SAP revolution:
In the year 1972, five German entrepreneurs namely Dietmar Hopp, Hans – Werner Hector, Claus Wellenreuther, Klaus Tschira, and Hasso Plattner had discovered this SAP company to increase the business potential. They named it SAP Systemanalyse und program Entwicklung (“System analysis and program development”).
SAP R/2 era: (1981 -1990)
Real-time business application touches more of the business-related applications: SAP R/2, it’s a fully packaged mainframe software application processes and integrates all the enterprise business functional applications. The growing power of mainframe servers is enabling SAP to expand its customer base to approximately 200 companies.
SAP R/3 era: (1991-2000)
Here the SAP real-time application reaches the Desktop: this is a client-server version of the standard application software that allows a large number of businesses to run more efficiently across the globe. SAP’s revenue and employee number continue their rapid ascent reaching DM 707.1 million and nearly 2,700 members respectively. The company now has more than 14 international subsidiaries and more than 2,500 customers in 32 different countries using its ERP software.
SAP Era: (2001 – 2010)
These SAP real-time moves to the web development applications, cloud computing, mobile developments, and in-memory computing open up the new version for real-time data access- anywhere, anytime. SAP expands mySAP.COM, making it a comprehensive technology for business applications. As a result, SAP has the architecture it needs to help many larger companies integrate a wide variety of information technology systems.
SAP Era: (2011-Present)
SAP launches the new module known as SAP S/4 HANA and SAP C/4 HANA, 4th generation enterprise software to help customers become business intelligent enterprises. Customers, already more excited in 2010 by SAP’s in-memory computing, are able to take full advantage of its benefit in 2011. Initial customers implement the first-in memory application product, the SAP HANA platform, enabling them to analyze data in seconds rather than days or weeks. SAP’s strategy for mobile business applications is also bearing fruit since its acquisition of Sybase, an SAP company.
Now it’s time to know the definition of SAP:
What do you know about SAP?
SAP can be abbreviated as a System application and products in data processing. SAP is also known as Enterprise resource planning (ERP). SAP system application contains various fully integrated functional modules that help to manage business development applications. SAP is a no.01 ERP application and has more than 150,000 installations, 85,000 customers in 125 countries.
SAP is a German multinational software company located in Wall Dorf. SAP develops enterprise software to manage business operations and establishes customer relations. The company is popularly known for its ERP software services. SAP enterprise application offers “best-computing Cloud ERP solutions” that will empower the next generation of business development applications.
Why SAP is required?
The following are the major reasons that will explain why we need SAP ERP;
- ERP SAP supports the business integration process inside any organization.
- SAP also improves financial or capital planning. And also helps to execute the organizational strategies and planning.
- Helps an organization to speed up their decision-making process over the data analysis practices.
- SAP ERP application helps to extend the business network to wider their domains, product expansions, and reach their services to customers, partners, and suppliers.
- Helps in the identification of operational risks to improve governance.
- SAP ERP offers protection against enterprise data breaches and security to information leakage.
- Makes any enterprise adaptable to any rapid changes in the business application process according to the requirements.
- Helps in getting the long-term profit that improves the customer base.
SAP Architecture:
SAP R/3 is three-tier architecture and we will explain the important components.
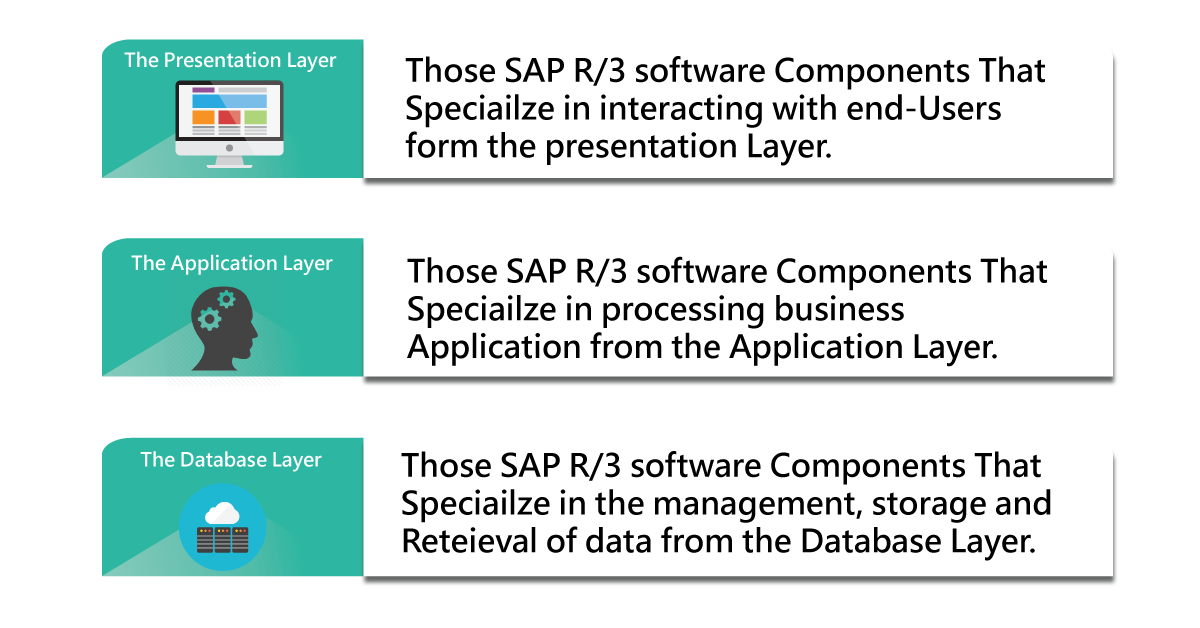 SAP R/3 is three-tier architecture and new generation enterprise software from mainframe computing technology (we can also call it client-server architecture). This three-tier architecture contains a database, application, and user interface servers.
SAP R/3 is three-tier architecture and new generation enterprise software from mainframe computing technology (we can also call it client-server architecture). This three-tier architecture contains a database, application, and user interface servers.
Let me explain them one by one;
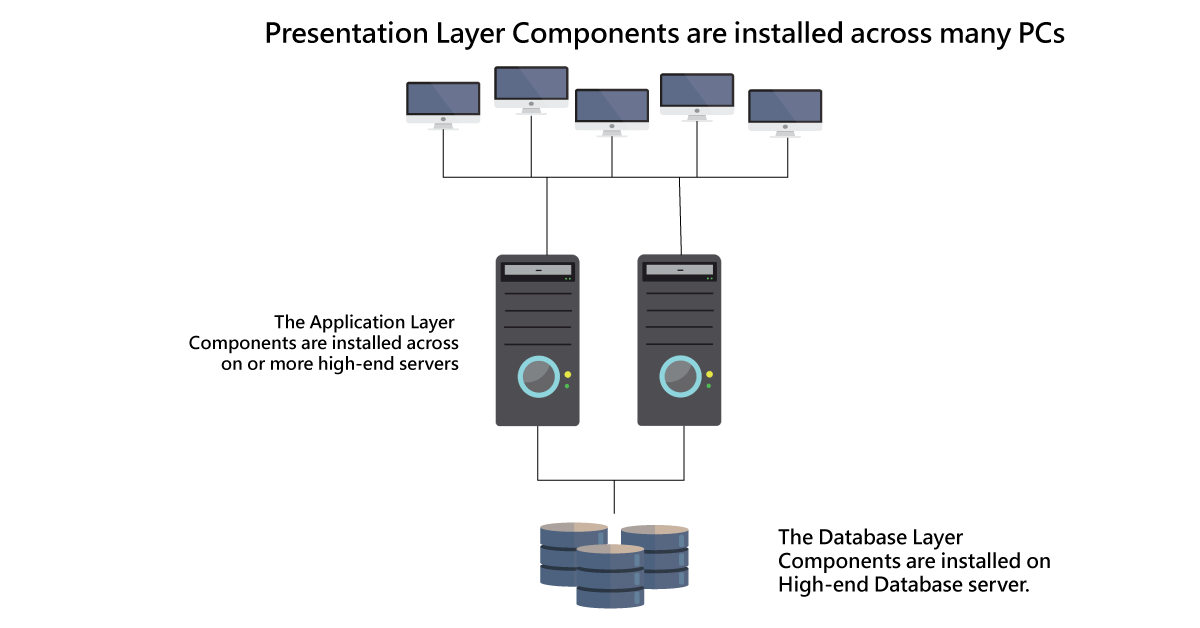
1. Presentation server:
Presentation server helps to create the system capable graphical interface.
