bundle into the nearby storehouse, for use as a reliance in different undertakings locally.
- deploy − done in a mix or discharge condition, duplicates the last bundle to the remote storehouse for offering to different designers and ventures
Explain some striking features of Maven.
Ans : Here is a list of the primary features of Maven:
- Simple to utilize: Maven gives simple task settings that depend on certified practices.
- Fast: You can get a new undertaking or module that started in fewer seconds in Maven.
- Easy to learn: Maven use and orders are quite simple to learn overall activities. Hence increase time for new designers going onto a venture is less.
- Dependency the board: Maven gives prevalent reliance on the board including programmed updates and transitive conditions.
- Multiple Projects: You can undoubtedly chip away at different ventures simultaneously by utilizing Maven.
- Huge Library: Maven has a huge and developing vault of libraries and metadata to use out of the container.
For what reason would it be advisable for one to utilize Maven?
Ans:
- It helps in setting up the undertaking rapidly and it maintains a strategic distance from confused form documents like build.xml. the pom.xml document is at the center of Maven.POM.xml is an assortment of conditions of your Java Project which one can determine to Maven. After this Maven will download every one of them from the web and store it to some storehouse for example nearby store, focal vault, and remote storehouse.
- It assists with packaging all the containers in your bundle for example in your War document or Ear record since every one of them will be put away in the archive. So next time any place you introduce this application that storehouse will be utilized for any conditions query. Right now, the arrangement record will be light.
I don't get it's meaning when you state Maven utilizes Convention over Configuration, please explain!
Ans:
- In the instance of Configuration, engineers need to make the assemble forms physically and they need to indicate every single setup in detail. Be that as it may, Maven utilizes show where the engineers need not make the manufacture forms physically.
- Also, for the show, clients don't have to determine the design in detail. When an engineer makes a task in Maven then Maven will consequently make a structure. Designers simply need to put the documents suitably. There is no compelling reason to indicate any design subtleties in the pom.xml document.
What do you understand by a goal in Maven?
Ans: In Maven, “Goal” refers to a particular task recommending building and managing a project. Some phases define the build life cycle series to achieve the goals, and they are executed in which the desired tasks are executed.
Explain about a Build Profile.
Ans: In Maven, a build profile is a set of values that helps to build a project through multiple configurations, and it also supports customizing builds for various domains. Moreover, build profiles are helpful to customize builds for different spaces like Production, Development, etc.
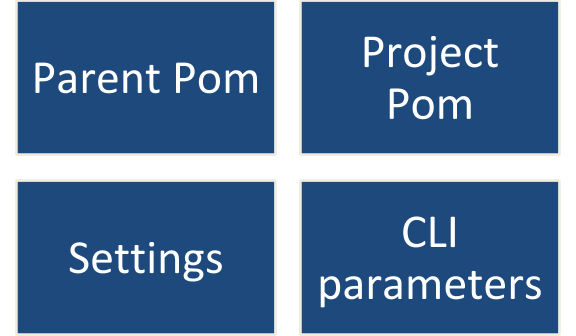
. What is the order of inheritance in Maven?
Ans: The order of inheritance in Maven is-
. What do you understand by the term system dependency in Maven?
Ans: Dependency with scope framework is constantly accessible and doesn't gaze upward in the storehouse, they are generally used to educate Maven concerning conditions that are given by the JDK or the VM. Along these lines, framework conditions are particularly helpful for settling conditions on ancient rarities that JDK typically gives.
. Why should one utilize optional dependency?
Ans: You can check any transitive dependency as discretionary utilizing the "discretionary" component. For instance, X relies on Y and Y relies on Z. Presently Y stamped Z as discretionary. At that point, X won't use Z.
. What do you gather by the phrase dependency exclusion?
Ans: You can bar any transitive reliance utilizing the "exclusion" component. Assume if X relies on Y and Y relies on Z, at that point X can be stamped Z as barred.
. Differentiate between a Central Repository and a Remote Repository
Ans: Central Repository is the Repository given by the Maven people group. It contains countless usually utilized libraries. At the point when Maven doesn't discover any reliance in neighborhood vault, it begins looking in focal archive utilizing the following URL: http://repo1.maven.org/maven2/.
Whereas now and then, Maven doesn't discover a referenced reliance in focal store too then it stops the fabricate procedure and yields mistake message to support. To forestall such circumstances, Maven gives an idea of Remote Repository which is an engineers' custom store containing required libraries or other undertaking containers.
. Define Archetypes in Maven.
