- What is RPA?
- Why RPA?
- RPA Benefits
- Industrial applications of RPA
- RPA Architecture
- RPA Lifecycle
- Analysis phase
- Development of the bot
- Testing Phase
- Deployment and Maintenance
- RPA tools
- Functionalities of RPA tools
- Categories of RPA tools
- How to select the right RPA tool
- RPA tools list
- RPA UiPath
- UiPath Components
- UiPath Studio
- UiPath Robot
- UiPath Studio
- UiPath Orchestrator
- UiPath Architecture
- Recording and Screen mapping in UiPath
- Screen Mapping in UiPath
- How to invoke a workflow?
- Why do we need workflows?
- Data Manipulation
- Citrix Automation
- UiPath Coding and Debugging
- UiPath Automation Debugging
- Conclusion
What is RPA?
RPA Automation is a business process automation technology that's also focused on the mixture of its predecessors. It is strongly reliant on screen scraping and workflow automation and is based on Artificial Intelligence. RPA Full Form – Robotic Process Automation (RPA Automation) is a type of software used to automate key tasks in software applications such as how a person executes them.
The software robot can be trained in a workflow/process with various steps and applications, such as receiving documents, submitting a receipt note, checking forms for completeness, logging the form in a folder, and updating a spreadsheet with the name of the form, the date registered, etc. The aim of RPA programming is to reduce the weight of monotonous, straightforward tasks/work on staff.
Become a RPA Certified professional by learning this HKR RPA Training !
Why RPA?
With RPA, all of the redundant functions a person performs on a daily basis are automated by a computer. It follows the same steps that a person is taking to complete a task and does so without any human intervention.
For example, at the data entry stage, the data entry clerk visits the same source every day, gets the data from it and fills it, say, in the Excel sheet. This method has a number of specified steps, such as visiting the website, extracting data from it and adding it to the sheet. If a robot can be equipped to do this by just giving it a few basic commands, then why not, okay?
The robot follows these instructions and operates quicker and more specifically.
This is only one of the millions of tasks that can be carried out using RPA technology. Many companies use RPA for end-to-end automation of day-to-day business operations.
RPA Benefits:
RPA is increasing very quickly because manual processes are not very effective. Manual processes are prone to error and lead to discontent among employees. Whereas, the use of RPA will support organizations in the following ways:
- Savings in prices
- Improved accuracy and decreased operating risk
- Save Time
- Simplicity
- Flexibility
- Security
- Insights and Research
Industrial applications of RPA:
There are a number of industry-based RPA applications. Some of these are listed below:
Healthcare: Hospital administrative work, such as patient monitoring, medical history, claims system such as complaints, appeals and other data collection works
Insurance: Data handling, reporting, collection and processing of documents and streamlining workflows. Banking/Financing: copying of data from remote central networks, automation of error-reducing billing system, customer care, credit card, mortgage processing, fraud detection, KYC process, report automation, and account closure process
Tax: data sorting, automating the data retrieval process, filing a tax appeal on the basis of the information obtained and reducing manual data entry processes.
Retail: categorization of goods, updating of orders, handling of counterfeit accounts and processing of shipments notifications.
Human Resources: Applicant sourcing, employee background verification, on-boarding, payroll automation, employee data management, cost management and absence management.
Operations: updating inventory records, issuing refunds, procurement processes, such as updating vendor records, and administrative functions, such as commercial finance, order alerts, shipment notices, etc.
Telecommunications: control of subscriber feeds, fraud management and update of customer data
IT and Customer Services: Optimization of routine activities such as data entry, system checks, day-to-day backup, system management tasks, diagnostics running, sending scheduled bulk emails, and so on
Miscellaneous: quota-to-cash, procure-to-pay, data-cleaning, and data extraction from various applications such as PDF, Excel, Word, etc.
RPA Architecture:
The Robotic Process Automation (RPA) architecture is a combination of multiple tools, frameworks and different infrastructure elements to form a full RPA tool.
Several blocks are available in the RPA solution are shown in the following diagram.