- Presentation layer is also called a Client layer and this layer acts as user interactions.
- In SAP –ERP also supports user interaction purposes with the help of a Graphical user interface.
- Example for this type of server is Desktop, Laptops, and Mobile devices.
The below diagram will explain the process of the presentation server;

2. Application server:
The application server contains specialized system devices such as multiple CPUs and varieties of RAMs.
- Application layer also known as the Basic layer or Kernel layer.
- Almost all the SAP application programs are executed at the application layer level.
- Application layer also helps to establish the communication between the presentation and database layer.
- In the application layer, where the workload is distributed to the different work processes.

3. Database servers:
This database server contains specialized system applications with fast and larger hard-drives.
- Database server helps to store the data.
- Datastore can be of different types of data, they are business data, SAP tables, SAP programs, and SAP system data.
- Examples for database servers are Oracle, PeopleSoft, Microsoft SQL, IBM DB/2, Sybase, and Siebel.
Client: A client is a logical portion of any SAP ERP R/3 database server. According to a business standpoint, a client can be defined as a logical group of various companies.

SAP Certification Training
- Master Your Craft
- Lifetime LMS & Faculty Access
- 24/7 online expert support
- Real-world & Project Based Learning
The below diagram will illustrate Client functionality:

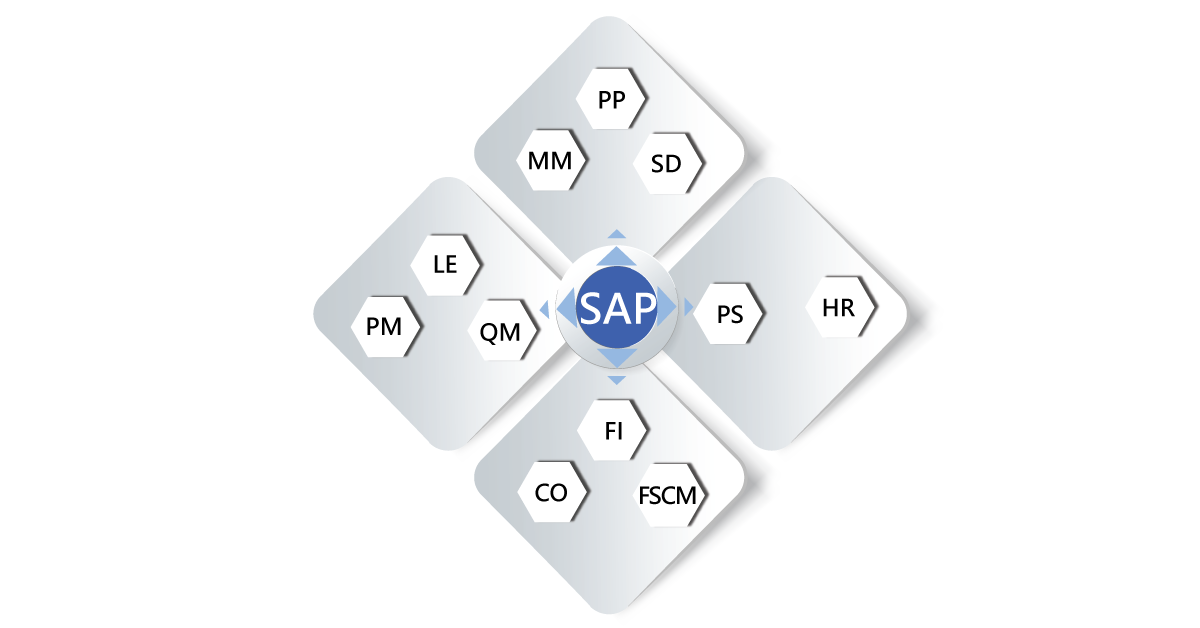
SAP Modules :
SAP ERP solution consists of various functional modules, which are used to provide transaction execution key business applications, they are;
- Financial Accounting (FI)
- Financial Supply chain management (FSCM)
- Materials Management (MM)
- Controlling (CO)
- Sales and distributions (SD)
- Logistics Execution (LE)
- Production planning (PP)
- Quality management (QM)
- Plant maintenance (PM)
- Project systems (PS)
- Human Resources (HR)
 Now it’s time to know the advantages of SAP ERP:
Now it’s time to know the advantages of SAP ERP:
Advantages of SAP ERP:
Below are a few advantages of using SAP ERP software:
1. Improve alignment of strategies and business operations:
- Run your enterprise in accordance with strategy and plans.
- Accessing the right information in real-time to identify concerns in the early stages.
- Pursue business opportunities proactively.
- Achieve corporate objectives by aligning workforce and workforce and organizational objectives.
- Find the best people and leverage their talent in the right job at the right time.
2. Improve productivity and insight:
- Leverage self-service and analytics across your organization.
- Improve operational efficiency and productivity within and beyond your enterprise.
3. Reduce Costs through increased flexibility:
- Use Enterprise services architecture to improve process standardization efficiency and adaptability.
- Extend transactions, information, collaboration functions to a broad business community
4. Support changing industry requirements:
- Take advantage of the SAP NetWeaver platform’s latest open, web-based technology to integrate your end-to-end processes seamlessly.
5. Reduce risk and solve complex business challenges today with SAP:
- Your trusted partner for Long-term growth with 30-years of experience working with organizations of all sizes in more countries than any other vendors.
- Join SAP’s world-class partner network, uniquely qualified to support the best business practices in more than 25 industries.
6. Improve financial management and corporate governance:
- gain deep visibility into your organization with financial and management accounting functionality combined with business analytics.
7. Increase profitability, improve financial control, and manage risk.
8. Optimize IT spending Integrate and optimize business processes.
- Eliminate high integration costs and the need to purchase third-party software.
- Deploy other SAP business suite applications incrementally to improve cash flow and reduce costly borrowing.
9. Gain higher ROI faster:
- Install SAP ERP using a rapid implementation that costs less than half what traditional approaches cost.
SAP business suite:
SAP business suite is nothing but a collection of all fully integrated business applications namely SAP CRM (customer relationship management), SAP ERP (Enterprise resource planning), SAP PLM (product lifecycle management), SAP SRM (supplier relationship management), and SAP SCM (supply chain management).