Ans: Maven archetypes are formats to make an assortment of Java venture structures, including web applications explicit to a holder, for example, Wildfly. At the end of the day, it is an instrument that makes the stuff you manufacture the task on.

Maven Training
- Master Your Craft
- Lifetime LMS & Faculty Access
- 24/7 online expert support
- Real-world & Project Based Learning
. In what sequence does Maven search for a dependency library?
Ans: You can find dependency in the neighborhood vault arrangement of your product. Now and again, it is hard to find or distinguish in the neighborhood archive. Along these lines, I can discover or glance in the focal archive framework and on the off chance that it shows the reliance missing, at that point one can glance in the remote storehouse to discover the reliance. On the off chance that it despite everything shows something very similar over and over, at that point the framework will show mistake in finding the conditions. Also, on the off chance that the conditions are found in the nearby storehouse, at that point it will be naturally downloaded in the focal vault for some time later.
. What are the various project types that are available in Maven
Ans: There is more than thousand Java venture as there are formats, skeleton gave to you by Maven with the goal that you don't need to recall a fundamental design detail or an essential arrangement of that specific kind of task which Maven is going to offer it to you. It incorporates models like fundamental Java venture, Spring Project, Spring MVC, Spring Web Flow, and Spring Boot.
. How Maven handles and figures out what rendition of dependency will be utilized when the various form of a Maven artifact is experienced?
Ans: Maven figures out what rendition of reliance are to be utilized when various forms of a curio are experienced. On the off chance that two reliance adaptations are at a similar profundity in the reliance tree, the primary proclaimed reliance will be utilized. This is called reliance intercession.
If you have any doubts on Maven, then get them clarified from Maven Industry experts on our Maven community
. What is the way to reference a property that is defined in your pom.xml file?
Ans: To reference a property characterized in your pom.xml, the property name utilizes the names of the XML components that characterize the worth, with "pom" being permitted as a pseudonym for the venture (root) component.
So ${pom.name} alludes to the name of the undertaking, ${pom.version} alludes to the variant of the task, ${pom.build.finalName} alludes to the last name of the document made when the fabricated venture is bundled, and so forth.
. What is Mojo?
Ans: Mojo is a Maven plain Old Java Object. Every mojo is an executable goal in Maven, and a module is the dissemination of at least one or more related mojo elements.
. What is the difference between Apache Ant and Maven?
Ans: Ant is just a tool compartment while Maven is about the use of examples to accomplish a foundation that shows the attributes of perceivability, reusability, practicality, and comprehensibility. It isn't right to consider Maven as a build tool and only trade for Ant.
. State about the elements that are minimally required for a POM to be classified as a POM?
Ans: The elements that are minimally required are-
. What is the process to successfully produce execution debug output or the error messages in Maven?
Ans: If you want to produce execution debug output you should call Maven with the X parameter or the e parameter.
. What is the method to run test classes in Maven?
Ans: If you want to run test classes in Maven, you will firstly need a secure sure-fire plugin, then you need to properly check as well as configure your necessary settings in the setting.xml extension and the pom.xml extension for a property named "test."

Subscribe to our YouTube channel to get new updates..!
. What is the manner to specify profiles in Maven?
Ans: We can do that by simply utilizing a subset of the existing elements in the POM in the question itself.
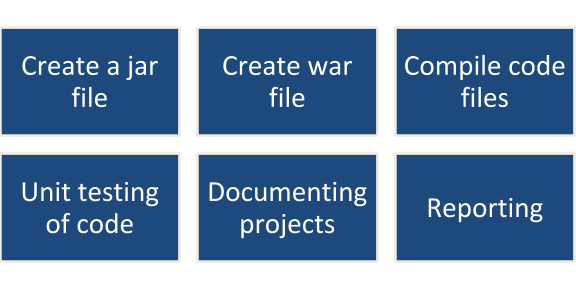
. Why do you use Maven Plugins?
Ans: We use the Maven plugins to
. Let us say that you have failed to define particular information, where will your pom inherit that missing information from?
Ans: All POMs are inherited from a parent regardless of expressly characterized or not. This base POM is called Super POM and it contains values that are acquired naturally.
. How can you stop the compiling of propagation plugins to the child POMs?
Ans: We can do that by giving the following command
set
. State the command that you can use to create a fresh project that is based on an archetype.
Ans: mvn archetype: generate
. What do you mean by Maven?
Ans. Maven is an open-source project management tool based on Java that is useful for developing, publishing, deploying, and managing multiple projects. It helps to automate the project's build infrastructure, making it easier for the development team. Moreover, it simplifies the developer's daily work and helps manage projects based on Java.
. Name the various aspects that Maven helps developers to manage?
