- What is Power BI?
- Installation of power BI
- Architecture of Power BI
- Power BI Dashboard
- Power BI data modeling
- Comparison with other BI tools like tableau
- Conclusion
What is Power BI?
Power BI is a Business Intelligence and Data Visualization device for changing over information from different information sources into intuitive dashboards and analysis reports. Power BI provides cloud-based administrations for intuitive visualizations with a basic interface for end clients to make their own reports and dashboards. Other Power BI variants like Desktop, Service-based (SaaS), and portable Power BI applications are utilized for various stages. It gives numerous software connectors and administrations for business intelligence
Become a Power BI Certified professional by learning this HKR Power BI Training !
Why use Power BI
- Power BI permits real time dashboard refreshes.
- Pre-constructed dashboards and reports for SaaS Solutions.
- Provide secure and solid association with your information sources in the cloud or on-premises.
- It provides Quick sending, hybrid arrangement, and secure climate.
- Permits information investigation utilizing common language query.
- Provides highlights for dashboard representation routinely refreshed with the local area.
Who uses Power BI
- Consumer for End User Report
- Developer & Database Administrator
- Data Scientist
- Business & Data Analyst
- IT Team, IT Professional
- PMO - Project and Portfolio Manager
History of Power BI
Power BI was conceptualized by Ruler and Dhers Netz of the SQL server coverage services team at Microsoft. In 2010, it was designed by West Chadic George named as Project Crescent. In 2011, It was bundled with SQL Server Codenamed Mount McKinley. Microsoft revealed the first preview to Power BI in September 2014. The first version of Power BI was delivered on 24 July 2015. It depended on Excel Based Add-ins like Pivot, Power Query, view, and Map.
Installation of Power BI
To check the framework necessities, installation documents detail, clients need to explore “Advanced download options”. Following are the system necessities to download Power BI tool
Supported Operating Systems
- Windows 7, Windows 10,Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, Windows Server 2012, and Windows Server 2012 R2
- Microsoft Power BI Desktop requires Internet Explorer 9 or higher
- Microsoft Power BI Desktop is available for 32-bit (x86) and 64-bit (x64) platforms
- Clients can choose a language where they need to install Power BI and following documents are accessible for download.
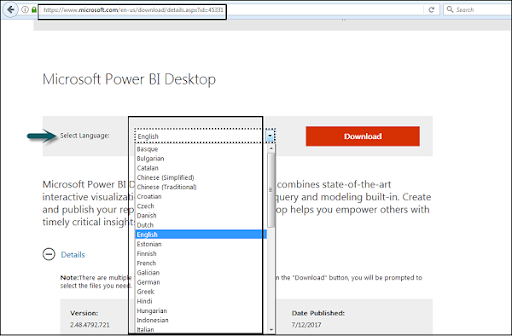
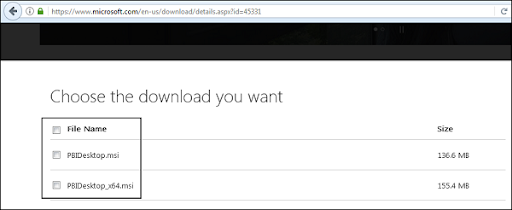
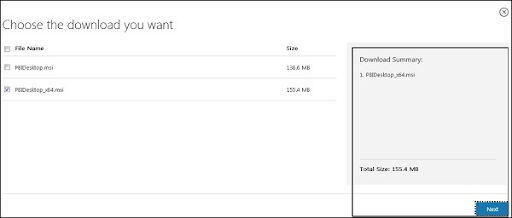
PBIDesktop_x64.msi displays a 64-bit OS file. Choose the file you need to install as per OS type and click Next. Save the installation file on the local drive.
At the point when you execute the installation record, the given screen is displayed.
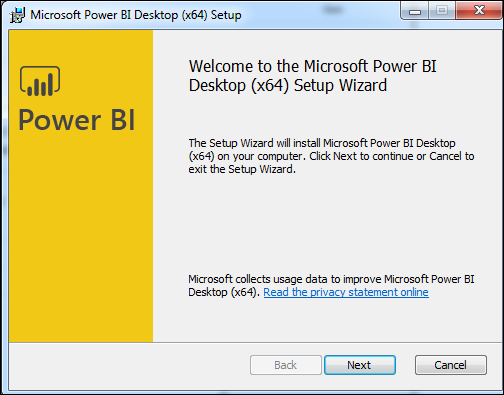
Accept the license agreement and adhere to the guidelines on the screen to complete the installation.
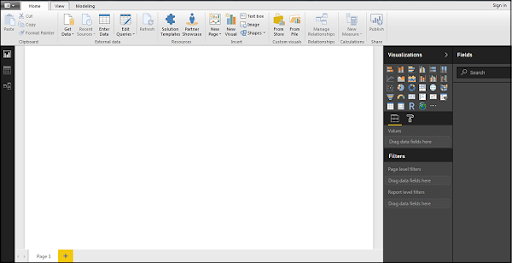
It dispatches a welcome screen,when Power BI is introduced. This screen is utilized to dispatch various alternatives identified to get information, enhance the current information models, make reports just as distributed and share reports.