SAP Business Suite applications:
a.SAP HANA:
SAP HANA is a high-performance business suite that supports analytical appliances by using in-memory computing, and this is one of the break-through technologies. The main motto of using this business suite application is to enable business analysis on a large scale, non-aggregation of data available at an unprecedented speed only for local memory enables the user to work on complex analyses, plans, and simulations using real-time data, this business suite also provides multi-model data processing and enables you to provide advance level data analytics.
b. SAP Convergent Charging:
SAP convergent charging offers a rating and charging business solution for high-volume data processing in service-based industries. The main motto of using this SAP convergent business suite is to deliver price design capabilities, high-performance business ratings, and balance management.
c. Customer relationship management (CRM):
Unlike other Customer relationship management, the SAP’s Customer relationship management (CRM) a part of the SAP business suite. The main motto of this business suite application is to reduce the application cost, increases the decision-making abilities, address the short-term business services with effective outcomes, and achieve differentiated capabilities over the long term services.
d. Enterprise resource planning:
ERP business suite is a foundation to compete and win in the business global marketplace. The SAP ERP business application supports the basic functionalities of business processes and operations. This is the specific need for many business application modules such as SAP ERP financial management, SAP enterprise resource planning (ERP), SAP ERP HCM (Human capital management, SAP enterprise resource planning (ERP) operations, and SAP ERP corporate service management.
e. SAP Environment, safety, and health management:
SAP business suites support various environments, business occupational, and safety-related to product services, regulatory compliances, and responsibility. This business suite application is accomplished by several corporate policies, business compliances, and environmental setup, health and safety measurements with the global business process for human resources, business logistics, productivity, and finance management.
f. SAP global traceability:
The SAP business suite allows you to trace objects like a batch which is implemented across both SAP and Non-SAP systems. When in the event of recall or withdrawal process, SAP global batch traceability assures timely compliance with legal timelines. This SAP GBT helps you to minimize the resource cost and reduces the risk exposure. With the help of SAP GBT, you can also analyze multiple business objects, for example, batches, in a single run.
g. SAP product life cycle management:
This business suite is applicable to those whose service wants to survive in the ever-changing tech environment. With the help of products, life cycle management enables you to create and deliver innovative products or services. The SAP Product life cycle management (SAP PLM) offers 360- degree business support for all the product or service related process (this may include requirements to product manufacturing process).
h. SAP supplier life cycle management:
SAP supplier life cycle management considered to be one of the holistic approaches to manage supplier relationships. This business suite also helps to establish the relationship between the suppliers, customers, and organization.
i. Supply chain management:
While working with any project, you may face a lot of pressure to reduce maintenance costs, increase product innovation, and provide effective customer services. SAP supply chain management (SAP SCM) offers collaborations, planning, analysis, execution, and coordination of the entire supply management network, and also empowers the supply chain process to ever-changing business environments.
j. Supplier relationship management:
With the help of SAP, supplier relationship management enables you to examine the forecast purchase behavior, reduce the time of procurement cycles, and also helps you to work with real-time partners. This business suite helps to develop long-term business relationships with all the suppliers and also offers better communication with reliable partners.
TOP 30 SAP GRC Interview Questions !

Subscribe to our YouTube channel to get new updates..!
k. Governance, risk, and compliance:
You cannot avoid the risk, but it’s possible to manage the risk. With the help of SAP governance, risk, and compliance you can balance the risk and opportunities.
l. Sales and operations planning:
This type of business suite provides long-term future demand; the services included are sales and marketing, finance, demand planning stricture, and supply chain planning demands.
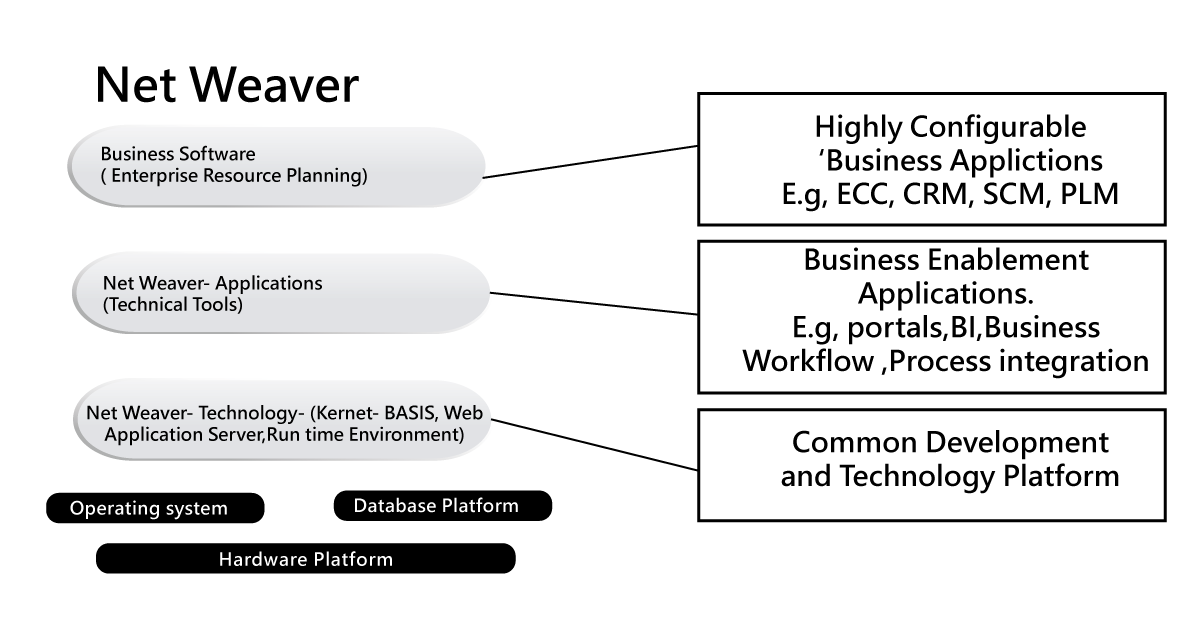
SAP NetWeaver:
SAP NetWeaver is a combination of SAP kernel (This kernel is also known as SAP operating system basically of type web Application system) and SAP software tool for business environments.
This SAP NetWeaver specifies all the software types and services used for business process enablement. As I said earlier, SAP business suites like ECC and SRM consist of software components.
Below are the important points to be considered while working with SAP NetWeaver:
- SAP NetWeaver is popularly known as an open technology platform and provides a comprehensive set of multiple technologies for running critical business applications and enables to the integration of people, information, and process.
- SAP NetWeaver is a web-based application, supports open integration, and an application platform that serves as the foundation for various enterprise service architecture (This is also known as enterprise SOA) and helps to integrate information, and business processes.
- the help of SAP NetWeaver helps you to utilize the open standard business applications and also enables you to make use of any open-source and technology.
- SAP NetWeaver is also considered as the foundation for SAP business suite and also helps many business applications to adopt SAP designs. This also helps in empowering partner solution and custom-built applications.
The below diagram will illustrate the SAP NetWeaver application:
SAP NetWeaver components:
The following are the important components of SAP NetWeaver;
1. SAP NetWeaver application server:
This SAP NetWeaver application server offers platform-independent web application services, business applications, and standard developments, and also enables you to leverage already existing technologies for various web-based service-oriented solutions.
2. SAP NetWeaver business warehouse:
This component enables you to integrate business data across the organizations and enterprise into practical business information. And also provide an effective decision-making facility.
