Juniper Tutorial
Last updated on Nov 07, 2023
introduction to the Juniper system:
Juniper is one of the most popular networking systems and offers high performance networking capabilities. This Juniper cyber security offers services and networking for enterprise companies. Juniper is an American based Multinational Corporation Company; the company headquarters located in Sunnyvale, California. The main purpose to develop this product is to offer networking services through routers, networking management software, switches; software defined networking technology, and networking security products. Juniper device allows multiple distributed enterprises in the network to share a common protocol and common management plane. Sometimes, these devices are not referred to as edge or core switches and later this approach is known as a “Fabric” rather than a network. This fabric allows the user to create a single and very large kind of networking fabric with any two low level latency end points.
Why is Juniper such an important networking system?
Juniper networking system directly competes with another popular networking system – “Cisco”. Juniper system offers viable routing, security solutions, and switching services. The below are the top 5 reasons to use Juniper cyber security system;
1. This is one of the top networking devices for routing, security, and switching:
The main focus of Juniper Company is to offer top networking solutions for services like routing, security, and switching. Juniper device provides speed and secured networking systems. This may lead to slow down cyber security attacks. Juniper’s operating system is more modular, robust, and flexible than Cisco's.
2. Provides exceptional values for specific needs:
Juniper device concentrates on delivering high data to design valuable products, ISP networking, and Enterprise customers. It uses a chip called “ASCI’s” or Application specific integrated circuit to transfer the data, and flexible product development.
3. It’s an open architecture system:
Juniper is an open architecture system due to the adaptation of open flow open networking services and this architecture offers a top notch line market approach. Juniper provides a high level automatable infrastructure system. Junos operating system is an API driven and manages to build easy administrations.
4. Agility at its leading edge:
Agility indicates the integration of the various device components, and we already know that Juniper resources consist of routers, switches, and security devices. These resources are now applied to areas like network virtualizations, software defined networks, and remote office supports.
5. Keeping the Cisco device honest:
Juniper network may not be big as Cisco, and their device meets the core networking services and offers valuable services to provide customers. Customers look into Juniper and many small share networking vendors make use of Juniper. Cisco is used by top enterprises and business companies.
Benefits of Juniper system:
The following are the key benefits of using the Juniper networking system; let me list a few of them;
1. Juniper network devices enhance the business partnering for ease of doing their businesses.
2. This Networking device also helps in the business growth, high growth areas for various revenue acceleration environments.
3. Improves the portability for growing their business and high growth rates.
4. Juniper provides integrated products, services, and distribution networking programs into a single JPA data framework.
5. Streamline product authorization, cloud accreditations, and adds revenue requirements for elite network systems.
6. Helps in the simplification of program requirements, improves the predictability and execution of MDF.
7. Supports marketing for business growth systems like Educate, Grow and Equip.
8. Offers consolidate programs and demand generation tools.
9. This is now considered as a champion program for technical proxy competency.
Juniper Architecture overview:
The architecture of Juniper defines the components, features, and work nature. In this section, we are going to explain the routers and connectors. Now see the architecture of juniper;
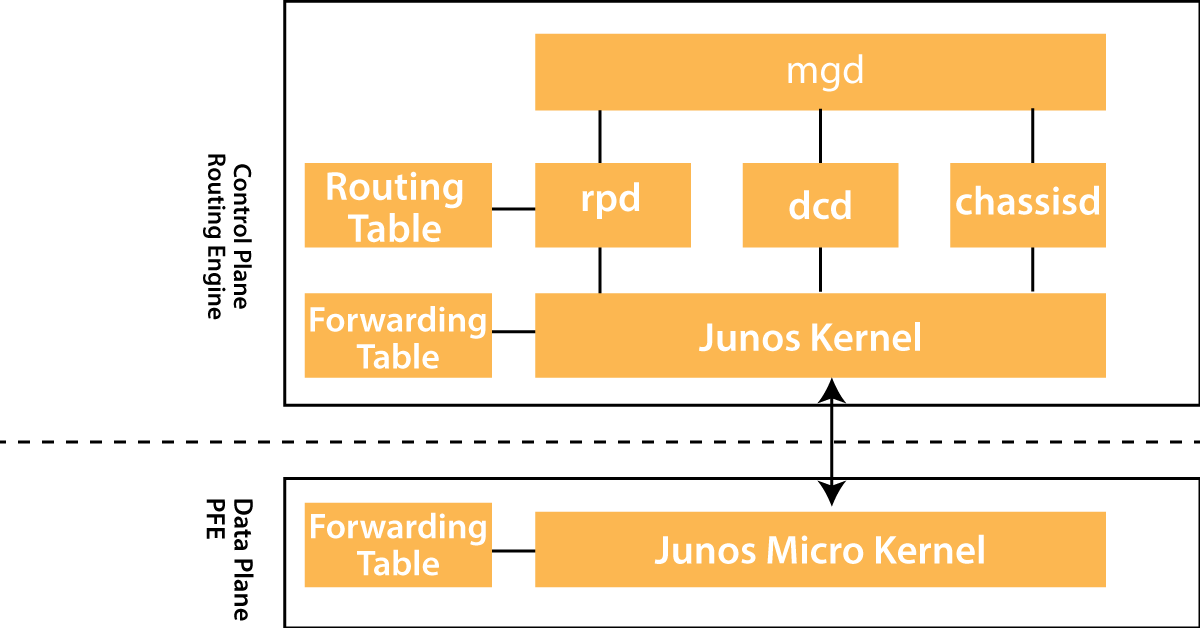
Juniper architecture consists of major two components:
1. Packet forwarding engine component: this component performs Layers 2 and Layers 3 packet switchers, packet forwarding services, and router look ups.