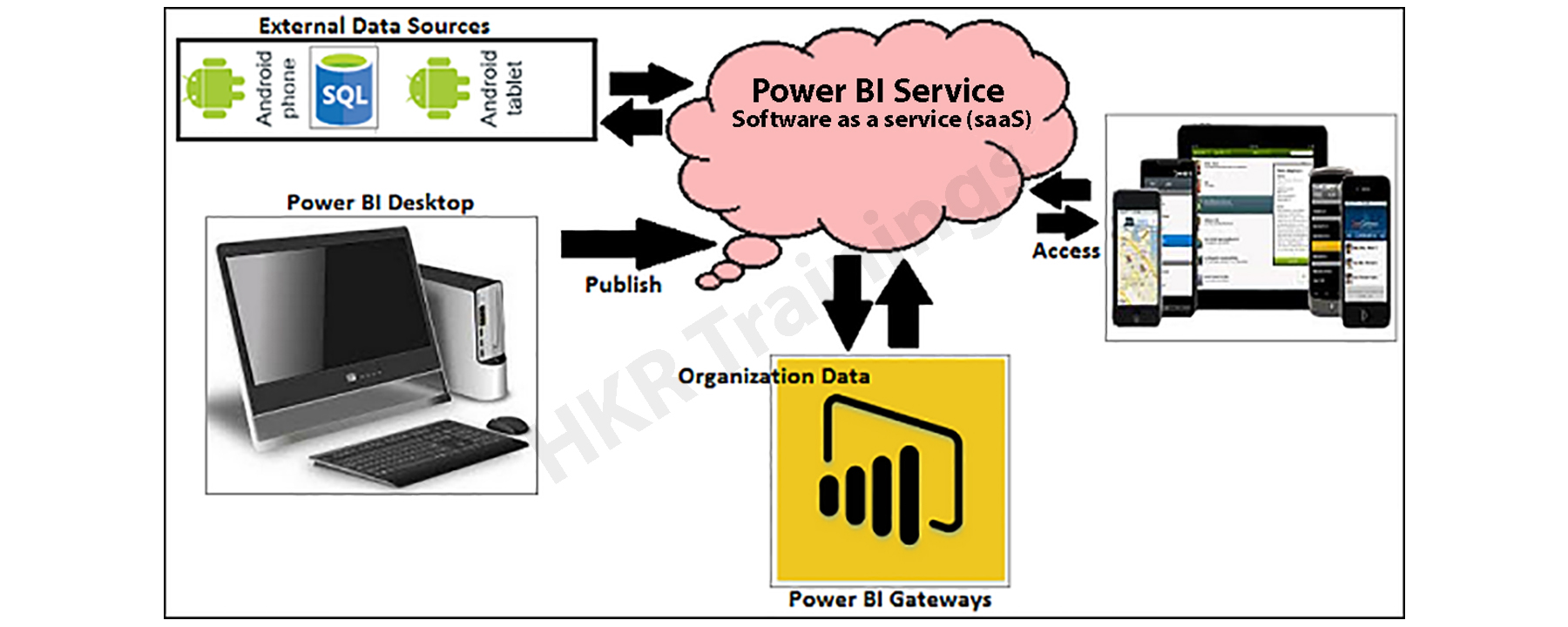
Architecture of Power BI
Related Article: Power BI Architecture
Data Processing:
The coordinated information is as yet not ready for representation as the information requires processing. This information is pre-handled. For instance, excess qualities, missing qualities will be eliminated from the data collection. The business rule ought to be applied to the information when the information is cleaned. You can stack that information back to Data Warehouse.
Data Integration:
An association requires to work with information that comes from various sources which could be in different record layouts. The information ought to be separated from an alternate source that can be from various servers or databases. This information is coordinated into one standard configuration in a typical arranging region.
Data Presentation:
When the information is stacked and prepared, it tends to be envisioned much better with utilization of different visualisations that Power Bi has to bring to the table. Utilization of dashboard and report aids one address information all the more naturally. The visual report encourages business end clients to take business choice dependent on the bits of knowledge.