3. SAP NetWeaver Gateway:
This SAP NetWeaver component enables developers to create the business application that links the business user to the SAP software environment.
4. SAP NetWeaver Master Data management:
This component supports cross-system data consistency and integrates the business process development across the extended value chain management.
5. SAP NetWeaver process orchestration:
This type of SAP NetWeaver component improves the process, simple workflow methods to integrate a business process that offers the span applications and organize the boundaries. The functions included are business process management, business rules management, and process integration.
6. SAP NetWeaver Portal:
This unifies the critical information and business applications to provide users’ role-based view that helps you to understand the project lie cycle and also guides you to take advantage of resources.
7. SAP Auto-ID infrastructure:
This NetWeaver component gives all the capabilities to auto integrate devices namely RFID readers, Bluetooth devices, Printers, embedded systems, and USB devices.
8. SAP NetWeaver Identity management:
This component addresses the device access and helps you to solve the issues which are facing typical enterprise-related issues. NetWeaver identity management also enables you to create a new opportunity to integrate business processes and integrate devices in any heterogeneous IT environment.
9. SAP NetWeaver Information lifecycle management:
This NetWeaver component allows developers to perform data archiving and implement regulatory retention rules in the environment.
SAP – Logging Onto SAP system:
In this section we are going to explain how to login into the SAP system, Firstly let me explain about SAP logon:
SAP Logon:
SAP Logon is used to generate any icons to logging into SAP R/3 systems. One important to be considered here is that usually SAP logons are not placed in the SAP R/3 windows group, instead, they are generated through the SAP logon menu. This type of SAP logon is available once you have installed the SAP GUI at your workstations.
SAP Logon icon:
The below diagram will give an idea about the SAP logon Icon:
![]()
SAP logon Pads:

Point to remember:
- The SAP logon menu can be used as a one-stop shopping store, with the help of this logon, end-users can choose logon icons, logon groups, and also create customized logon icons.
- Logon icons will log any user into one specific application server. A logon group will help the user to log onto one of several application servers that depends on the best performance system environment.
Adding a new SAP application server:
Steps:
To create a shortcut for connecting the new SAP application server, you should follow these steps:
- The First click on the SAP logon from the windows desktop -> then SAP logon pad will open -> then click on the “new” button as shown in the below screenshot:

- Now click on the “next” button as shown below;
3.Next step is to fill in this information:
- Description: in this section, you have to provide meaningful short text details.
- Application server: here provide the IP address details of the application server, which is provided by the basic administrator.
- System number and System ID: this gives the system number details provided by the SAP basis administrator. Initially, it should be given as 00(by default).
- SAP router string: provide the SAP router string information, which is given by the SAP basis administrator, sometime it is available in the left blank.
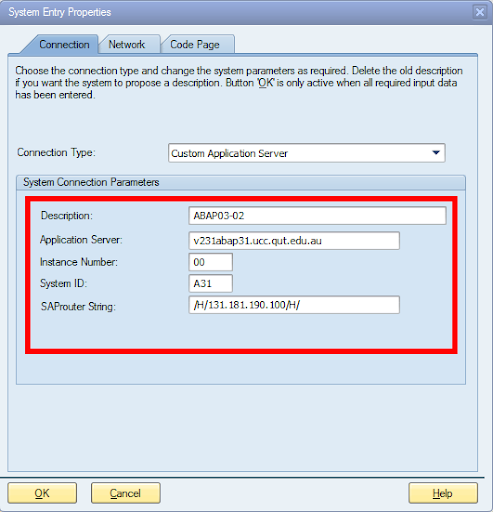
- Click on the finish button to complete the configuration. Now newly created SAP application server is available.
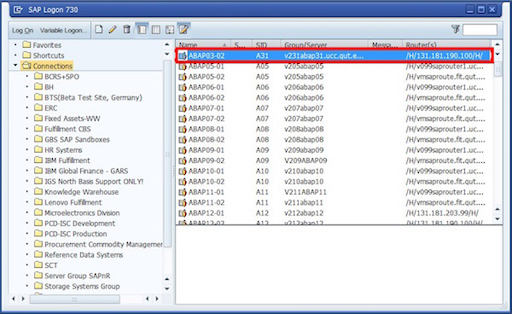
SAP GUI types:
Below are the important GUI types available;
- SAP GUI for Windows environments
- SAP GUI for Java environments
- SAP GUI for HTML environment.
SAP project life cycle:
This SAP project life cycle will explain the work environment and tells which transaction code, this project life cycle contains various stages and subsequent. The below diagram will explain this:
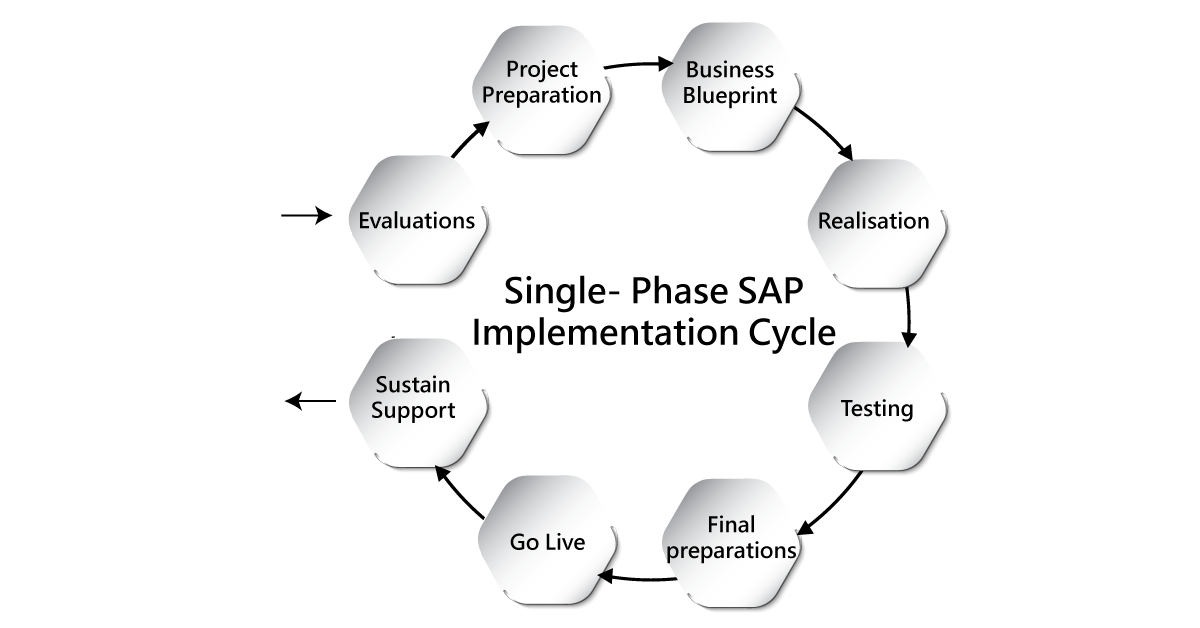
Stages of SAP project life cycle:
- Evaluation: this stage may be a decision that has to be chosen between different vendors or various product sections.
- Project preparation: this stage explains the SAP implementation and organization process details. The project preparation stage also provides complete knowledge of the business process.
- Business Blueprint: A business blueprint specifies the SAP product modules and mapping of the existing business process.
- Realization: here the actual work of customization begins and also helps to sync the SAP software with different organizations. In this stage, the business process can also be done.