2. Router engine: This component consists of layer 3 routers that offer services and various network management devices.
The packet forwarding engine and the router engine both components perform independently but they communicate with each other using 1000 Mbps internal links. This type of arrangement offers forwarding streamlines, router controls, and allows devices to run internet scaled network at high-speed connectivity.
The routing engine consists of these features:
1. Router protocol packet process: here these entire router protocol packets from the network devices will be directed to the router engine, and therefore it will never delay the packet engines.
2. Software modularity feature: this software modularity process available in a separate process. So any failure of one process does not affect the other software process.
3. in-depth IP functionality: Each router protocol network is implemented with complete IP feature sets and offers full flexibility for advertising, modifying, and filtering routers. Here routing policies will be set according to these parameters such as lengths, prefix, border gateway protocol, and prefix lengths, etc.
4. Scalability feature: Juniper operating system routing tables are developed to hold all types of routes used in current and near-feature networks. Juniper operating systems support a large number of virtual circuits and interfaces.
5. Storage and change management feature: This feature consists of configuration files, microcode, and system images; these are maintained in primary and two secondary storage devices to get permitted to local and remote upgrades.
6. Monitoring efficiency and flexible feature: here warning alarms and packets will be generated without affecting the packet performance.

Juniper Training
- Master Your Craft
- Lifetime LMS & Faculty Access
- 24/7 online expert support
- Real-world & Project Based Learning
Latest features of Juniper:
You can see a lot of new features added in the latest version of juniper. Let me explain them one by one:
1. Advanced policy based routing (ABPR):
This type of policy based routing allows user to schedule ABPR policy for a specified time duration. To make use of this type of scheduler, first, you should create a scheduler type while configuring the ABPR policy.
2. Application service bypass in advanced policy based routing:
With the help of this feature, the user can bypass the APBR configuration services in the profile rule. Once you are done with the APBR profile rule match and rerouting, you are able to specify the traffic matching of APBR profile rules.
3. DSCP support in rules:
Here with the help of this rule, DSCP or differentiate service code point value in APBR performs the advance policy based routing. You can also configure the DSCP value, dynamic application, and dynamic groups.
4. Default mechanism feature:
This default mechanism used to forward the networking traffic through the APBR rules. The default mechanism also acts as a default system to specify the next-hop device and transfer them to a destination.
5. URL based routing:
This feature is enhanced to include only URL categories networks and it works based on destination IP address. It includes these types of identifications such as Enhanced web filtering and local web filtering derived from UTM.
Juniper configuration overview:
To configure the juniper operating systems on a router follow these steps:
1. First connect the router to the device using the console port.
2. Then power on the device and has to wait for that router to boot.
Here the Juniper operating system boots automatically and this process completes when you see the command login: on the console.
3. Now it’s time to log in as a user root,
In the beginning, the root user account does not require any password. This is because the prompt on the system shown as root@#.
4. Then start with the Juniper operating system by using the command line interface.
root @# cli
root @>
5. Now enter the operating system configuration mode:
Cli > configure
[edit]
root @#
6. Now configure the hostname of any device. Here you are not supposed to use spaces in between the router name. However, the router name should be enclosed with a quotation mark (‘’ “).
[edit]
root @# set system host-name hostname
7. Now it’s time to set the router password, and enter the clear text password. This type of password should be encrypted by default or an SSH public key strings.
[edit]
root@ # set system root-authentication plain-text-password
New Password: type password
Retype new password: retype password
8. Now you should configure the device domain name:
[edit]
Root @# set system domain-name domain-name
9. Configure the IP address and prefix length for the system device management Ethernet interface. This type of management Ethernet interface offers a separate out-of-band management network for the device.
[edit]
root@ # set interfaces fxp0 unit 0 family inet address address/prefix-length
10. Now configure the IP address of a backup device or any default network system. Choose the device that will be directly connected to the local router by the way of the management interface.
