Cyber Security Tutorial
Last updated on Nov 21, 2023
- What is cyber security?
- History of cyber security
- Need for cyber security
- What can we do with cyber security?
- Business losses as a result of security breaches
- Motives for Cyberattacks
- Cybercriminals and their various subtypes
- Cyber Threats/Attacks Types
- Cybersecurity methods
- Introducing Automation and Cybersecurity Together
- Applications of cyber security
- Cybersecurity Benefits
- Conclusion
Introduction to cyber security?
Cybersecurity is a method of defending a network, computers, and other electronic devices against cybercriminals. Malicious attackers deactivate, adjust, or leak sensitive information, posing a significant risk to a company or an individual.
Cybersecurity serves to maintain information out of the hands of attackers by data integrity, anonymity, and accessibility (ICA).
Cybersecurity is divided into the following subfields:
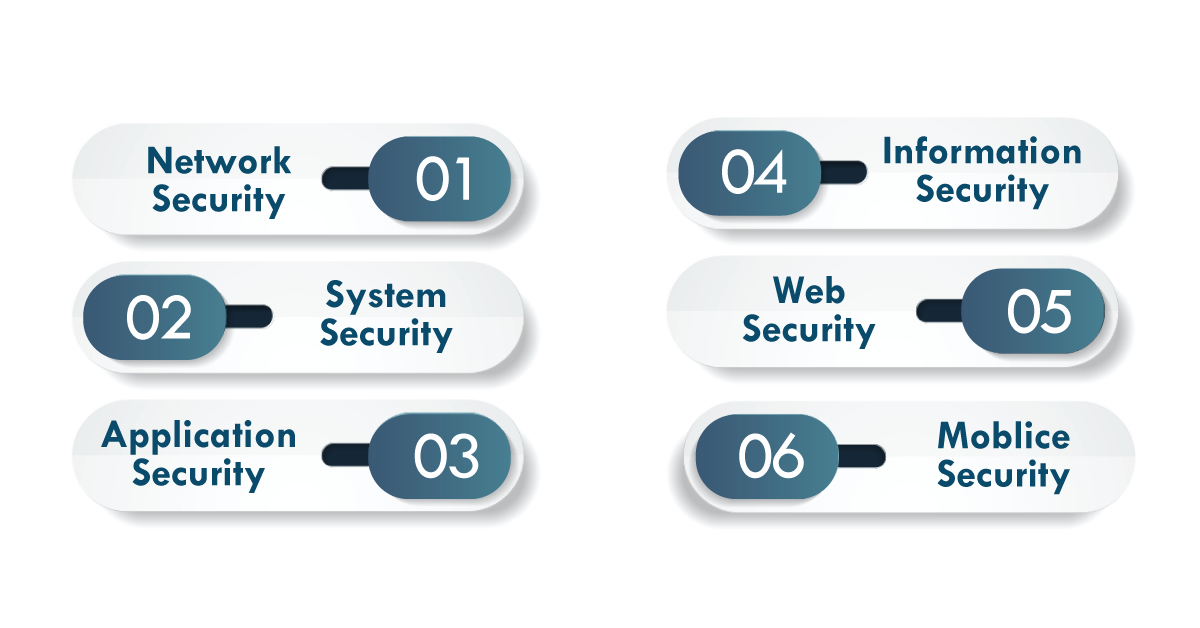
1. Network security:
A network plan is a process of rules and setups that are used to protect network traffic as well as data. They keep track of wireless networks to avoid data theft.
2. System security:
Protect the system and operating system from malicious intrusion, modification, and viruses.
3. Application security
This prevents the application from being hacked.
4. Information security;
Protects sensitive data from unauthorized access and prevents data misuse, disclosure, or destruction.
5. Web safety
Protects a web application from unauthorized personnel's security breaches.
6. Mobile security
All wireless computing devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, are protected.

Cyber Security Training
- Master Your Craft
- Lifetime LMS & Faculty Access
- 24/7 online expert support
- Real-world & Project Based Learning
History of cyber security:
In 1972, ARPANET hosted a research project on cybersecurity.
Bob Thomas, a researcher, created the first computer virus, which he named "Creeper." The Creeper moved across the network, leaving a trail of destruction in its wake. It carried the message "I'M THE CREEPER: CATCH ME IF YOU CAN" wherever it went.