- Testing: The changes made in the realization stage need to be tested for effective results. Testing can be done by SAP testers, and there are different types of testing available.
- Final preparation: here the production system will be prepared on the basis of changes made from the realization and testing phase. Certain system activities also take place in this stage.
- GO –live: once you are done with the final product, now it’s time to release this product to the end-users. This type of go-live may be done in a phase-by-phase manner.
- Sustain or support: The now the product will move to the “sustain or support stage.” Here you can find whether the end-users are happy with the final product or not if they are not then you have to cross-check the final product and do all needed steps.

SAP transaction codes:
Transaction codes in SAP are used to access various stages. Let me list them:
ABAP/ Tables /Data Dictionary
- SE 11 – dictionary definitions
- SE14 – Database utility
- SE16 – Data browser
- SE16n – Modify the sap edit.
- SD11 – data model
- SM30/SM31 – table view maintenance
- SE54 (SOBJ) – tables or View cluster
- SE37 – function module editor
- SE38 /SE39 – program editor or split-screen
- SA 38 – program execution
- SE80 – ABAP development workbench
- SE84 – Object navigator
- SE18 – BADI definition
- SE19 – BADI implementations
- SE24 – Class builder
- SW01/2 – Business object builder or browser
- SMARTFORMS – smart forms administrations
- SE71 – SAP scripts (Form painter)
- SE43 – Area menu maintenance
- SE91 – message maintenance
- SE93 – transaction maintenance
Runtime/ logs/ database
- SM21- system log SM31 update requests
- ST22 – ABAP Runtime errors
- SM12 – table look entities
- SM56 – number range buffers
- SNRO – number ranges
- SE30 – runtime analysis
- ST01 – system trace
- ST05 – SQL trace
- DB02, ST04 – database tools or performance
- ST02, ST06 – database tune summary
- SCU3 – table logging
Jobs/ Batches / events
- SM36 – job definition
- SM37/ SMX – job overview
- SM50 – process overview
- SM34 – view cluster maintenance
- SM49/ SM69 – External commands
- SM66 – process overview
Batch Input:
- SM35 – batch input: session overview
- SHDB – batch input recorder
Paths and connections
- AL 11 – SAP file directory
- FILE – Logical file path
- SM58 – transactional RFC
- SM59 – RFC connections
Spool (Output)
- SP02 – Spool request selections
- SP02 – List of own spool requests
- SPAD – spool administration.
Conclusion:
In this SAP tutorial blog, I have explained SAP’s definition, history, advantages, and what makes it so popular ERP system. Learning this blog will help you to gain theoretical knowledge but to get some hands-on experience; you must take any online course. In today’s business market SAP ERP module has been dominating other programming applications. Due to this reason almost all the fortune 500 companies are coming forward to recruit SAP consultants with good packages.
SAP FICO Tutorial
What is SAP FICO?
SAP FICO module is a highly powerful module that covers nearly all business processes experienced in different industries. This module is extensively implemented within SAP and is the preferred design module for both external and internal reporting on accounting processes. The main purpose is the collection and recording of all financial transactions which are displayed by an entity to provide accurate financial statements at the end of the trading period.
With SAP FICO, companies can improve their financial administration. It aims to manage finance perfectly. It will be very hectic, complex, and stressful to use the workforce in financial accounting management. The Sap FI module helps relieve workforce stress by dealing more effectively with a company's financial and accounting needs. It also enables them to examine the company's financial situation on the market in real-time as well. That's why the SAP FI module has become the most popular module implemented successfully across organizations. This can be integrated into other SAP modules such as SAP PP, SAP SD, SAP SCM, SAP MM, etc. SAP FI consultants implements financial accounting and cost accounting through SAP ERP Financials.
Become a SAP FICO Certified professional by learning this HKR SAP FICO Training !
Why are we using SAP FI?
The SAP FI module allows you to manage data related to financial accounting in an international framework of several currencies, languages, and companies. The critical components of the SAP FI module are General ledger, Cash journal, Parallel valuations, Tax accounting, Financial statements, Accrual, Inventory, Master data governance, Accounts receivable and payable, Fixed asset, and Fast close functions.
The SAP FI includes the following subcomponents:
- General Ledger
- Asset Accounting
- Accounts Receivable
- Accounts Payable
- Banks
- Fixed Assets
- Funds Management
- Travel Management
- Legal Consolidation
- Shared service center
SAP FI module:
General Ledger: A general ledger includes every detail of a company's transaction. It serves as the main record for keeping all accounting information. General ledger entries include Customer Transactions, Supplier Purchases, and Company Internal Transactions. Some of the common T-codes used for the maintenance of General Ledger accounting are FBCJ, FB50, FB02, F-06, F-07.
Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable: It contains details like how much amount is paid by the client and how much amount is paid by the company to the provider. This means that the Accounts Payable contains all transactions of the Vendor, and the Accounts Receivable contains all transactions of the client.
Some of the common SAP Accounts Receivable T-codes are FRCA, VD01, FD11, FD10.
Some of the common SAP Accounts Receivable Tables are KNVV, KNA1, BSIW.
Some of the common SAP Accounts Payable T-codes are MK01, MK02, XK01, FCHU.
Some of the common SAP Accounts Payable Tables are LFBK, LFM2, LFA1.
Asset Accounting: Asset Accounting covers all of the company's fixed assets and provides full details of the fixed asset transaction. The Financial Accounting's asset accounting module works in close collaboration with other modules such as SAP Plant Management, SAP MM, EWM, etc.
Some of the common T-codes in Asset Accounting are AUN0, ASEM, AT01, AT03
Banks: Bank Accounting covers all transactions carried out via banks. It consists of balance management, all incoming and outgoing transactions, and the master data of banking transactions. You may create and handle all types of banking transactions with the component Bank Accounting.
Commonly used Bank Accounting module tables are KNBK, BNKA, LFBK
Some of the common T-codes in Bank Accounting are FF_6, FI13, RVND.
Funds Management: The purpose of this module is to manage funds within an organization. It covers all transactions relating to the receipt of funds, expenditures of funds, and future expenditures. It interacts with other modules like General Ledger, SAP Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable, SAP Material management, etc., for obtaining the details of funds. It assists a company in preparing budget forecasts and using the funds appropriately.
Some of the common T-codes in SAP Funds Management are FMWA, FM5I, FMEQ.
Commonly used SAP Funds Management tables are FMIT, FMIFIIT, and FMFCTR.
Travel Management: The purpose of this module is to manage any business travel costs. It covers all travel requests, their planning, and the expenditures involved in all travel requested. It assists an organization in managing travel expenses effectively by enabling integration with any other SAP modules.
Some of the common T-codes in Travel Management are PR00, TRIP, PR05, PRTS.
Commonly used Travel Management tables are FTPT_PLAN, FTPT_ITEM, PTRV_HEAD, TA22B.
Legal Consolidation: It assists an organization in treating its multiple units as one company; it, therefore, makes it possible to consider all the details as one financial statement for every company in the group. An organization may have a clear understanding of its financial agency as a unique entity.
Commonly used Legal Consolidation module tables are T000K, MCDX, GLT3, FILCP.
SAP CO Module:
Another important SAP module available to an organization is SAP Control (CO). It supports monitoring, optimization, and coordination of all the processes across the organization. SAP CO comprises the management and configuration of master data covering internal orders, cost and benefit centers, and other functional areas and cost elements. SAP CO consists of recording both services provided and production factor consumption by an organization. The primary focus of the SAP control module is planning. It allows you to identify variances by comparing real data with plan data, allowing you to control your organization's business flows.
