Mulesoft Tutorial - Table of Content
- What is mulesoft?
- Mulesoft ESB
- Difference between Point to Point integration and ESB integration
- Components of Mule ESB MuleSoft
- Functionality of Mule ESB
- Advantages of Mule ESB
- Mulesoft Architecture
- How do you install a Mule?
- Key features of AnyPoint Studio
- FAQ
Let's now walk through the Mulesoft Tutorial with examples in a more detailed way.
Who Can Benefit From This Tutorial?
The information stipulated in this blog is beneficial for the developers who want to create complex ecosystems by integrating APIs, databases, and other applications.The primary target audience of this mulesoft tutorial is for the ESB developers and businesses who are willing to migrate their entire application to the Mule ecosystem.Apart from the developers, it also benefits the students and researchers who have an interest in technology.
The data is geared at the developer who wants to create and incorporate APIs, servers and other frameworks into the advanced ecosystem. The main focus of this tutorial will be the developer working on ESB and the company looking to move their current application to the Mule world. Along with these two, this tutorial is useful to students and researchers who are interested in technology.
Now let's have a look at the core concepts in depth.
What is Mulesoft?
MuleSoft seems to be the most extensively used integration platform for linking the cloud as well as on SaaS and business applications.MuleSoft was acquired by Salesforce in 2018 with the goal of speeding up clients' digital transitions. MuleSoft's integration platform helps organizations to not only unlock data from legacy applications, cloud apps, and devices but also to make smarter and faster decisions and provide end-users with highly interconnected experiences.
Salesforce Integration Cloud now includes MuleSoft's Anypoint Platform. MuleSoft, on the other hand, has a pre-built connector for Salesforce that allows for smooth integration.
Interested in learning the Mulesoft Course ? Enroll in our Mulesoft online Training program now!
Mulesoft ESB:
ESB stands for Enterprise Service Bus and at its core, a framework with a set of guidelines and concepts for connecting many apps across a bus-like network. The main principle of the ESB design is linking multiple applications by creating a communication bus between them and then enabling each application to talk to this bus.
This model of communication approach by ESB decouples systems, allowing them to communicate without relying on or being aware of the actions of others. Moreover Mule, Anypoint Platform's runtime engine, is indeed a versatile ESB solution that helps to boost agility by providing a simple, well-defined, scalable "pluggable" system.
How do you Implement ESB?
The Mule ESB's goal is to decouple applications from one another and effectively communicate in a massively scalable and fast network Bus. That's a communication network that's easily predictable and reduces the chance of information leakage. The Adaptor and the BUS can be used to construct ESB as shown below.
Mule makes use of messaging servers such as JMS and AMQP, that enable the development of BUS connectivity by separating the applications. Mule Servers are the only way to get the Bus up and running.
- Adaptors are in charge of acting like a telephone network, allowing you to connect with one another. Similarly, the adaptor enables the creation of a communication network for data interchange across apps.
- The ESB Bus enables information and data to flow consistently from one application to another. Mule achieves the highest level of software connectivity over an unified platform in this approach.
Mule provides cloud-based application interaction and communication networks to facilitate application activities, instead of utilizing several distinct applications and APIs over multiple networks to administer your application.Adaptors are not single-end operation controllers, rather it also handles security, network faults, tracking, and message routing operations.
Why is ESB needed?
One of the most prevalent motivations for firms to use an ESB as the backbone of their IT architecture is to increase organizational agility by shortening time to market for new operations. An ESB architecture makes this easier by providing a simple, well-defined, scalable "pluggable" solution. Furthermore, ESB connectivity allows you to take advantage of your existing systems by exposing them to new applications.
Now lets see where the mule ESB is primarily needed.
- Whenever there is a need for integrating multiple applications on a unified or single platform, then ESB is required.
- In the process of migrating the applications to the cloud.
- To guarantee secure data communication from one application to the other, ESB uses FTP, HTTP, and JMS internet transfer protocols.
- ESB additionally ensures a smooth communication network by transmitting messages between apps. In this environment, the message header, body, and content can all be transferred from one end to other.
- It's indeed essential when you really need to offer services with composition and consumption.
ESB's guiding principles:
The ESB guiding principles are indeed known as the Mule Key Principles in general.
- Orchestration: It is the technique of coordinating two or more applications such that data and processes flow in a continuous stream.