[edit]
root@ # set system back-up router address
11. Configure the IP address of a DNS server system. The router uses the DNS server name to transmit the hostname of the IP address.
[edit]
root@# set system name-server address
12. By default, display the configuration statements.
[edit]
root@ show
system {
……
…..
}
13. Commit the configuration; this activates the configuration mode on the device.
[edit]
root @# commit
14. Exit from the Command line interface mode:
[edit]
root@hostname # exit
root@hostname>
15. Back up the configuration method, once you have finished the entire configuration and run the configuration.
The request system snapshot command helps to back up the file root system, and /altroot will also cause the backup process.
Juniper – Command line interface (CLI)
The juniper operating system is popularly known as “Junos”. This Juniper software is the type of modular and standard based. The main feature of the Junos operating system is that the software platform is independent type (that means that juniper is a hardware system, and does not require any other type of vendor hardware systems), so it delivers the same scalability and security feature across hardware platforms.
Juniper command line interface is simple to use and text-based command interface. We use various commands on CLI to configure, monitor, and troubleshoot the software platforms.
In Juniper we can see two types of Command line interface modes:
1. Operational mode:
When you begin to log into the router-> immediately CLI starts. This operational mode available at the top level of the router and commands are used for the following purposes:
a. Control the command line interface environment.
b. Monitoring and troubleshooting the network connectivity.
c. Initiate the configuration system mode.
The important commands used to ping, traceroute, configure, and show, etc.
2. Configuration mode:
We mainly use the configuration mode to configure the Junos software by generating a configuration statement hierarchy. We should enter the configuration mode with the help of a command called “Configure”;
user @host > configure
entering configuration mode
[edit]
user @host#
Issuing this command one after the other at a time with the help of CLI can also configure the “JUNOS” router alternately. We can also configure by creating a text (only make use of ASCII) file format that consists of statement hierarchy. At last, activate the configuration by using the command called “Commit” on the router side.

Subscribe to our YouTube channel to get new updates..!
Juniper – Router Interface configuration:
Here we can see two types of router interfaces namely
1. Permanent interfaces
2. Transient interface
Let me explain them one by one;
1. Permanent interface:
These types of interfaces are always present at the router.
There are two subtypes of permanent interfaces available:
a. Management Ethernet interface: this interface allows us to access router types by using .ssh and telnet file types. This type of interface makes use of out of band connection and does not offer any packet forwarding capabilities to transmit the data packets.
b. Internal Ethernet interface: This interface connects the router engine to the packet forward engine. The router mainly uses this type of interface as a communication link between the JUNOS software system and also a component of the packet forward engine. This interface is configured automatically when the Junos operating system software boots.
2. Transient interfaces:
The transient interfaces are types of interfaces that accept the user’s data packets from the networking packets. These interfaces are located at the physical interface card. This card can be inserted and removed at any time.
Each router consists of two serial ports such as labeled console and auxiliary. Here the console port can be used to connect only tty types of terminals to the routers. The auxiliary port can be used to connect the modems.
Examples for Router interface configuration:
user @host>configure
[edit]
user @host = edit system
user @ host = set host-name juniper
[edit system]
user @juniper #
Juniper command syntax and interface representation:
The following are the important commands used to represent the interface.
1. Media_type: this command type uniquely identifies the physical interface type. It is a two character word command type.
2. FPC: this is the physical plot number available in the chassis where the interface is placed.
3. pic: this is the plot number on the FPC where the interface is placed.
4. port: is the type of location on the pic command where the interface port is placed.
5. unit: this is the logical portion of the interface used to configure the router connectivity.
Cisco versus Juniper:
I think this is one of the important sections, you people might be thinking about which one is the best cyber security system. Here you go,
Cisco:
1. Cisco consists of more global adoptions with a market cap of over $150 billion which dwarf the market cap of that Juniper system.
2. Cisco system routers and switches are designed to go beyond the standard routing and switching for a better network infrastructure.
3. Cisco has a simple CLI which makes it easy to learn and master.
4. Cisco IOS is consistent and intelligent with a more user-friendly user interface. All variants of the IOS are modular.
5. Cisco creates multipurpose networking products which are tailored for enterprise-level networking solutions. It does not provide in-depth debugging as Junos.
Juniper:
1. Juniper consists of a significant share in the hardware space but trails behind in the enterprise-level networking products.
2. Juniper networking products are more cost effective and are mainly focused on speed and reliability rather than consistency.
3. Juniper has a bit complex CLI with an equally complex network configuration which makes it a little tough to learn.
4. Junos is a single cohesive system with a common modular architecture across all platforms.
5. Junos is more developer friendly so integrates easily with application development environments.
Juniper SRX firewall system:
The SRX is a widely used firewall system across the globe. The main purpose of using a firewall is to protect every network based transaction and end user understanding of the metamorphic name. The SRX firewall offers a new class of device connectivity called “Service gateway”. Deep packet inspection is an important service offered by the SRX firewall system and the latest invention of Juniper. Within the juniper network SRX service gateway, you will get an answer to scale the platform’s features to solve complex networking problems.