Ans. The following are the aspects that Maven offers to developers to manage:-
- Builds
- Reports
- Documentation
- Dependencies
- Distribution
- Mailing list
- Releases
. Define the Build Tool in Maven?
Ans. Build tool helps the entire building process, and it covers many purposes. It helps in producing and compiling source code, builds documentation using the source code, helps to package the compiled code into a JAR file, and installs the packaged code to a server, local or central repository.
. Explain Maven Repository?
Ans. The repository in Maven refers to a place or a directory that contains all the JAR files, plugins, and other project-based artefacts. In other words, it is a storage folder that saves all the projects and files like JAR, WAR, etc.
Maven has three types of repositories like Local, Central, and Remote Repository.
. Define the various types of Maven Plugins?
Ans. Below are the two types of plugins available in Maven:-
- Build Plugin - The build plugins are helpful while executing the build, and they are configured within the element
of pom.xml.
Reporting Plugin - The reporting plugins are performed in the site production and are configured within the element
. What is the use of Maven's external dependency?
Ans. Dependency management is the concept used by Maven in the Maven Repositories. If there is an absence of dependency in any remote and central repositories, then External Dependency is used by Maven.
. Define the settings.xml file in Maven?
Ans. Maven offers a settings.xml file as a settings file that includes various elements to define values that help to configure Maven execution differently. The various configurations it consists of are proxy, remote, local, and central repository configurations.
. Explain Transitive Dependency?
Ans. There is an excellent use of transitive dependency in Maven. By adding transitive dependencies automatically, Maven eliminates the need to find and define the libraries that your dependencies require.
. What do you mean by Dependency Scope within the context of Maven?
Ans. The dependency scope in Maven consists of dependencies as per the existing build stage. Also, it restricts all the dependency's transitivity. There are various types of dependency scopes available in Maven:- Compile, Test, Runtime, System, Import, etc.
. List out the various Build Profile types?
Ans. The following are the different types of build profiles:-
- Per User - This build profile is defined within Maven's setting.xml file.
- Per Project - This build profile is defined within the project POM file "pom.xml".
Global - This build profile is defined within the global settings.xml file of Maven.
. How can we automatically run the clean plugin in Maven during the build?
Ans. To automatically run the clean plugin, you have to place it within the pom.xml files' execution tag.
. What forms the project's completely qualified artefact name in Maven?
Ans. In Maven, the POM must configure the groupID, version, and artifactID, which form the completely qualified artefact name. You can write this as
. Name the command helpful to create a Maven site?
Ans. We can easily use the "mvn site" command to create a Maven site.
. Name the different Clean LIfecycle stages in Maven?
Ans. Pre-Clean, Clean, and Post-Clean are the various stages of the clean lifecycle in Maven.
. Is it reasonable to store JARS in the local repository rather than the remote repository?
Ans. In Maven, a local repository is a storage folder or a directory within the system where the Maven runs. Using a local repository to store JAR files is better because it takes less storage space. Also, it checks out a project much faster without using the versioning of JAR files.
. What is meant by SNAPSHOT in Maven?
Ans. In Maven, Snapshot refers to a special version under the Maven package that specifies the latest development code. For each build, Maven searches for a new SNAPSHOT version inside a remote repository, unlike standard versions.
. Name the different Maven Build Plugins.
Ans. The following are the various build plugins in Maven:
- QueryDSL Plugin
- Shade Plugin
- Antlr Plugin
- Test Report Plugins
. Define Parent POMs in Maven.
Ans. In Maven, the Parent POM (Project Object Model) acts as a parent for all child projects. Organizations generally use it to describe the set of plugins or versions their teams use in a project. Moreover, parent POM allows you to reveal plugin configurations, split dependencies, and build settings. Thus, it assures steadiness throughout different projects.
. Define Archetype goals.
Ans. The following are the different Archetype goals in Maven:
- Generate
- Create
- Create-from-project
- Crawl
. Define the use of MVN clean command in Maven.
Ans: In Maven, a build profile is a set of values that helps to build a project through multiple configurations, and it also supports customizing builds for various domains. Moreover, build profiles are helpful to customize builds for different spaces like Production, Development, etc.
Conclusion:
This is all we have in store for you today! I am sure a good reading of this list of Maven interview questions is a good enough preparation for you to ace any Maven interview.
In case you face a question that you do not know the answer to, do not panic. It is not possible to know everything under the sun. You can simply say that you are not aware of the answer.
Upcoming Maven Training Online classes
| Batch starts on 28th Feb 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 4th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 8th Mar 2026 |
|