- Transformation: This is really the process of converting data from its original format to a format that may be used in a particular application procedure.
- Transportation: It is a procedure comparable to the transportation layer which facilitates the transport of messages via FTP, HTTP, JMS protocols for network transmissions.
- Several interfaces were supplied to accommodate multiple application interactions with multiple service versions.
- Non-Functional Consistency: This guideline assures that the integrated environment has mechanical support for handling transactions and security.
Mulesoft TutorialMulesoft TutorialCheck out our Latest Interview Questions video. Register Now Cyber Security Online Training to Become an expert in Cyber security.Check out our Latest Interview Questions video. Register Now Cyber Security Online Training to Become an expert in Cyber security.Check out our Latest Interview Questions video. Register Now Cyber Security Online Training to Become an expert in Cyber security.
Difference between Point to Point integration and ESB Integration:
With the demand to provide services, web hosting, messaging, database manipulation, storage, and so many other associated problems, the number of integrations for a medium or upper level application rapidly increases.
You can create the architecture to support the application using the P2P integration technique, but the architecture will become complex as the number of applications grows.
Also, P2P had limits over platform compatibility and language support. To further comprehend this, consider the following scenario.
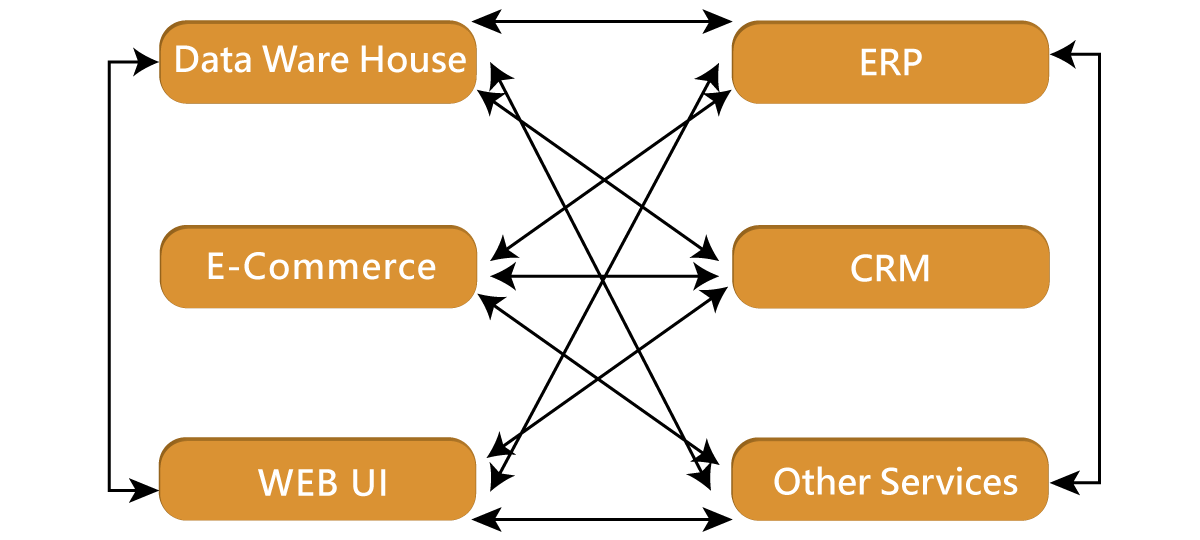
Mule ESB is required due to the limitations of connecting to a different platform and the complexity of various application integration.
Mule ESB provides world-class integration flexibility without having to worry about language support or application architectural compatibility constraints.
Integrating activities into a unified platform, it improves the application's reusable capabilities. As demonstrated in the graphic below, applications can be simply connected in a synchronized manner.

Mulesoft Training Certification
- Master Your Craft
- Lifetime LMS & Faculty Access
- 24/7 online expert support
- Real-world & Project Based Learning
Components of Mule ESB MuleSoft:
Core components, such operations in connectors and modules, are key building blocks of Mule app flows. The logic for processing a Mule event as it travels through the app in a series of linked phases is provided by core components such as the Scheduler, For Each, and Logger components.
By selecting Core from the Mule palette in Studio, you can access Mule components.