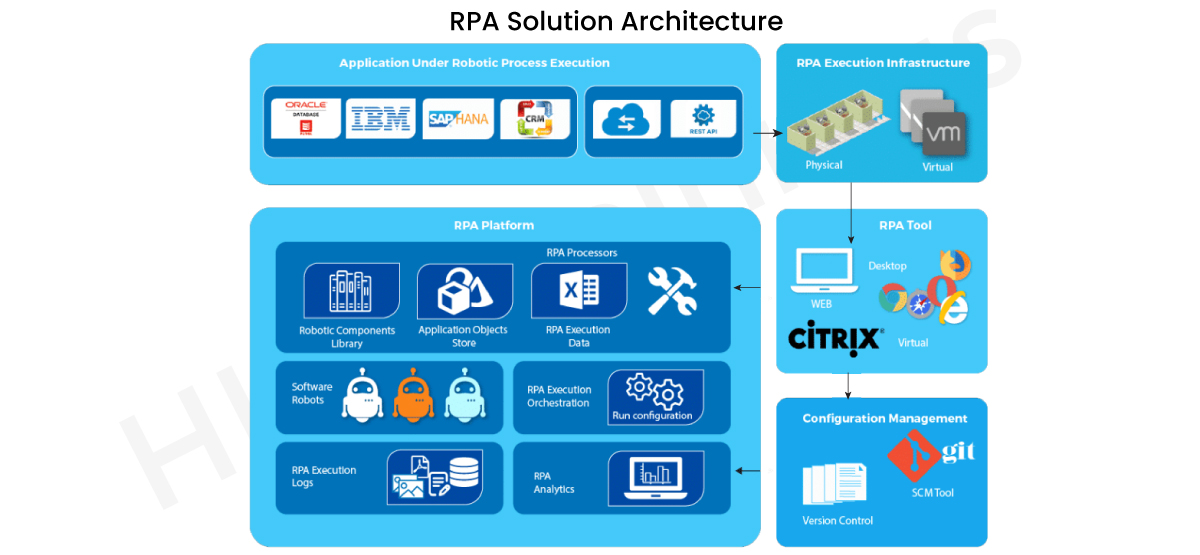
Robotic process execution systems – This is well suited for business applications such as ERP, SAP or any other record management programme. These programmes are data intensive and filled with repetitive tasks.
RPA Tool – Build software robots to automate applications in the Desktop, Web and Citrix environments. Excluding handling, ability to write to/from different data sources and create reusable components.
RPA Framework – RPA Software bots can be placed in a centralized repository and shared through software robot libraries. The RPA platform has the potential to develop practical insights into the bots and the execution process.
RPA Execution Infrastructure – Serves as a bank of parallel physical or virtual lab machines managed by patterns of use. Computer scale up or down parallel to achieve automation may also be carried out.
Configuration management – Upgrading bots to a newer version is finished. Branching and merging of RPA bots is also carried out as they can be reused through libraries.
RPA is a mix of different platform layers and resources that make up the entire architecture. These layers include process, subprocess, object, and component.
- The process layer is meant for Business rules,Hand-off point and prioritization. It focus on the business rule without the need to build ties and Simplify the transitions.
- Subprocess layer is meant for reusable business logic, identity, verification etc.
- Object layer is meant for performing some specific tasks.
- The component layer is meant for individual screen interaction.
RPA Lifecycle:
The life cycle of RPA does not have a fixed structure, but in general, there are four stages of RPA. They're:
Analysis: identification of the business process for the production of RPA
Development: meeting the requirements
Testing phase: efficiency of quality tests
Deployment and management: deployment and maintenance of bots
Now let's explain in detail:
Analysis phase:
Analysis is the beginning of the life cycle of RPA. A team of market analysts and RPA architects work together to come up with a proposal for why they need RPA and how it can be useful to them. They use developmental methods to develop a technique for automating activities in order to minimize manual labor as much as possible. The leader of the RPA agrees on a timetable to get this strategy to work. After the paperwork and the rest of the formalities, the production process begins.