Integrating SAP CO into financial accounting
SAP CO and SAP FI modules are two different elements within an SAP system. There is a steady flow of data between these components. Data flows related to cost flows to financial accounting control. Simultaneously, the system assigns costs and revenues to various controlling account allocation objects, like business processes, cost centers, projects, or orders.
Become a SAP FICO Certified professional by learning this HKR SAP FICO Training In Delhi !
Major sub-modules of the SAP CO system
The following are the major sub-modules of the SAP CO system:
- Product Cost Controlling: It computes the cost of manufacturing a product or providing a service. It lets you compute the price by which you will be able to market it in a profitable way.
- Profit Center Accounting: It serves to assess the gains or losses of individual and independent sectors of an organization. These sectors are responsible for their costs as well as their revenues.
- Profitability Analysis: Its purpose is to analyze the benefit or loss of an organization according to individual market segments. It provides a basis for decision-making. For example, it helps determine packaging, price, distribution, channel customer, and market segment.
- Cost Element Accounting: Cost and revenue accounting gives you an overview of an organization's costs and revenues. Most values automatically move from financial accounting to controlling. The accounting for cost and revenue elements calculates only those costs which have no other expense or only a single expense in the financial accounting.
- Activity-based Accounting: It is used for the analysis of business processes related to cross-departments.
- Cost Center Accounting: For controlling purposes in your organization, Cost center accounting is used.
- Internal Orders: They are used to collect and manage based on the job involved. You can allocate budgets for those jobs that are monitored by the system to make sure they are within the established budgets.
Conclusion:
In this tutorial, we have covered all the basic information related to SAP FICO. I hope you found this information helpful. For more information related to SAP FICO, stay tuned.
Sap Security Tutorial
Introduction to SAP security:
SAP security is one of the essential function modules that is required to secure the SAP system requirements and critical data from any unauthorized access while transferring data in the distributed environments. SAP security enables organizations to maintain and review the profile policies, and system policies locally or remotely. To secure your system, it’s important to understand the user access policies, data encryption, authorization methods, and profile policies. SAP security enables you to regularly check “SAP system Landscape” and always keep your eyes on changes you made in the configuration and access profiles. With the help of SAP security, standard super-users will be well protected, user profile parameters, and values.
Want to Become a Master in SAP Security? Then visit here to learn SAP Security Training from hkrtrainings
Why is security required?
The following are the few scenarios that explain the needs of SAP security;
- Leaked data while data transmission in the remote system, lack of password policies, superuser profiles are not well maintained, and many more reasons.
- Unable to maintain the strong password policies in the organizations.
- Profile parameters are not properly well defined in the system.
- Unsuccessful login attempts and the users’ sessions policies are not well defined.
- Failed to maintain the network communication security while sending data over the internet or intranet, and not properly maintaining encryption keys.
- Failed to maintain database users properly and no security measures were considered while performing system configurations or installations.
To overcome all the above reasons we need a security system that should define the security policies in the SAP environment. Database security is one of the severe problems that commonly occur, so it’s mandatory to maintain the database users and check for the passwords are well protected or not.
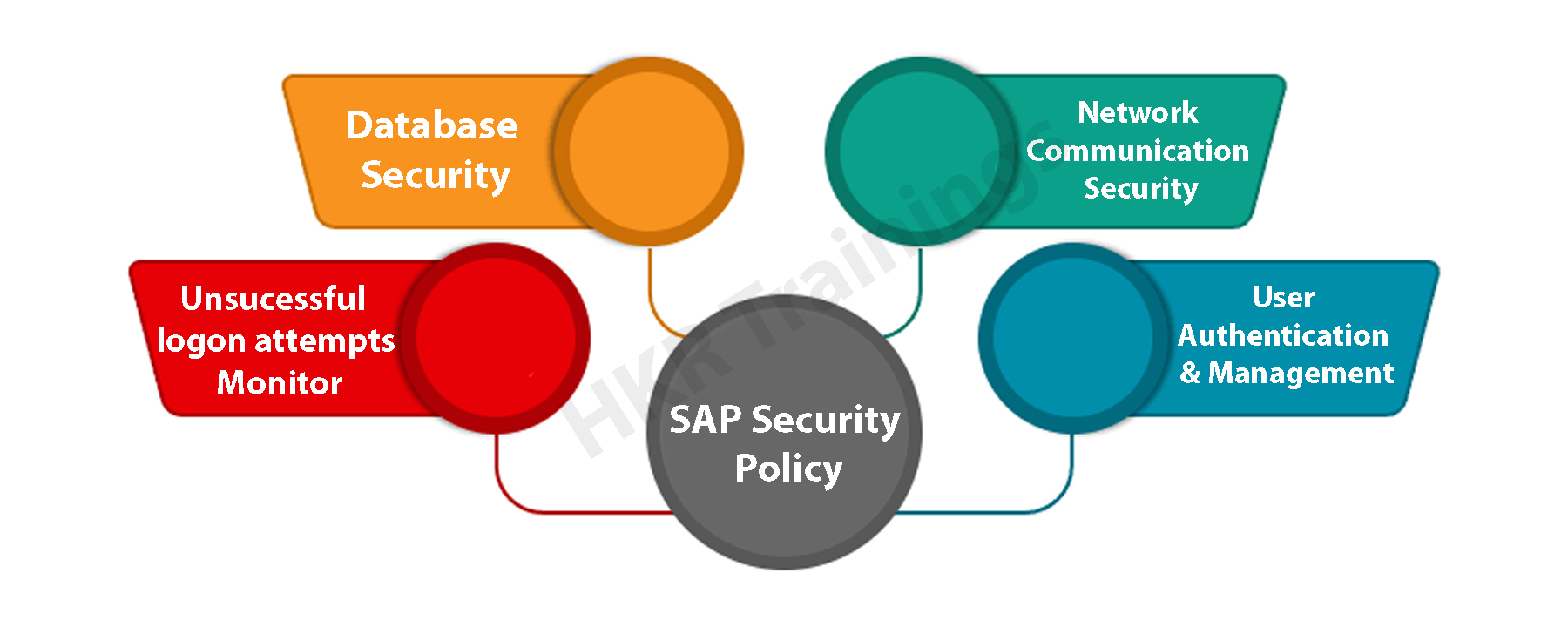
Below is the important security mechanism that should be applied in the SAP system environments. They are:
- User Authentication management.
- Network communication security management
- Protecting the super users and standard users
- Unsuccessful login protections.
- Well-maintained profile parameters and password policies.
- Adaptation of SAP security policies in Unix and Windows platforms.
- Maintaining single sign-on(SSO) concepts.
The following image gives you a complete idea of SAP security policies:
Benefits of the SAP security in the organizations:
- Reduces the risk of granting inappropriate access through the application of a standard role design approach.
- Reduces fraud and compliance through close management of the powerful IDs.
- Visibility and auditing of the superuser access that includes automation of the processes to log, review, and approve the activities performed with superuser access.
- Offers full automation of user administration and secure role processes, including workflow for requesting, reviewing, and approving changes to user access and SAP security roles.
- Elimination of time-consuming and manual activities during the access approval process.
- Increased reliance on preventive security controls (as opposed to detective reporting controls) to maintain clean SAP control environments.
- Implementation of an overall information governance framework.