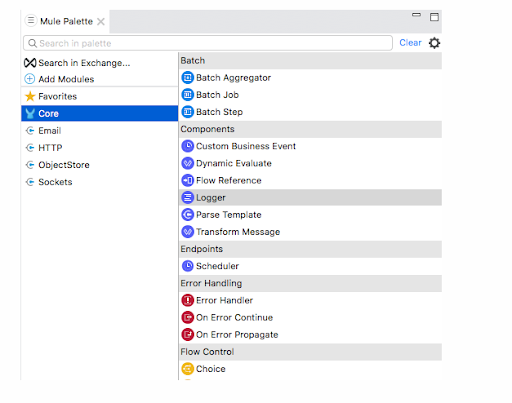
These Core components are responsible for a multitude of tasks, including:
- Custom Business Events: These events are used to collect data on the flows and message processors that handle your business transactions.
- Dynamic evaluate:Instead of forcing you to hardcode a script through the Transform Message Component, you may use Dynamic Evaluate to dynamically select one.
- Flow reference:Within a Mule app, a Flow Reference is used to route a Mule event to another flow or subflow.
- Logger: Used to keep track of crucial information about your Mule programme, such as error messages and status updates.
- Parse Template: This method is used to process a template and return a result.
- Transform Message: This message is used to convert input data into a different output structure or format.
Functionality of Mule ESB:
The ESB acts as a transit system for transporting data between applications within your company or across the Internet, allowing diverse apps to communicate with one another. Mule offers a wide range of capabilities, including:
- Service generation and hosting – use the ESB as a lightweight service container to expose and host reusable services.
- Service Mediation:Protect services from message formats and protocols, decouple business logic from messaging, and enable location-independent service calls via service mediation.
- Message routing: It is based on content and rules, route, filter, collect, and re-sequence messages.
- Data transformation: It is the process of converting data between different forms and transport protocols.
Advantages of Mule ESB:
The major advantages of the Mule ESB are:
- API LED connectivity:Mulesoft's API LED connection design simplifies integration solutions.
- Connector:Mulesoft has over 400 connectors to help you overcome your integration issues with any system.
- Development Environment:Mulesoft APIs are created with anypoint studio so simple hat we can use simply drag & drop components from the pallet, in order configure and utilize them.
- Centralized platform:It provides centralized monitoring and administration from a single location.
- Security:It provides comprehensive corporate security capabilities that allow businesses to function in a highly secure environment.
- MuleSoft safeguards you from on-premises/cloud data breaches by allowing you to work over a secure Gateway connection.
- Through registered access, the Service Registry manages the dissemination of data and services.
- You can use the web-based administration console to gain access.