Development of the bot:
The development team is beginning to work on the automation specifications. Depending on the type of automation needed, coding may or may not be involved. Typically, there's no coding here. But there may be exceptions to this.
Testing Phase:
Depending on the form of automation built and the company, the bot is tested either by the development team itself or by a separate testing team, which is similar to normal software testing.
Deployment and Maintenance:
After the successful development and testing of the bot, it is now ready to be deployed. Once deployed, if there appears to be a problem, the development team is reviewed and tested again. Every time the bot is deployed, it is maintained and updated.
Next we will learn about the RPA tools.
Get ahead in your career with our RPA Tutorial !
RPA tools:
As RPA steadily becomes a dominant emerging technology in the industry, more and more businesses are leaning towards inculcating RPA in their back-office tasks. This has also contributed to an exponential rise in demand for RPA software. Various methods for implementing RPA are available on the market. These methods are used by companies to describe a job workflow that needs to be automated using RPA. In this RPA tool tutorial, we will look after the different RPA tools.
Now we will learn the following concepts in the RPA tools.
Functionalities of RPA tools:
The key features of a good RPA tool are as follows:
- Based on feedback received from other systems, the bot should be able to make decisions and carry out the assigned actions.
- The bot should be able to communicate with other systems by screen scratching or other API interactions.
Categories of RPA tools:
The three main categories of Rap tools are:
Programmable RPA Bots: They're the first generation of RPA software. It involved programming, and the programmers needed to code and understand their work to get the bots to carry out tasks.
Self-awareness tools: After vigorous employee action, the developer/employee understood the procedure, took over the platform and began executing the task.
Intelligent or Cognitive Automation Bots: Cognitive Automation Bots are self-learning Bots with advanced features such as Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing, and Image Recognition. They can handle both structured and unstructured data.
How to select the right RPA tool:
The RPA industry has no shortage of providers of RPA software who say that their product is the best. With so many RPA tools on the market, it shouldn't come as a surprise that companies struggle when selecting the right RPA tool. The option can vary for different organizations depending on their requirements, but the key selection criteria remain the same.
The key features to be searched for in any RPA tool when selecting one are described below.
Architecture: The architecture of the RPA tool depends on where you plan to use it. Various controls and commands built into the RPA tool can define its features and capabilities. Deployment and maintenance of the RPA tool also rely on its layered architecture. The architecture checklist must have the following markings: stable delivery, reusability of materials, incorporation of robotics without altering the legacy framework, ease of accessibility, and support for common language.
Simple use: The RPA tool should be easy to work with for end-to-end business tasks, and it should be easy enough for an analyst with limited programming experience to understand and construct automation and configure the workflow in the RPA tool. The tool should be versatile enough to accommodate simple process automation with extended commands, wizards and GUIs.
Reliability: The RPA tool is said to be accurate based on the ability of the tool to manage diverse use cases with broad data and different circumstances. Output quality does not degrade when performing different iterations.
Scalability: The assessment of the RPA tool must involve how rapidly and efficiently it can respond to business requirements, changes, exceptions or increasing operations. It also contains the execution parameters where the tool is being evaluated to check whether it will support multiple bots to run multiple workflows.
Flexibility: The tool must be capable of supporting a variety of operating systems. It must also allow you to customize custom features without paying extra for customization to the vendor.
RPA tools list:
Several technologies are currently available for robotic process automation. But the five key methods used by different organizations around the world are as follows:
- UiPath
- RPA Blue Prism
- Automation Anywhere
- Kofax Kapow
- NICE
The RPA tools cannot automate processes on their own. All they can do is establish the workflow of the job. RPA tools are only used to build a programme or an application that determines the workflow of a task that needs to be automated. Entities programmed to perform the task by imitating human actions are called bots. Bots are essentially configurable machine configurations that are used to execute tasks with the aid of commands and codes in a specific sequence.