Power BI components are:
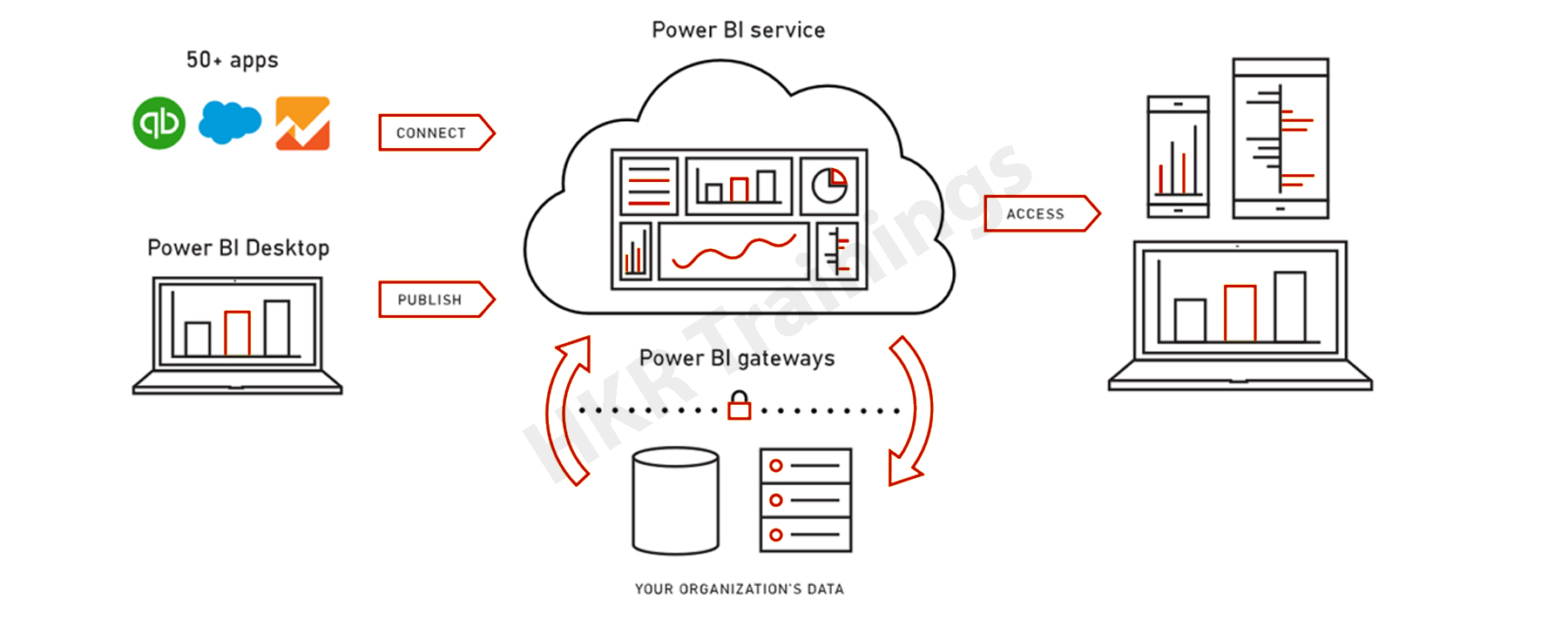
Power BI Desktop: This is utilized to make reports and information visualizations on the dataset.
Power BI Gateway: You can use Power BI on-premises gateway to keep your data fresh by connecting to your on-premises data sources without the need to move the
data. It allows you to query large datasets and benefit from the existing investments.
Power BI Mobile Apps: You can remain associated with their information from anyplace. Power BI applications are accessible for Windows, iOS, and Android platforms.
Power BI Service: This is a cloud administration and is utilized to distribute Power BI reports and information representations.
Top 50 frequently asked Power BI Interview Questions !
Power BI Dashboard
Power Bl Desktop is an expansion apparatus used to produce dashboards and reports. These applications will be availed by different clients through mobile devices and desktops.
There are Power BI segments with five main parts delivered in the market.
Power Query: It can be utilized to look for, access, and change public or potentially internal information sources.
Power BI Service: It permits you to share information perspectives and exercise manuals, which you can revive from on-premises and cloud-based information sources.
Information Catalog: This segment permits the client to find and reuse inquiries utilizing the Data Catalog. Metadata can be encouraged for search usefulness.
Power View: This segment permits you to envision, break down, and show information.
Data Management Gateway: It provides occasional information boosts, observes information, and uncover tables.
Power Map: It rejuvenates information with interactive topographical perception.
Power Pivot: It is utilized for information displaying for in-memory examination.
Power BI Q&A: It permits you to pose inquiries and find quick solutions utilizing a characteristic language inquiry.

Power BI Training
- Master Your Craft
- Lifetime LMS & Faculty Access
- 24/7 online expert support
- Real-world & Project Based Learning
Power BI data modeling
Using Data Modeling and Navigation
Data Modeling is used to interface numerous information sources in BI tools utilizing a relationship. A relationship characterizes how information sources are associated with one another and you can make fascinating information visualizations on numerous data sources. Using the modelling highlight, you can fabricate custom calculations on the current tables and these columns can be introduced into Power BI representations. This permits organizations to characterize new measurements and to execute custom figures for those measurements.
[ Related Article: power bi data modeling ]
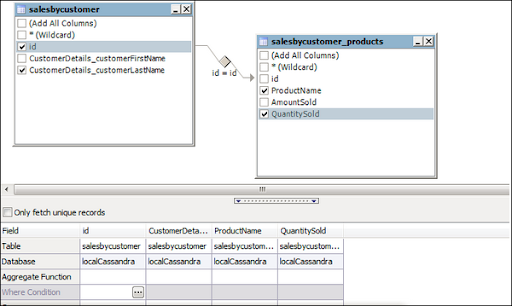
You can see a typical data model, in the above picture, which displays a connection between two tables. The two tables are connected utilizing a column name "Id". Also, in Power BI, you set the connection between two objects. To set the relationship, you need to drag a line between the regular columns. You can see the "Relationship" in a data model in Power BI. To make an information model in Power BI, you require to add all information sources in Power BI new report choice. To add a data source, move to the Get data alternative available. At that point, choose the data source you need to interface and snap the Connect button.
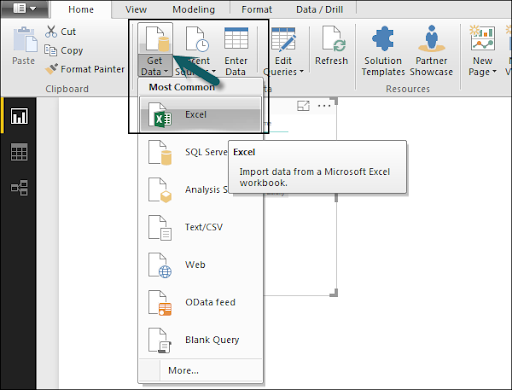
When you add an information source, it is introduced on the right side bar. In the accompanying picture, we have utilized 2 xls files to import information - Customer and Product.