User Authentication and Management in the SAP Security system:
Let me explain a common scenario that we face every day; If an unauthorized user tried to access the SAP system under a known authorized user, and tried to make configuration changes, manipulate the system configuration, and key policies. If an authorized user accesses the system and important data, there might be chances that unauthorized users can also access other critical information as well. So to reduce such scenarios, we need an authorized and secured system.
The user authentication mechanism in the SAP Security system;
Here is a few authentication methods provided,
- User Id and User management tools.
- Securing the network communications.
- SAP logon tickets.
- X.509 Client certificates.
User Id and User management tools:
The most common method to access the SAP system is by using the UserId and password, UserIDs are created by system administrators. SAP offers various parameters to define the password policies such as password length, password complexity, and default password change, etc.
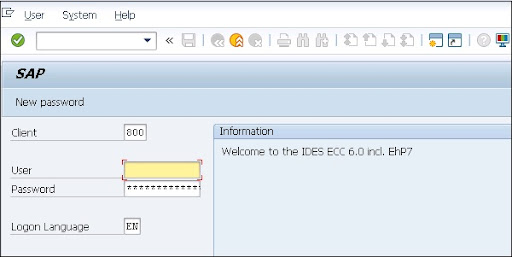
User management tools in the SAP system:
SAP NetWeaver system offers various user management tools that help to manage users in the environments. They also provide a strong authentication service for Netweaver applications such as JAVA and ABAP.
User management for the application server in ABAP (use the transaction code: SU01),
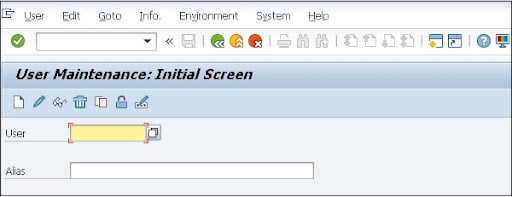
Network communication security:
Network communication security is used to login into an application server by using a secured authentication method. You can also use SNC (secure network communication) for user authentication that can be done through SAP GUI (graphical user interfaces) for windows or by using RFC (remote functional calls) connections.
Network communication security makes use of various network topologies that eliminate threats and prevent network attacks.
A well-defined network topology doesn’t allow intruders to connect to the organization’s LAN (local area network, hence there are no security loopholes on the network services.
In the following image, you can see the network topology;
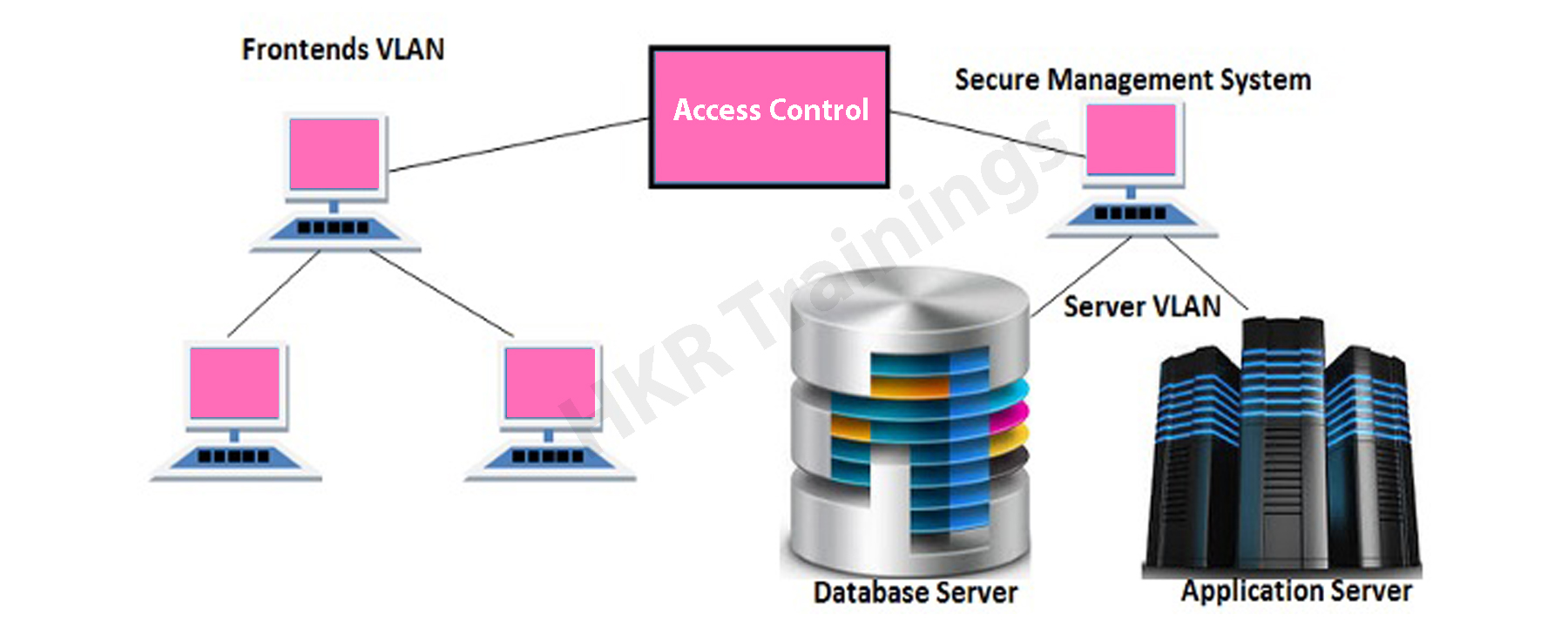
It is always good to place your database and application server in a separate VLAN (Virtual LAN). It allows users to improve the access control system and increases the security of the SAP system. Frontend SAP systems are implemented in different VLANs, so it’s not easy to get into the separate server VLAN, and that bypasses the security of the SAP system.
In your SAP system, the most common targeted areas of network attacks are Landscape, application servers, and Database. In the windows/ Unix, these network services are maintained in a separate file /etc/services as shown in the below the diagram;
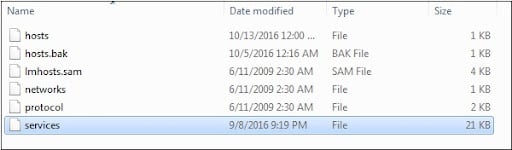
Become a SAP Security professional by learning this HKR SAP Security interview questions
SAP security- UNIX system:
When we talk about SAP security in the UNIX platform, the following are the important criteria that we should consider;
a. Password protection
b. Deactivating BSD remote services.
a. Password protection:
In the UNIX platform, an intruder or attacker uses a dictionary attacker program to identify the password stored in the UNIX operating system. So to avoid this, you can store your password in a shadow password file, only root users are able to access this file to improve the system security.
b.Deactivating BSD remote services:
BSD remote services that allow remote access to the UNIX systems. When a remote connection is initiated through the files /etc/host.equiv and $HOME/.rhosts. These file types consist of information about the hostname and IP address of the connection source and a wildcard character.