Ray Tomlinson, the inventor of email, developed the first antivirus program, dubbed "Reaper." Reaper would follow the creeper's trail and delete it. When the world went online in the late 1990s, computer viruses went from being a harmless academic prank to a serious threat.
Need for cyber security:
The cost of cybersecurity breaches is increasing rapidly, triggering companies to suffer significant financial losses. The global average cost of a data breach in 2019 is $3.92 million, a 1.5 percent increase from the previous year's survey.
Attackers have grown in the complexity of their attacks by employing smart tactics, posing a significant challenge for organizations to maintain adequate security.
Wish to make a career in the world of Cyber Security? Start with Cyber Security training!
What can we do with cyber security?
Cybersecurity enables us to safeguard our network and system resources, which contain critical business information. This is accomplished by enhancing data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
The various cybersecurity techniques assist us in securing information and minimizing the possibility of entry barriers, helping the firm to be financially viable.
How does Cyber Security make work so much easier?
Cybersecurity simplifies our day-to-day work by ensuring that resources are available in the network when needed.
A minor flaw can have far-reaching consequences for the company's resources and reputation.
Cybersecurity saves the day by reinforcing data privacy, security, and accuracy.
Business losses as a result of security breaches:
Even the most well-known corporations in the world have suffered catastrophic losses as a result of data breaches.
Adobe was the victim of a massive data breach in 2013, which compromised the credit card information of 3 million customers. Hackers accessed encrypted client login information, according to the company. The company was required to pay a legal fee of $1.1 million for the disclosing of customer records.
frequently asked Cyber security Interview questions and Answers !!
Motives for Cyberattacks:
Cybercrime can be motivated by any of the following:
- To harm an organization's reputation
- Financial gain through ransom
- For personal reasons, revenge
- Tends to cause of politics
- Instilling fear
Cybercriminals and their various subtypes:
Cybercriminals are attackers motivated by the desire to commit malicious activity on a network. They are classified as follows:
- Script Kiddies: These are thrill-seekers and enthusiasts who want to be hackers but lack the necessary technical skills.
- Spammers: Bulk messages are being sent to your inbox by these criminals. They attempt to steal your data and engage in fraudulent activities.
- Hacker organizations: These really are unofficial societies that really collaborate secretly with the same goal of breaching a target's security.
- Scammers: Phishers attempt to obtain personal information such as usernames and passwords. To obtain the required information, they pose as trustworthy entities.
- Insiders: Individuals inside an organization who really are willingly pilfering, harmful, or revealing a company's inner data.
- Agents of Advanced Persistent Threat (APT): They flawlessly carry out organized crimes against a target by maintaining a long-term presence on a network in order to mine highly sensitive data.
- Identity Theft: Hey grab some other person's identity without one's knowledge and ability to destroy evidence, such as attempting to make banking transactions.
Cyber Threats/Attacks Types:
There are several types of cyberattacks:
Cyber attacks are classified into two types based on the motivation of the attacker.
- Passive attack: The attacker's motivation is to obtain confidential information while causing no harm to the system or threatening the victim.
- Active attack: The attacker modifies the information and poses a threat to system resources, compromising the system's integrity.
The following are the various methods used by cybercriminals to breach security:
1. Malware: Malware is malicious software created by a hacker to harm a legitimate user's system. It typically spreads when you install malicious software or click on an infected link or email.
Malware is classified into the following types:
- Virus: A virus is indeed a self-replicating software program that really infects other clean documents as it propagates through all the computer systems.
- Trojan horse: It is a tainted code that appears to be real and misleads users about its original purpose. If the user believes it is a harmless file, the trojan spreads to other files and affects the desktop.
- Spyware: A program that secretly records user activities such as internet usage data and then uses the information to commit fraud.
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts the user's system. To regain access, the attacker demands a ransom. - Botnets: Botnets are networks of devices that are linked together via the internet. It is used to launch Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks against the user's website.
2. SQL injection: SQL injection executes Structured Query Language code in a website's database to access sensitive data such as private customer details.
3. Phishing: A method used by cybercriminals to steal user data such as login credentials and credit card numbers by impersonating a trusted party. It is easily activated via email or text message.