Important features of the Juniper SRX system:
1. Zones
2. Virtual routers
3. Deep packet inspections
4. Networking address translation (NAT)
5. Unified Threat management (UTM)
6. IPsec virtual private networks (VPN)
7. Dynamic routing
8. High availability management
9. Virtual firewalls
There are two types of SRX firewall software:
1. The branch SRX series: this type of SRX series are designed to manage small to large enterprises, that consist of hundreds of employees. In this type of location where the firewalls are typically deployed at the networking edge, separate the users from the internet.
2. The data center SRX series: this type of SRX series are Juniper's flagship high-end firewalls. These types of products are targeted at the middle level data centers and the service provider. They are designed to scale the services and deploy the data at the branch locations.
Networking and its types:
First, let us know the definition of the network; a network is a collection of internet devices such as computers, printers, switches, servers, and routers. Networks are the fundamental part of the day to day activities and located in the home, workplaces, and public areas. Networks allow all kinds of networking-enabled devices to communicate with each other.
There are 4 types of networking types available:
1. Personal area networks
2. Local area networks
3. Metropolitan area networks
4. Wide area networks
Now, it’s time to know the major differences between Local area network and wide area network:
1. LAN:
a. A LAN is a privately operated network that typically contained in a single building location.
b. A Local area network operates at a speed of 10 Gbps or higher.
c. A local area network is less congested when compared to other networking types.
d. A local area network can be managed and administered in-house.
2. WAN:
a. Wide area network is used to connect any graphically separated offices to each other. Multiple organizations may use WAN’s.
b. A wide area network is more congested when compared to other networking types.
c. A wide area network operates at maximum speeds of less than 1 Gbps.
d. A Wide area network typically requires the use of a third party to perform configuration and set up and also increases the cost.
Juniper network types:
There are five types of juniper networks available:
1. T-series or multi chassis IP/MPLS core routers:
T-series is the Juniper T-series and consists of a line of core routers. This type of T-series router is mainly designed for high-end and core networking activities. The main features of the T-series network included are Half-Duplex type throughput, Full-duplex Throughput, Rack space activity, fully redundant hardware, and multi chassis capable facility.
2. MX –series routers:
The Juniper MX-series routers are a family of switchers and Ethernet routers mainly designed by Juniper networks. The MX routers are designed to improve the bandwidth speed and a visualize MX 3D router. This MX router utilizes the juniper extension tool kit (JET) and third party software can be integrated with the routers.
3. Juniper M-series router:
Juniper M series is a line of Multiple service edge routers designed for enterprise-level and service level networks. The M40 products are the first ever product developed by Juniper Networks. These M-series juniper routers run on JUNOS operating systems.
4. PTX router series in Juniper:
This is the high-density interface distributed over the core networks and network applications. The only fully converged router that integrates the Internet protocol address, MPLS, and optical transport and deployed into a space power contained environment. This form of the foundation is mainly used in IP transport architecture, and offers interfaces for large scale networks.
5. ACX router series in Juniper:
ACX router or universal access router available in the form of small factors, fan-less router integrates the GPS receiver and security features. This series is hardened, cost optimized multiservice routers, and high-density routers offer the performance, capacity, and universal metro services. This router series also made up of eight T1/E1 interfaces, four copper or fiber GBE ports, and eight copper GBE ports.
Conclusion:
The main purpose of any networking administrator is to efficiently and effectively maintain the infrastructure of any organization. In this Juniper tutorial, we have explained basic to core level concepts to help you to master the technology. The juniper now a day competes with Cisco, but most of the middle and small enterprises like to adopt this networking device. While juniper is still able to manage the carve niche hardware market. As per the latest report, juniper also reported a significant growth in the switching revenues in recent time. There is a huge demand for network professionals, so you can expect most of the fortune 500 companies to show keen interest to recruit network professionals. An average salary for juniper fresher earns Rs. 6, 50, 000 and an experienced professional earns more than Rs. 15, 00, 000.
Other Article:
About Author
A technical lead content writer in HKR Trainings with an expertise in delivering content on the market demanding technologies like Networking, Storage & Virtualization,Cyber Security & SIEM Tools, Server Administration, Operating System & Administration, IAM Tools, Cloud Computing, etc. She does a great job in creating wonderful content for the users and always keeps updated with the latest trends in the market. To know more information connect her on Linkedin, Twitter, and Facebook.
Upcoming Juniper Training Online classes
| Batch starts on 10th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 14th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 18th Mar 2026 |
|