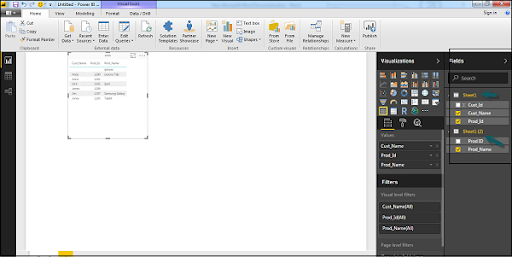
In Power BI on the left side of the screen, you have the given three tabs,
- Report
- Data
- Relationships

Subscribe to our YouTube channel to get new updates..!
Power BI visualizations options
Making Simple Visualizations
Visualizations are utilized to viably introduce your information and are the fundamental blocks of any Business Intelligence apparatus. Power BI includes different default information representation parts that incorporate basic bar diagrams to pie charts to maps, and furthermore complex models like pipes, measures, and numerous different segments.
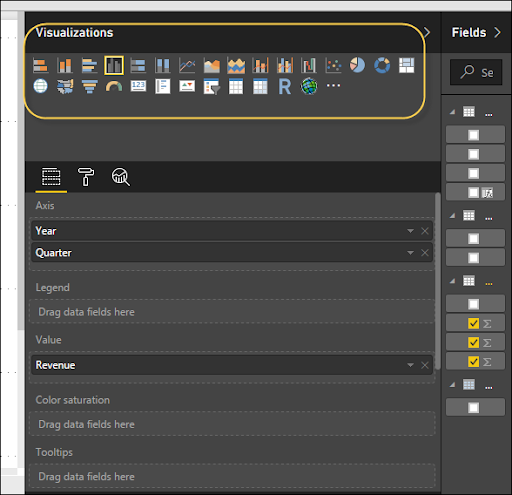
You can make visualization two methods in Power BI. First, by adding from the ride side sheet to Report Canvas. Of course, it is the table kind of representation that is chosen in Power BI. Another method is to drag the fields from right sidebar to the axis and value axis under Visualization. You can add different fields to every axis according to the necessity.
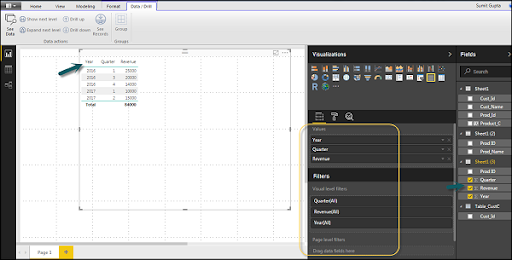
It is additionally conceivable to move your visualization on the detailing canvas by clicking and afterward dragging it. You can switch between various sorts of diagrams and visualizations from the Visualization sheet. Power BI endeavors to change your chosen fields over to the new visual sort as intently as could really be expected.
Power BI Excel Integration
Using Excel Data
Utilizing Power BI, you can import Excel manual documents from the local drive into Power BI. To import information from the excel sheet, you need to guarantee that every column has a legitimate name. To import an Excel record in Power BI, explore to Get Data → Files → Local Files.
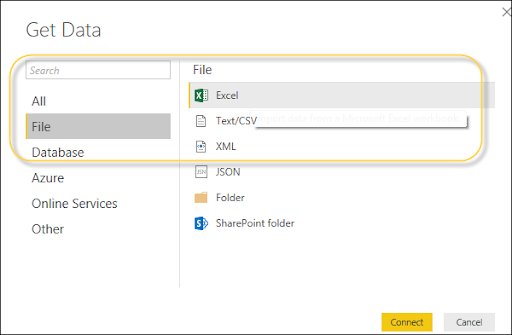
Importing xls Files
In Power BI Service, explore to My Workspace → File → Local File.
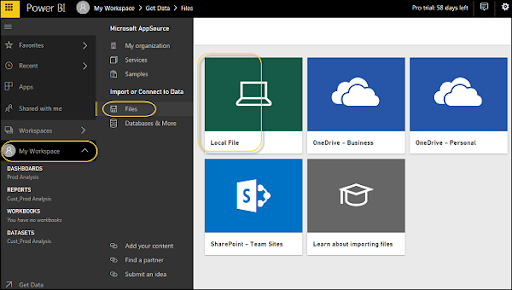
It isn't important your Excel document should just be saved on the Local Drive. You can import an Excel manual from OneDrive or even from SharePoint.
When the dataset is imported, you are prepared to make the reports in Power BI. Imported dataset is accessible under "DATASETS" choice in Power BI menu. Double tap Datasets. At that point, explore the Explore tab and then to Report Canvas. All the fields from your table and related columns are accessible under the Fields choice on the correct side of the screen. Choose any visualization and add the fields from the table to representation to make a report.