4. A man-in-the-middle attack: The MitM attack is an eavesdropping attack in which an unauthorized third party secretly intercepts two parties' communication.
5. Denial-of-service attack: The attacker reduces the size of all messages sent to a specific destination. This is accomplished by disrupting an entire network or overloading it with messages in order to degrade performance.
6. scareware: The assailant scares the consumer into buying an antivirus program. Once configured by the information system, it begins to display messages on the screen indicating that your system is under attack, causing the victim to panic. Then it directs the victim to a bogus website where they can purchase anti-virus software.
7. Keylogger: Keylogger is a piece of software that downloads a log of all of the system's keystrokes. It will be sent to the hacker's desktop in order to gain access to confidential material such as user ids and passwords.
Wish to make a career in the world of Cyber Security? Start with VAPT training!

Subscribe to our YouTube channel to get new updates..!
Cybersecurity methods:
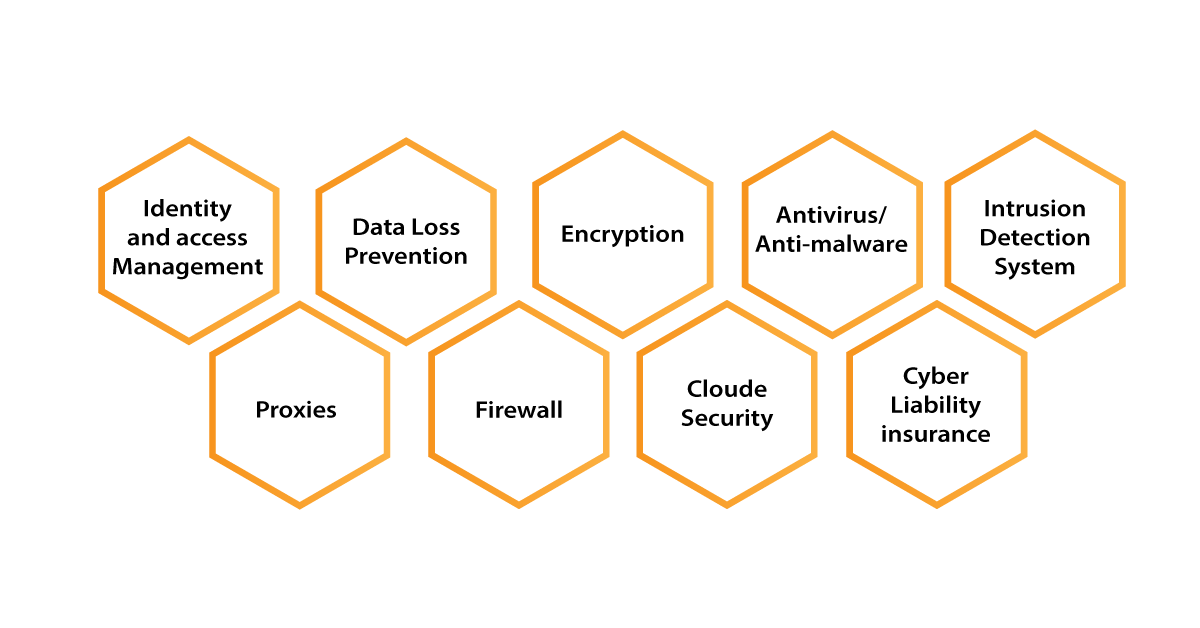
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP software detects data breaches by ensuring that sensitive information is not sent outside the corporate network.
- Cloud security: Cloud security is the safeguarding of data stored on cloud platforms.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) or Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) monitor the network and report potentially malicious activity to management.
- Identity and Access management system (IAM): A set of policies for managing individual network users' access privileges.
- Security encryption: Encoding raw data into an unreadable form in order to prevent theft in transit.
- Antivirus/anti-malware: Software for detecting and removing viruses and malware from a computer system.
- Proxies: It serves as a bridge between both the user and the internet. It enables the user to disguise the network id by concealing the user's IP address.
- Firewall: Sets up obstacles against untrusted networks using a set of predefined rules.
- Cyber Liability Insurance: Covers financial losses as well as operational liability resulting from data theft or breach.