You can deactivate any threat scenario by using the file name inetd. conf in the UNIX system as shown below;
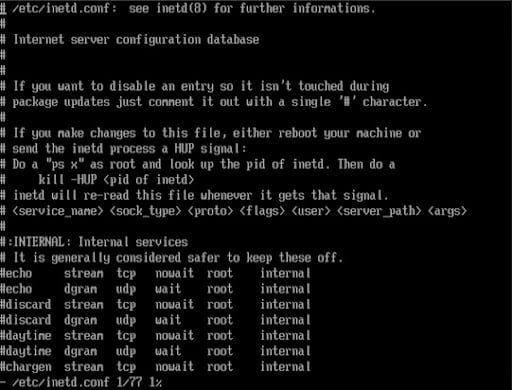
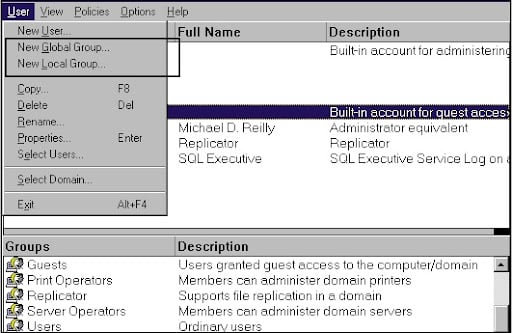
SAP security- Windows platform:
In your windows OS, you need to create different users and groups to run the SAP system securely. It is always good to add all WIN NT users to use groups to ease the management tasks. In the Windows OS, there are types of users groups used;
- Global groups
- Local groups
In the below image, you can notice the global groups and local groups;
1. Global groups:
Generally, all the global groups are available in WIN at the domain level and that can be used to assign users from multiple servers. You can choose the global group as per your requirements, although it is recommended to use a naming convention as per the SAP S/3 system installation. The standard global group name available in the SAP system installation is SAP_
The following are the commonly used global groups in the WIN;
- SAPadmin: this group consists of all the SAP administrators.
- SAPusers: this group consists of all the SAP application users.
- SAPservice: this group consists of a list of SAP system programs.
- DomainGroups: this group consists of the list of all the SAP users who come under the Domain side.
2. Local groups:
Local groups are limited to one server in the Windows domain, however, they increase the security of the SAP environment.
Users can notice the relation between local and global groups: let me make a list of them.
- A single user can be a part of the global group and a local group as well.
- In a few cases, you can also include a global group in the local group.
You can create a local group with the following file name;
SAP_
Standard users in a Windows platform:
Window NT User −
- Administrator − Administrator accounts with access to all the resources.
- Guest − Only guest access to all the resources in the system.
SAP System User −
ADM SAP − System Administrator with full access to all SAP resources. - SAPService
− Special user responsible to run SAP services.
Database Users −
− To run database-specific services on the Windows platform. -
− Database user to perform general DB operations.
Final take:
The SAP security tutorial article explains the fundamental concepts of SAP security such as Introduction, benefits, purpose, user authentications, SAP security in both Windows and UNIX environments. We hope our articles are helpful and reaching out to many tech communities across the world.
Related articles:
SAP Simple Finance Tutorial
What is SAP Simple Finance
The proper procedures of finance permit people and organizations to work together with more proficiency and to utilize the insights that help to stay in competition; it also manages the procedures of financial and operational execution. The financial value map recognizes the priorities of business and solutions which classifies them into the procedures of the logical, the products of the finance gave the support for the span portfolios such as SAP ERP financials, SAP solutions for EPM, SAP solutions for GRC, and the BI.
Become a SAP Certified professional by learning this HKR Trainings of SAP Training !
Finance value map
The solutions of its portfolios are based on innovations of technology like SAP and its customer experiences, their innovation helps the finance companies by allowing them to offer value for the instant insight businesses. It made the IT landscape with the change of replication reduction and provided advantages to the CIO that is included in the capability end to end procedures. It has the capabilities of analysis, simulation, and also the finance procedures used to recognize the best options for business strategy, to provide an immediate team of finance, timely instances, and also the decisions of the financial. Its abilities are created to make the procedures of the finance, for the customers of the suit thorough SAP power leveraging. that may be helpful for both the finance through process prospect and IT through architectural perspective.
Become a SAP Simple Finance Certified professional by learning this HKR Trainings of SAP Simple Finance Training !
Benefits of SAP simple finance
The given below are some essential benefits of SAP simple finance:
- we can have real-time analysis of data.
- We may delete the unwanted hardware complexity.
- There is no chance for database latency because of ELT jobs.
- It provides the database which is in memory.
- Its column keeps the calculations supported with the run.
- It conducts the procedure which is parallel.
- It is used for the compression of data.
Want to know more about SAP , Visit here SAP Tutorial.
Essential features of the SAP simple finance
The given below are some essential features of SAP simple finance
- Financial planning and analysis: By using this company may utilize the plan, forecast, budget, etc. while the process is going on, with this, we may forecast the effect of organizations' decisions in the company's financial reports.
Accounting and Finance: Through its latest feature of finance and accounting companies may satisfy the legal terms and finish the reports of finance on time. - Financial risks management: with the help of this predictive analysis, companies may identify the problems of the financial procedure at an initial stage and various ways for their migration. It is simple to identify suitable investment rates according to the standards of the market.
Risk and compliance management: With strong financial procedures, we can eliminate unauthorized access simply for companies' sensitive information. We can also identify the abuse and fraud which companies may manage the risk of complete financial procedures. - Technical system landscape: It is developed by using NetWeaver of SAP and the business suit of SAP ERP. Below is the minimum backend landscape of the system. It includes the updated version of ERP 6.0 as SAP ep8 for SAP ERP 6.0 which can integrate with other applications of ERP such as distribution, management material, sales, etc.
- There is no requirement of special prerequisites as this is a tutorial of elementary, we can understand its concepts that are explained simply without any strain, they are like the basic understanding of financial deals, it is more useful for you to have more knowledge like account exposure and to know the financial information.
Key facts of sap simple finance
- SAP simple finance displays the power of one. The posting on a journal of one unified replaces the posting it on different individual ledgers like a material ledger, assistant accounting, co, etc.
- The table of a journal entry is designed through the transitions of organizations in SAP general leader, old general ledger, co, FI-AA, and also the components of the cost determination.
- SAP decreases its data redundancy instances and duplication among the modules of the FI, and the extension of ACDOCA contains the coding block but one of the difficult tasks FI implementation in any company to reconcile the postings of FI.
- By using this SAP simple finance we can report and transact at a time as our system houses the system of SAP BW which deletes the offloading report requirements and the analytics for our system of SAP BW.
- We can also say that there is no requirement of ELT for our SAP BW instance so there is no place for delays in reporting with that we can report in real-time which units the data of transactional and historical, that permits us to design both tactic and strategic decisions that are based on earlier information.
Conclusion
In traditional applications, the SAP database is used to store the complete data to conduct the calculations and expose the result at the layer of the application. Almost most of the time is spent on these calculations and the aggregation. But when it comes to SAP simple finance, its applications offer an excellent performance of applications into the database. All the information is stored in a database in memory that is much faster than the old one. It helps to replicate and delete the waste data load in real-time. If you have any queries or questions that need to be answered, please make comments below to get your question answered quickly by our HKR expert trainers.
Other Related Articles:
About Author
As a Senior Writer for HKR Trainings, Sai Manikanth has a great understanding of today’s data-driven environment, which includes key aspects such as Business Intelligence and data management. He manages the task of creating great content in the areas of Digital Marketing, Content Management, Project Management & Methodologies, Product Lifecycle Management Tools. Connect with him on LinkedIn and Twitter.
Upcoming SAP Certification Training Online classes
| Batch starts on 24th Feb 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 28th Feb 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 4th Mar 2026 |
|