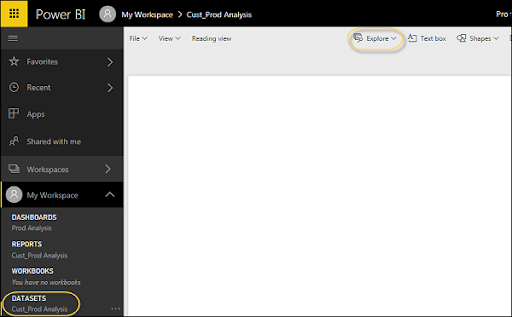
DAX functions in Power BI
DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) is a formula expression language and can be utilized in various BI and visualization apparatuses. DAX is called a function language, where the full code is placed within a function. DAX programming equation includes two data types: Numeric and Other. Numeric incorporates - integers, cash and decimals, while Other incorporates: string and library object. Following is an illustration of DAX formula, which utilizes a function to compute a column in a table.
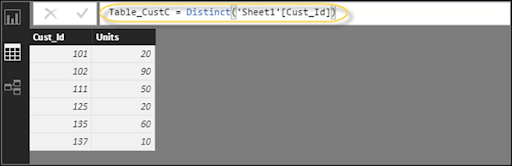
Related Article: DAX In Power BI
DAX functions can incorporate other functions, conditional statements, and value references.
DAX Functions
In Power BI, you can utilize diverse function types to investigate information, and make new columns and measures. It incorporates functions from various categories, for example,
- Aggregate
- Text
- Date
- Logical
- Counting
- Information
Power BI gives a simple method to view all the functions. At the point when you begin composing your function in the formula bar, you can view the rundown of all functions beginning with that letter in order.
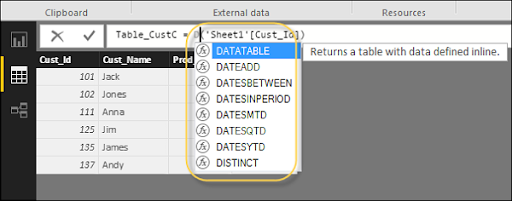
Aggregate Functions
- MIN
- MAX
- Average
- SUM
- SUMX
Logical Functions
- AND
- OR
- NOT
- IF
- IFERROR
Counting Functions
- DISTINCTCOUNT
- COUNT
- COUNTA
- COUNTROWS
- COUNTBLANK
INFORMATION Functions
- ISBLANK
- ISNUMBER
- ISTEXT
- ISNONTEXT
- ISERROR
TEXT Functions
- REPLACE
- SEARCH
- UPPER
- FIXED
- CONCATENATE
DATE Functions
- DATE
- HOUR
- WEEKDAY
- NOW
- EOMONTH
Comparison with other BI tools like tableau
Tableau is believed to be one of the main instruments in the BI market. Power BI is a rising instrument in close rivalry with Tableau due to its backend information control highlights and connectivity with the list of information sources. Tableau is a standout amongst other data visualization apparatuses in the firm and is utilized by medium and enormous ventures. Power BI is firmly incorporated with the Office 365 suite, and subsequently it is viable from different sources, for example, SharePoint.
Costing
Tableau is costly when contrasted with Power BI yet at the same time under spending plan for little and medium venture.
Power BI gives a free form 1GB cutoff on the dataset. Power BI Pro is a less expensive arrangement when contrasted with some other BI apparatus.
Data Visualization
Tableau gives solid information visualization and is one of the primary information visualization apparatus on the market. Power BI gives a solid backend information control highlight with admittance to straightforward representations.
Implementation
Tableau gives diverse implementation types according to hierarchical necessities panning from not many hours to few weeks.
Power BI utilises cloud storage and incorporates straightforward implementation measures.
Size of Dataset
Tableau can interface a lot bigger datasets when contrasted with Power BI.
Power BI has a constraint of 1GB information in free form.
License and Pricing
Tableau Online with private cloud: USD 42/user/month
Tableau Desktop Personal: USD35/user/month and it can connect to data sources such as Google Sheets and Excel files.
Tableau Desktop Profession: USD70/user/month and it can connect to hundreds of data sources.
Tableau Server: Minimum 10 users with the cost of USD35/user/month
Power BI: Free
1 GB storage
10k rows/hour data streaming
Power BI Pro:
USD9.99/user/month
10 GB storage
1 million rows/hour
Data Sources
Tableau covers a huge scope of information sources to interface with for information visualization. You select the dataset first and representations are utilized on the fly in Tableau. Power BI covers the majority of the information sources accessible in Tableau. It is firmly coordinated with Office 365, thus gives availability to SharePoint. Power BI online form bolsters direct representation on Search Engine, however, just Bling is supported now.
Advantages of Power BI
- Post distributing the information into Power BI web administration can plan revival without manual intercession.
- Provides pre-assembled dashboards and reports for SaaS Solutions.
- Give constant dashboard refreshes.
- Reconciliation with both Python and R coding to utilize representations.
- Query gives numerous choices identified with cleaning the information.
- Power BI provides brisk arrangement, hybrid design, and a protected climate.
- Information investigation utilizing normal language inquiry.
- Secure and dependable association with your information sources in the cloud or on-premises.
- New highlights added that are incredible for excel clients.
- Broad database availability capacities Q&A include distribution to the web.
- Highlight for dashboard representation
- Power BI supported by the superpower with computerized reasoning and AI.
Disadvantages of Power BI
- Dashboards and reports just imparted to clients having similar email domains.