- You can use a service flow analyzer to quickly test applications and services.
Top 70 frequently asked Mulesoft Interview Questions for freshers & experienced professional
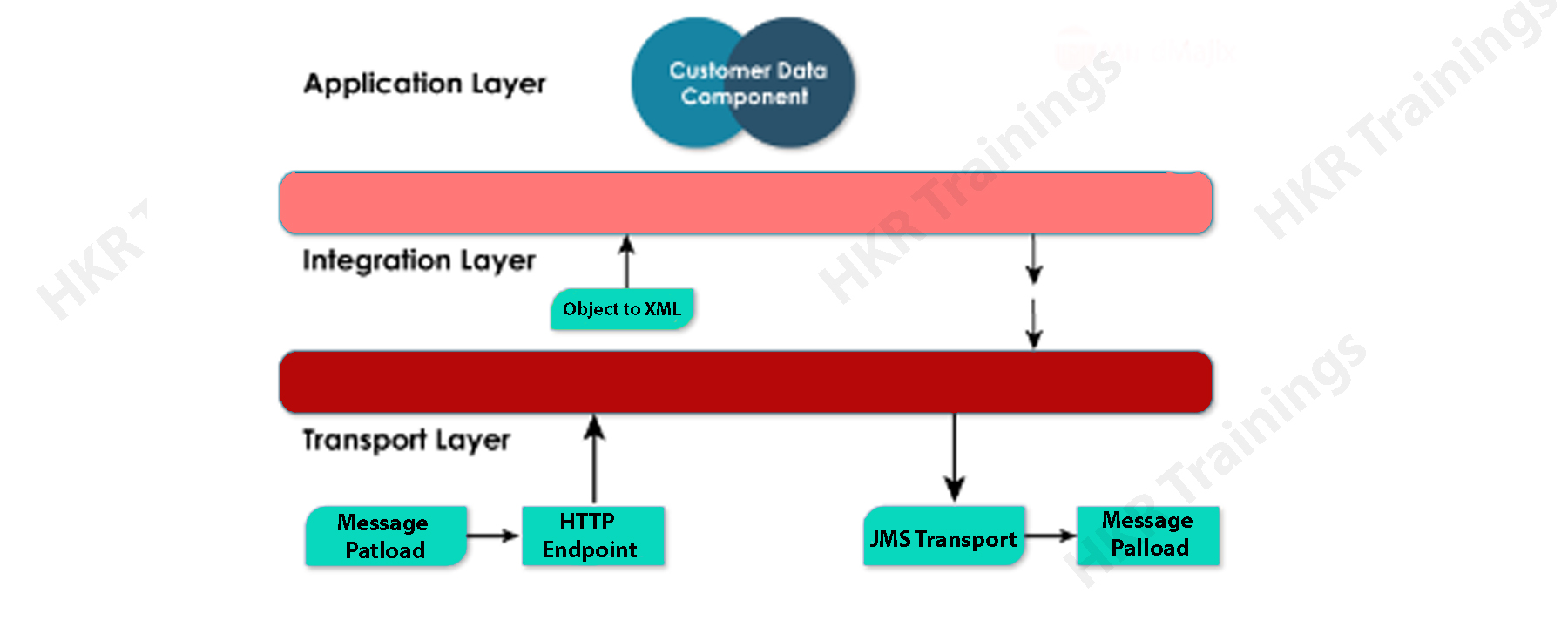
Mulesoft Architecture:
For application integration and data processing, MuleSoft follows a three architecture. The application layer, the integration layer, and the transport layer are the three layers. The architecture is depicted in the diagram below as shown.

Mule Development has three different work types that may be adjusted and customized.
- Service Components Development:
This activity entails encouraging the POJOs and spring beans to be reused. POJO and Spring Beans can be easily understood by developers who are familiar with spring development.
POJO is a spring-generated class that supports obtaining and setting methods, as well as cloud connectors. Business logic for application development and message enrichment is contained in spring beans.
- Service Orchestration:
It acts as a service mediator, allowing the configuration of message processors, adaptors, and routers with transformers and filters to be integrated.
- Integration
Integration of different applications is critical in the creation of large-scale applications. It provides a lot of versatility in terms of connecting many various built applications, regardless of the protocols they utilize.
Using the transport technique simply allows messages in the source and destination channels to travel from one end to the other. It builds a high level of communication association between the applications to transmit messages within the environment. You can use any available transport method or you can customize the transport method as per your needs.
The data that moves through an application via one or more flows is referred to as a Mule message. It is divided into two sections:
- The message header, which contains the message's metadata.
- The message payload is which comprises your company's business data.
Mule messages are contained within Mule message objects. Variables, attachments, and exception payloads may be present in some Mule message objects.
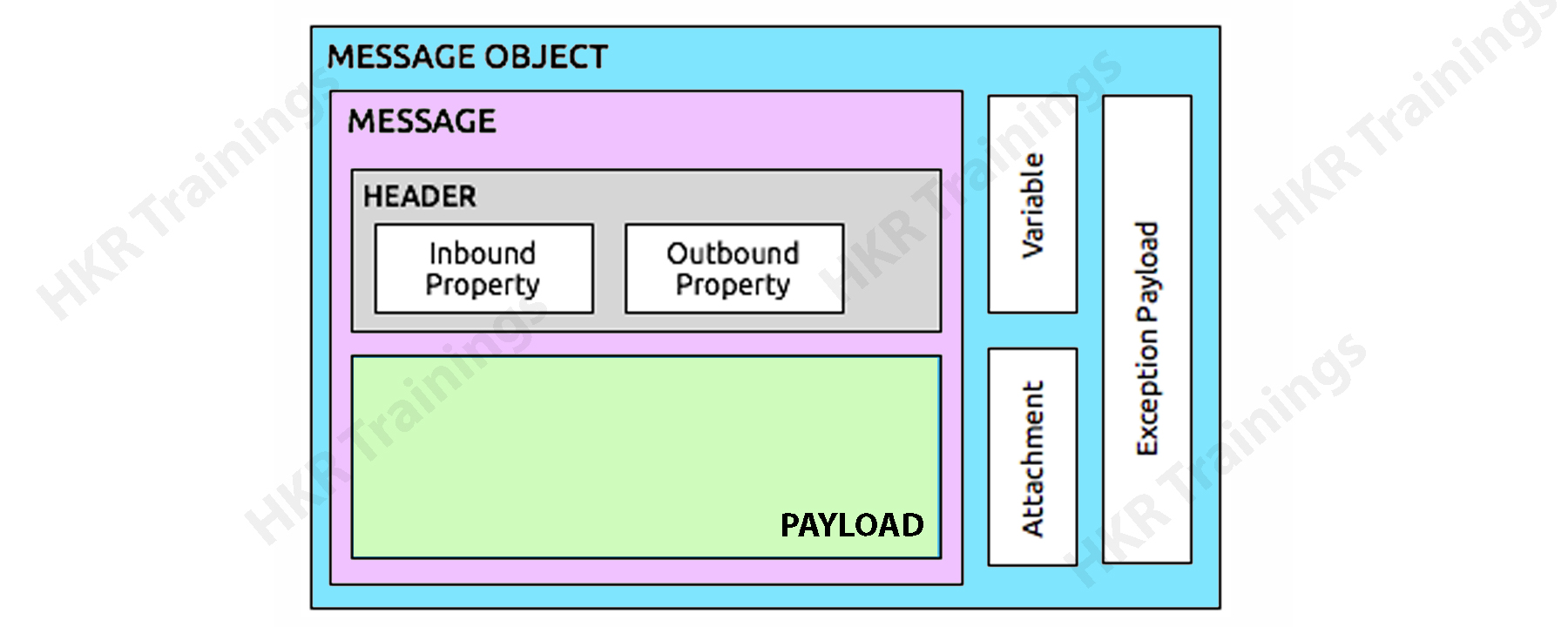
Header: The Mule header, like any other header, contains the information's metadata. It has two properties listed below.
Inbound Properties: The inbound property reflects the messages received directly from the source application. The message's value and structure cannot be changed or updated to meet the demands of the user.