Introducing Automation and Cybersecurity Together:
Automation in cybersecurity allows for faster detection of system intrusions. Generally, automation in cybersecurity involves the use of AI and ML technologies to improve the corporation's predictive capabilities.
Only a few automation tools are currently in use. Automated systems that really can advantage a company's security include robotic process automation (RPA), security orchestration automation and response (SOAR), and security incident and event management (SIEM).
Applications of cyber security:
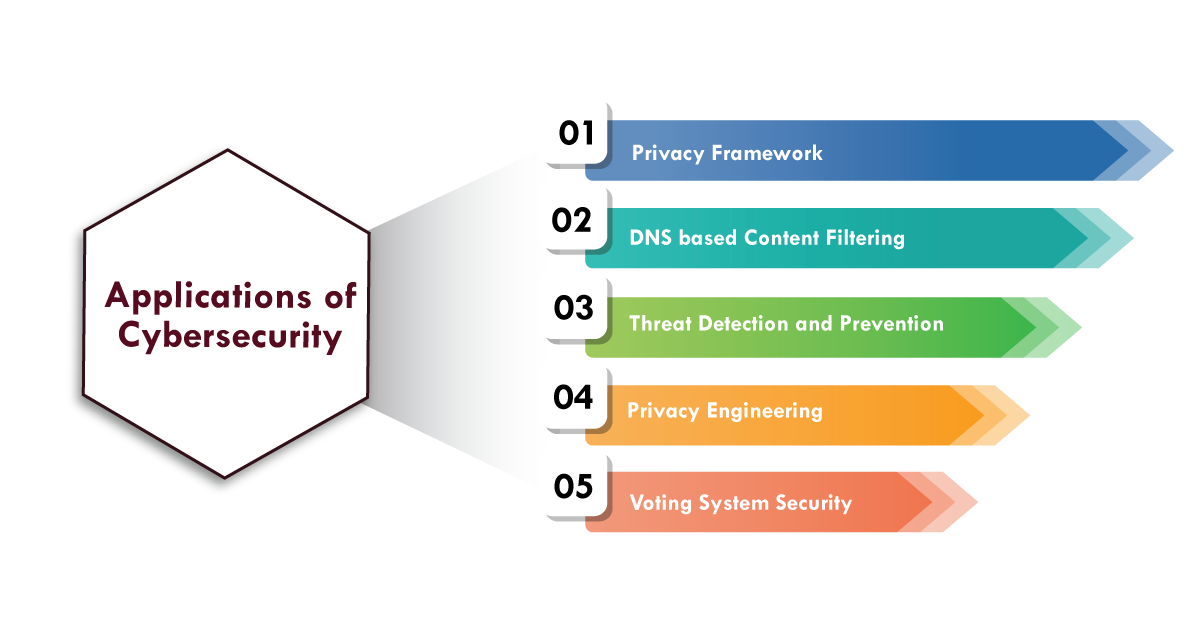
- Privacy Framework – This refers to protecting private data from intruders.
- DNS-based content filtering entails blocking access to websites that contain malware or ransomware.
- Threat detection and prevention entails identifying the threat and preventing it.
- Privacy engineering entails investigating the dependability of cyber technology.
- Security of voting systems – This refers to having a secure voting system during elections.
Cybersecurity Benefits:
- An organization's wealth is its data. Data security and reliability are ensured by cybersecurity.
- It prevents unauthorized access and protects the confidentiality of confidential versions of your software and operating system.
- Set up anti-virus software on your computer.
- Make use of strong passwords.
- Open emails from unknown senders with caution.
- Avoid utilizing public Wi-Fi.
Conclusion:
In the above blog post, I had covered all the important concepts related to the cybersecurity types of cyber security, and how it helps organizations to secure their sensitive data from the hackers. Had any doubts drop your queries in the comments section.
related articles :
About Author
A technical lead content writer in HKR Trainings with an expertise in delivering content on the market demanding technologies like Networking, Storage & Virtualization,Cyber Security & SIEM Tools, Server Administration, Operating System & Administration, IAM Tools, Cloud Computing, etc. She does a great job in creating wonderful content for the users and always keeps updated with the latest trends in the market. To know more information connect her on Linkedin, Twitter, and Facebook.
Upcoming Cyber Security Training Online classes
| Batch starts on 10th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 14th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 18th Mar 2026 |
|