- Power Bl won't blend imported information, which is availed from real time connections.
- Power Bi won't acknowledge the document bigger than 250MB and zip file which is packed by the information of X-speed in-memory database.
- Power BI can't acknowledge record size bigger than 1 GB.
- Dashboards never acknowledge or pass client, account, or other substance boundaries.
- Not many information sources that license real time associations with Power BI reports and dashboard.
How can data be transformed in Power BI using the Query Editor?
In Power BI, the Query Editor provides a range of functionalities for transforming data. After loading the data, it becomes visible in the Fields Tab. From here, we can modify the datasets using the Query Editor, regardless of their data source.
One way to transform data is by renaming a dataset or removing single or multiple columns. This can be done easily in the Query Editor. By clicking the Edit Queries button on the Home Ribbon, we can access the Query Editor and perform these manipulations.
Another transformation that can be done is creating a custom column. For example, using financial data, we can shape the data to meet our needs by creating a custom column called New Manufacturing Price. This column can be defined using formulas and can be based on existing columns.
Changing the data types of columns is also possible through the Query Editor. For instance, if a column has a floating-point data type, we can easily adjust it to a whole number.
Moreover, the Query Editor provides the option to remove columns that are not adding value to the dataset. By selecting the column and choosing the Remove Columns option, we can easily eliminate unnecessary columns from the dataset.
Additionally, the Query Editor offers other functions such as adding and removing rows, transposing data, pivoting, and splitting. These functions can be easily performed within the Query Editor.
How can Power BI be connected to different data sources?
Power BI offers a wide range of connectivity options to connect with various data sources. By selecting the Get Data icon, users are presented with a comprehensive list of available options to import data into Power BI. Some of the commonly used data sources include Excel data, web sources, and a variety of other data sources.
To connect with Excel data, users can choose the Excel option from the Get Data icon. This allows them to import datasets saved in Excel files directly into Power BI. Whether the data is stored locally or in online platforms like OneDrive or SharePoint, Power BI provides a seamless integration with Excel.
In addition to Excel, Power BI enables users to connect with web-based data sources. This includes importing data from websites, web services, or even data stored in cloud platforms like Azure SQL Database, Azure Data Lake Storage, or Salesforce. With the help of Power BI web connectors, users can easily fetch the desired data and integrate it directly into their Power BI reports and dashboards.
Furthermore, Power BI offers connectivity to a large variety of other data sources. This allows users to extract data from databases, such as Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle, and many more. Additionally, users can connect with file-based data sources like CSV, XML, JSON, or SharePoint lists.
Once the required data source is selected and connected, Power BI enables users to explore and view the data in the Fields pane. This pane allows users to observe the available fields and entities within the loaded data, providing a clear understanding of the dataset structure.
What are the different views available in Power BI and what are their functions?
In Power BI, there are three main views available, each serving different purposes:
1. Report View: This is the primary view where the Dashboard is created. In this view, users can design and build interactive reports by dragging and dropping visuals, charts, tables, and other elements onto the canvas. The Report View allows users to create, customize, and format the visuals as per their requirements. It also enables users to add interactive features such as filters, slicers, and drill-through functionalities, making it easy to explore and analyze data.
2. Data View: The Data View provides a comprehensive overview of the entire dataset being used in Power BI. It allows users to preview and manage the data, and assists in understanding the structure, values, and relationships among different tables and columns. With the Data View, users can perform data shaping operations such as filtering, sorting, and transforming data using Power Query Editor. It helps users verify the data being imported, ensure accuracy, and make necessary modifications before creating visualizations in the Report View.
3. Relationship View: The Relationship View plays a vital role in showcasing the connections and relationships between various objects or tables within the dataset. It allows users to define and manage relationships between tables by specifying common fields or keys. The Relationship View helps users establish data associations and create a structured data model, enabling seamless data analysis across multiple tables. By managing the relationships effectively, users can easily create accurate calculations, implement cross-filtering and drill-down functionalities, and maintain data integrity in their reports.
What is the Power BI workspace and its major components?
The Power BI workspace refers to the environment in which users can create and work with their data visualizations, reports, and dashboards. It consists of several major components that facilitate the data analysis and reporting process.
1. Visualization Tools: Power BI provides a variety of visualization tools to create compelling data visualizations. These tools allow users to present data in the form of charts, graphs, maps, tables, and other visual representations. Users can easily customize these visualizations to suit their specific needs.
2. Data Modeling Tools: The workspace also includes data modeling tools that enable users to shape and transform their data to fit their reporting requirements. With these tools, users can perform tasks like data cleansing, merging multiple data sources, creating calculated columns or measures, and defining relationships between different data tables.
3. Query Editor: The Query Editor is a powerful tool within Power BI that allows users to extract and transform data from various sources. It offers a user-friendly interface to perform data cleaning, filtering, merging, and other data transformation tasks without requiring complex coding or scripting.
4. Power BI Desktop: Power BI Desktop is a standalone application within the workspace that provides a complete authoring environment for creating reports and visualizations. It offers an intuitive interface with drag-and-drop functionalities, allowing users to effortlessly design and arrange their data visualizations.
5. Power BI Service: The Power BI Service is the cloud-based component of Power BI that enables users to publish, collaborate, and share their reports and dashboards with others. It allows for seamless integration with other Microsoft products, such as SharePoint and Teams, and provides features like data refreshing, scheduling of report updates, and access control.