It's consistent all the way from the beginning to the end of the voyage. In terms of technology, it's an immutable message that can't be modified throughout any stage of processing.
Outbound properties: These would be messages that contain metadata identical to inbound messages but are modifiable and changeable along the flow. Mule can either set it or the users of the application can change it.
The message becomes immutable when it passes via an inbound source endpoint. When outbound flows from one end to inbound flows from the other end, the message becomes immutable.The context of the message cannot be changed or modified by the user. The message is delivered using the transport method.
Payloads:The payload is a message that carries an object that contains the business's real message.
Variables:The user-defined metadata about the messages is stored in variables. Variables are a short-term representation of the data stored in messages.
It is not necessary to pass a variable along with the message into the message flow to the destination. Variables in the ESB are divided into three groups such as flow, session and group variables.

Subscribe to our YouTube channel to get new updates..!
How do you Install a Mule?
- In order to install, the mule you need to download the mule from the official website:https://www.mulesoft.com/lp/dl/mule-esb-enterprise
- Next download the mule zip file to your local system
- Below is the process of installation of the mule onto your file.
- Run the Mule 4 binary exe after unzipping the file.
- Create a Mule directory beneath the place where you extracted the downloaded file and set the environment variable to Mule _Home.
- Let's have a look at how to set the environment variable in a Windows environment.
- For version 4.1.5, you can set the variable in a Windows, Linux/Unix environment.
Windows Environment Variable Example
$ env:MULE_HOME=C:Download Mule-enterprise-standalone-4.1.5
Linux/Unix Environment Variable Example
$ export MULE_HOME=~/Downloads/mule-enterprise-standalone-4.1.5/
Once the environment variable is set now, You can check whether the mule is functioning properly or not using the RUN command as follows.
Windows Command for Mule Testing
$ $MULE_HOMEbinmule.bat
Linux/Unix for Mule Testing
$ $MULE_HOME/bin/mule
By utilizing the above-stated commands you can easily run the mule in the foreground Mode. Once this command is activated you cannot run any other command in the terminal. If you want to stop the running command use the key ctrl-c.
The process of starting Mule servicesThere are 2 ways to start Mule services. You select either windows services or Linux/Unix demon services.
Now let’s first start with windows services:
Follow the below-given steps to start windows services ---- Install windows services by using this command
$ $MULE_HOMEbinmule.bat install
- Run windows services using the below command
$ $MULE_HOMEbinmule.bat start
Let’s take another example to start Linux/Unix Demon services using Mule ---
- Install Linux/Unix services by using this command
$ $MULE_HOME/bin/mule install
- Once installed you can run the Linux/Unix services by below command
$ $MULE_HOME/bin/mule start
Example of starting Mule as demon services
$ $MULE_HOME/bin/mule start
MULE_HOME is set to ~/Downloads/mule-enterprise-standalone-4.1.5
MULE_BASE is set to ~/Downloads/mule-enterprise-standalone-4.1.5
Starting Mule Enterprise Edition...
Waiting for Mule Enterprise Edition to run and it is in the process as shown below.
running: PID:34567
How to deploy the mule apps
One can easily deploy the mule application by using things such as:
- Anypoint Runtime Manager
- Anypoint Studio
- CloudHub CLI
- Flow Designer in Anypoint Design Center
- CloudHub API
- Mule Maven plugin
Now let's explore each and every point in a more detailed way.
Deploying from Anypoint runtime manager to cloudhub:
In order to deploy one needs to go through the following points.
- First sign in to anypoint platform.
- Then select the runtime manager.
- In the applications page, just click the deploy application.
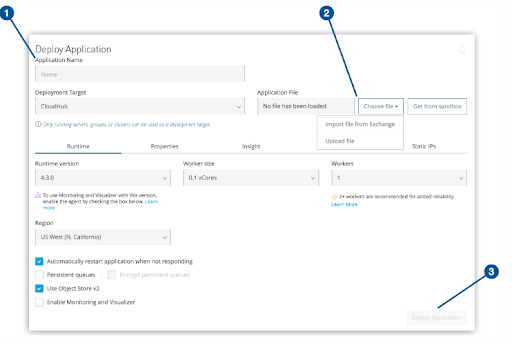
In the above image you can see (1) the Application Name field, (2) the Choose file menu, and (3) the Deploy Application button on the Deploy Application page.
- Give a name for your application.
- In the Deployment Target menu, select CloudHub, if it is not already selected.
- Specify the application file:
- Import a file from Exchange:
- Click Choose file > Import file from Exchange.
- Select Application for the type.
- Enter the name of your application in the search box.
- Select the application to deploy, select a version from the Version menu, and then click Select.
- Upload an application archive (ZIP or JAR) file:
- Select Choose file > Upload file.
- Select the file to upload and then click Open.
- The application file size limit is 200 MB.
- Copy an application from a nonproduction environment.
- See Copy an Application from Sandbox to Production.
- Click tabs to configure application options.
- Click on the deploy application button.
Deploy an Application from Studio:
Your applications are deployed straight to CloudHub from Studio. This option is useful if you want to test your app while it's still being developed.
Except for Design, you can deploy an application from Studio to any environment. The design environment is specific to Anypoint Design Center apps. From Flow Designer, see Deploy a Mule Application.
To deploy from Studio to CloudHub:
- Open your application in Studio.
- In Package Explorer, right-click the project folder and select Anypoint Platform > Deploy to CloudHub.
- If this is your first time deploying from Studio, provide your Anypoint Platform credentials at the prompt.
Studio stores your credentials for future use. You can manage these credentials by selecting Anypoint Studio > Preferences > Anypoint Studio > Authentication.
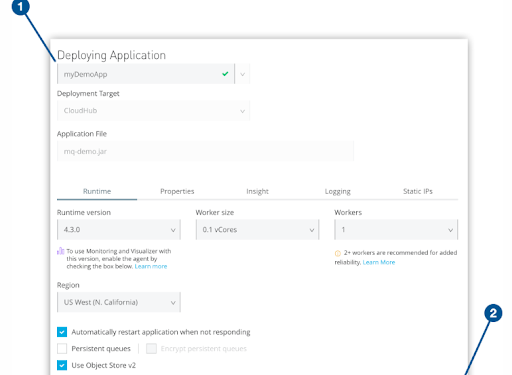
After you sign in, you see the Deploying Application page:
Application Name field and the Deploy Application button
- The image shows (1) the Application Name field, (2) the Deploy Application button on the Deploying Application page.
- Change the application name, if necessary.
- Click tabs to configure application options.
- See Configure Application Settings.
- Click Deploy Application.