6. Mobile Apps: Power BI also offers mobile apps for iOS and Android devices, allowing users to access their reports and dashboards on the go. These apps provide interactive and responsive views of the data and enable users to stay connected with their business insights anytime and anywhere.
How do you get started with Power BI?
To get started with Power BI, follow these steps:
1. Install Power BI Desktop: Begin by installing Power BI Desktop on your computer. You can download it for free from the official Microsoft website.
2. Launch Power BI Desktop: After installation, open Power BI Desktop to access the application's interface.
3. Familiarize Yourself with the Workspace: The Power BI workspace consists of several important components. Take a moment to explore and understand these elements:
- Ribbon: The ribbon is located at the top of the window and contains various tabs, such as Home, Modeling, and View. Each tab provides different functionalities for designing, modeling, and visualizing your data.
- Canvas: The central part of the workspace is the canvas, where you build and design your reports, dashboards, and visualizations. You can drag and drop various visual elements onto the canvas to create interactive data representations.
- Fields Pane: The fields pane, usually located on the right side of the window, displays the available data fields from your data source. You can select and drag these fields onto the canvas to define the structure and content of your visualizations.
- Visualizations Pane: The visualizations pane, typically found on the right side of the window, enables you to customize the appearance and behavior of your visualizations. Choose from a wide range of chart types, styles, and formatting options to enhance your data presentation.
4. Connect to Data Sources: Power BI allows you to connect to various data sources, such as Excel spreadsheets, databases, online services, and cloud platforms. Use the "Get Data" option on the Home tab to establish the desired connection and import your data into Power BI.
5. Build Reports and Dashboards: Once you have connected to your data source, start building reports and dashboards. Drag and drop the desired fields onto the canvas, select appropriate visualizations, apply filters, and create relationships between different data components to create meaningful insights.
6. Enhance Visualizations: Customize the appearance of your visualizations by modifying colors, labels, titles, legends, and other visual settings. Power BI offers extensive formatting options to make your reports visually appealing and easy to interpret.
7. Publish and Share: After creating your reports and dashboards, you can save them locally or publish them to the Power BI service. Publishing allows you to share your work with others and collaborate on data analysis and visualization projects.
How do you install Microsoft Power BI?
To install Microsoft Power BI, you can follow these steps:
1. Begin by checking the system requirements for Power BI. It is compatible with various operating systems such as Windows 10, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, and Windows Server 2012 R2. Make sure you have Internet Explorer 9 or a newer version installed.
2. Proceed to the Microsoft Power BI download page. To access the advanced download options, navigate to the appropriate section on the website.
3. On the download page, you will find the available installation files. Power BI Desktop is compatible with both 32-bit (x86) and 64-bit (x64) platforms. Choose the appropriate file based on your operating system type.
4. Click on the desired file and save the installation file to your local drive.
5. Once the download is complete, locate the installation file saved on your computer and run it.
6. The installation process will commence, and you will be presented with a screen displaying the license agreement. Read and accept the agreement.
7. Follow the on-screen instructions to proceed with the installation. The process may take a few minutes to complete.
8. After the installation is finished, Power BI will launch. You will be greeted with a welcome screen that provides access to various features and options.
9. Explore the different options available within Power BI, such as getting data, enhancing existing data models, creating reports, and publishing and sharing reports.
What are the data sources for Power BI?
Power BI offers various data sources to gather and analyze data. These sources include:
1. Excel (.xlsx, .xlsm): Power BI allows importing data from Excel workbooks. Users can either manually enter data or query and load data from external sources into Excel before importing it into Power BI.
2. Comma Separated Value (.csv): Power BI supports importing data from CSV files, which are simple text files consisting of rows of data. Each row can have one or more values, separated by commas.
3. Power BI Desktop (.pbi): Power BI Desktop is a powerful tool that enables users to create reports and visualizations. It also allows querying and loading data from various external sources directly into Power BI.
4. Cloud Databases: Power BI allows connecting to databases hosted in the cloud, such as Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Data Warehouse. This feature enables users to establish live connections and fetch real-time data from cloud-based databases.
5. On-premises Databases: Power BI enables connecting directly to on-premises databases, specifically SQL Server Analysis Services Relational model databases. To establish a connection, a Power BI Enterprise Gateway is required, ensuring secure and efficient data transfer between on-premises databases and Power BI.
What are the key terms used in Power BI?
Key Terms used in Power BI:
1. Visualization: A visual display of information designed to achieve specific objectives. It presents information in a concise and easy-to-understand manner, offering a single-screen view. Visualizations can be used to highlight issues, problems, operational data, performance metrics, or personal insights.
2. Datasets: Datasets are the core components in Power BI, representing imported or connected data sources. These datasets can be customized, including renaming, refreshing, removal, and exploration. They serve as the foundation for creating reports and dashboards.
3. Dashboard: A dashboard in Power BI is a collection of tiles and widgets. It provides a customized view of selected data subsets, allowing users to monitor and analyze key metrics. Dashboards enable the combination and arrangement of visualizations to provide a comprehensive overview.
4. Reports: Power BI reports are comprised of one or multiple pages filled with visualizations. These reports can be created from scratch, imported into dashboards, or built using existing datasets. Reports offer a detailed and interactive presentation of data, allowing users to dive deeper into specific insights.