Key Features of AnyPoint Studio
The key features of the AnyPoint Studio are:
- Streamline integration and API development with an integrated development environment (IDE) that includes pre-built modules for common integration needs, such as accessing backend systems, routing events, business transformation logic, and error handling.
- By dragging & drop components, you may easily create APIs and integrations. Easily integrate with open source development tools like Maven, Git, and Jenkins.
- MuleSoft and our developer community have produced hundreds of prebuilt connectors, templates, samples, and APIs that you can use right away in Anypoint Exchange. Alternatively, you can utilize our SDK to enhance and create bespoke, reusable connectors.
- APIkit may be used to scaffold APIs based on the OpenAPI and RAML standards, allowing you to begin API development and take advantage of design-first development approaches.
- With DataWeave, Anypoint Platform's data transformation language, you can normalize, join, filter, or map any data type, including XML, CSV, JSON, pojos, EDI, and flat files.
- Enhance code quality by using MUnit to automate the construction of unit and integration tests for Studio applications, and use a built-in exception handling framework to prevent researching misleading errors.
FAQS :
- What is MuleSoft used for?
MuleSoft is indeed a data integration platform that allows you to link several data sources and applications, as well as execute analytics and ETL procedures. MuleSoft also has created connectors for SaaS applications, allowing users to analyze SaaS data alongside cloud-based and traditional data sources.
MuleSoft Anypoint is built on the Mule Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) and Event-Driven Architecture (EDA) (EDA). Through APIs, the platform builds a network of data, applications, and devices. MuleSoft's extended view of integration allows you to incorporate technological advances without having to custom code each one.
- Is MuleSoft hard to learn?
The MuleSoft Certified Developer Mule4 Level exam is a difficult one to study for. Despite having completed the 5-day online Fundamentals course. The important lessons from how I passed the exam are listed here.
Last week, I failed my first attempt at the exam. The next week, I scheduled another appointment and concentrated on the abilities and concepts that I lacked.
- What are the basics to learn MuleSoft?
The learner should have a basic understanding of Java and Eclipse. He should also be familiar with the fundamental terminology of database and programming languages such as Python, Ruby, and JavaScript.
- Does MuleSoft have a future?
MuleSoft will play a crucial role in this transformation. MuleSoft, as a result, presents a lucrative career path for eager software developers and architects aiming to advance their development abilities and realize their full potential.
- What programming language is MuleSoft?
DataWeave seems to be a functional language for doing data transformations in Mule applications. You must first learn the fundamental concepts of programming and the essential capabilities of functional programming languages before you can utilise DataWeave to build your own powerful and complicated data transformations.
- Does MuleSoft use Apache?
Definitely yes because both Apache Camel and Mule ESB are integration solutions that aid developers in connecting disparate parts of software. Both platforms are open-source, although their implementations of the open-source approach differ greatly. Apache Camel is a free, stand-alone application that is completely supported by its developer community. Mule ESB is the MuleSoft Anypoint Platform's runtime engine, which is a licenced and professionally supported solution. Enterprise-level firms, who have more time, funding, and business need for custom-built connectors than smaller businesses, primarily use both solutions.
- Is MuleSoft cloud-based?
MuleSoft's CloudHub is a cloud-based environment where the Mule runtime server and related services are hosted. MuleSoft's CloudHub allows you to deploy an API or a Mule application on a MuleSoft-managed infrastructure.
- Is Java required for MuleSoft?
Mulesoft Expert does not require any prior understanding of Java or Spring. Mulesoft is a programming language-independent integration tool.
- Can a fresher learn MuleSoft?
Yes, but you don't need to be a seasoned Java developer to get by. No problem, you can get started learning Mulesoft right away. It's fine if you don't know much about java; in mule, you don't have to code as much because you can orchestrate your logic by dragging and customizing shapes.
Other Related Articles:
About Author
Kavya works for HKR Trainings institute as a technical writer with diverse experience in many kinds of technology-related content development. She holds a graduate education in the Computer science and Engineering stream. She has cultivated strong technical skills from reading tech blogs and also doing a lot of research related to content. She manages to write great content in many fields like Programming & Frameworks, Enterprise Integration, Web Development, SAP, and Business Process Management (BPM). Connect her on LinkedIn and Twitter.
Upcoming Mulesoft Training Certification Online classes
| Batch starts on 16th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 20th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 24th Mar 2026 |
|