5. Tile: A tile refers to a single visualization placed within a report or on a rectangular dashboard box. Each visual represents a specific aspect of the underlying data and can include charts, graphs, tables, or other visual elements. Tiles provide a snapshot of information and can be customized to display real-time data.
These key terms form the fundamental building blocks of Power BI, enabling users to transform raw data into meaningful and actionable insights through effective visualizations, datasets, dashboards, reports, and tiles.
What are the types of Microsoft Power BI tools?
There are several types of Microsoft Power BI tools that serve different purposes.
1. Power BI Desktop: Power BI Desktop is a powerful authoring and publishing tool. It is primarily used by developers and power users to create new data models and reports from scratch. With Power BI Desktop, you can import, transform, and visualize data, and then publish the created reports to the Power BI service.
2. Power BI Service: Power BI Service is an online Software as a Service (SaaS) platform that hosts Power BI data models, reports, and dashboards in the cloud. It provides functionality for administration, sharing, collaboration, and access to data visualizations and reports. With Power BI Service, users can access and interact with reports from anywhere, using a web browser.
3. Power BI Data Gateway: Power BI Data Gateway acts as a bridge between Power BI Service and on-premises data sources. Through the gateway, you can establish a secure connection and access data from sources like DirectQuery, Import, and Live Query. It allows administrators to manage and monitor access to on-premises data for Power BI reports and dashboards.
4. Power BI Report Server: Power BI Report Server is a solution for hosting and managing reports. It can host paginated reports, KPIs (Key Performance Indicators), mobile reports, and reports created with Power BI Desktop. It is regularly updated and installed and managed by the IT team. Users can modify Power BI reports and other reports developed by the team using Power BI Report Server.
5. Power BI Mobile Apps: Power BI Mobile Apps are available for various platforms such as iOS, Android, and Windows. These apps allow users to access reports and dashboards on the go. With the ability to connect with Microsoft Intune, administrators can manage and secure the mobile app access for their organization.
These various Power BI tools provide a comprehensive suite of capabilities for data modeling, report creation, data access, collaboration, and mobile access.
What is Microsoft Power BI and how does it work?
Microsoft Power BI is an advanced data analytics tool that enables users to transform their unstructured data into visually engaging reports and interactive dashboards. Comprising various components such as Power BI Desktop, SaaS Power BI Service, and mobile apps for iOS and Android, this tool leverages the power of Big Data to facilitate data analysis.
At its core, Power BI integrates data from diverse sources, regardless of their format or location, and consolidates them into a unified and easily interpretable format. This process enables organizations to gain insights and make informed decisions based on a holistic view of their data. By combining information from multiple sources, Power BI creates visually appealing and customized data sources that not only convey information but also provide a clear understanding of the actions to be taken.
One of the key features of Power BI is its ability to generate real-time dashboards. It effectively sifts through large volumes of data from various sources, presenting them in a consolidated and easily digestible format. This empowers businesses to efficiently manage their customers, operations, and future strategies by providing a comprehensive overview of their performance metrics and KPIs.
Moreover, Power BI offers extensive capabilities for data exploration and manipulation. Users can apply data transformations, perform complex calculations, and create relationships between different datasets. This empowers analysts to uncover hidden patterns, discover trends, and gain actionable insights from their data.
What is Business Intelligence (BI) and why do we need it?
Business Intelligence (BI) is an essential concept in today's data-driven world. It refers to the set of methods and tools that organizations utilize to analyze and make sense of the raw data they collect. In other words, BI enables companies to extract valuable insights from the vast amounts of data they accumulate from various sources.
Why do we need BI? The answer lies in the competitive nature of the business landscape. As organizations gather more and more data, it becomes increasingly important to transform that data into meaningful information that can drive strategic decision-making. BI allows companies to do just that. It provides the means to process, analyze, and visualize data, resulting in actionable intelligence.
The process of BI often involves several stages. The first step is data extraction, where relevant information is gathered from diverse sources such as databases, spreadsheets, and even external systems. Next comes the transformation phase, wherein the data is cleaned, organized, and structured for analysis. Finally, the loaded data is stored in a database and made accessible for various tasks, including data mining, online analytical processing, and business reporting.
The advantages of implementing BI tools cannot be overstated. These tools enable organizations to identify trends, uncover patterns, and gain insights into their operations, customers, and market performance. By providing a comprehensive view of the business, BI empowers decision-makers to make informed choices that drive growth, improve efficiency, and increase profitability.
Conclusion:
BI encourages you to analyze information and to give noteworthy data that assists corporate heads, business supervisors to settle on educated business choices. Power BI is a Business knowledge and Data Visualization device that causes you to change over information from a different information source. If you have any queries kindly mention that in the comment section.
Related Article:
About Author
As a senior Technical Content Writer for HKR Trainings, Gayathri has a good comprehension of the present technical innovations, which incorporates perspectives like Business Intelligence and Analytics. She conveys advanced technical ideas precisely and vividly, as conceivable to the target group, guaranteeing that the content is available to clients. She writes qualitative content in the field of Data Warehousing & ETL, Big Data Analytics, and ERP Tools. Connect me on LinkedIn.
Upcoming Power BI Training Online classes
| Batch starts on 26th Feb 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 2nd Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 6th Mar 2026 |
|