There are 3 bots namely:
- Task bots
- Meta bots and
- IQ bots
RPA UiPath:
RPA UiPath is a pioneering RPA platform that helps the enterprise efficiently automate business processes. RPA UiPath is an open platform that is easy to learn and work with. It is also extensible, with hundreds of built-in, flexible and deep integrations with ERP, BPM and AI technologies. It delivers quick results and has been shown to offer 40% faster automation design and implementation. Using RPA UiPath, we can train bots through machine learning and they are enterprise scalable and stable.
Now let's go through the various components of UiPath and architectural history.
UiPath Components:
The UiPath platform consists of three major components. Hey are:
- UiPath Studio
- UiPath Robot
- UiPath Orchestrator
Now let's go through these components one after the other.
UiPath Studio:
UiPath is a visual designer that lets you create automation workflows with pre-built activities. The characteristics of UiPath Studio are as follows:
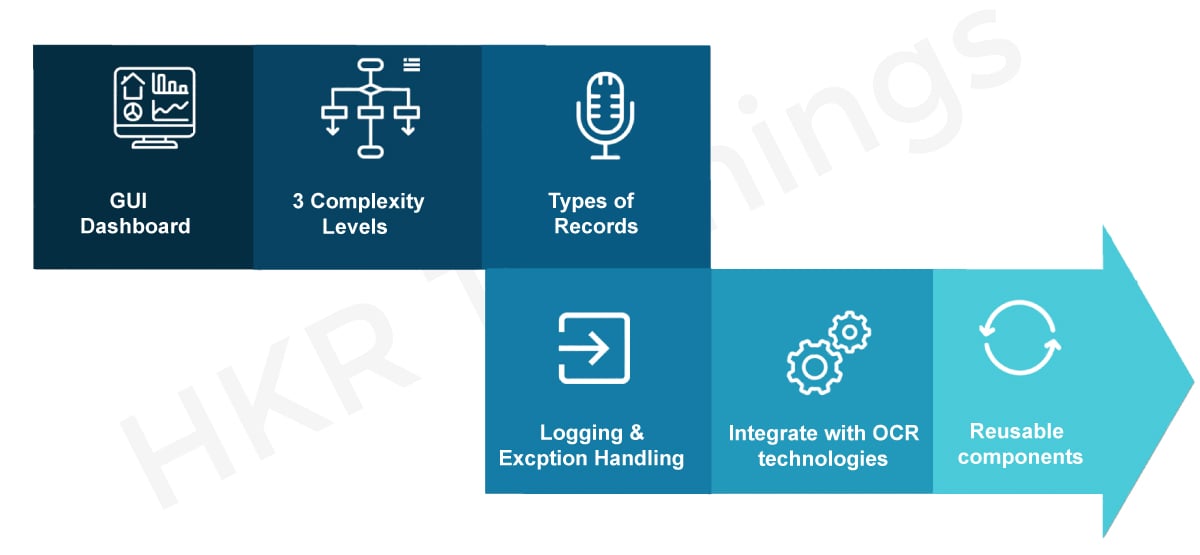
- GUI Dashboard – offers a visual dashboard with predefined activities to create automation workflows.
- 3 Complexity Levels – UiPath Studio allows you to create projects based on 3 levels of complexity, such as Sequence, Flowchart and State Machine.
- Recorder Types – UiPath Studio offers different types of recorders to record actions on multiple platforms, such as Basic, Desktop, Web, Image, and Native Citrix.
- Logging & Exception Handling – UiPath Studio's Ribbon Tab provides a range of debugging and exception handling options, such as Debug, Open Logs, Slow Stage, etc. If you would like to learn how to use these options, please refer to my Error Handling post.
- Integrate with OCR technologies – UiPath Studio can integrate screen scraping with various OCR technologies.
- Reusable Components – You can build reusable components with the UiPath Studio to publish them together as Libraries.

Robotic Process Automation Training
- Master Your Craft
- Lifetime LMS & Faculty Access
- 24/7 online expert support
- Real-world & Project Based Learning
So in simple terms, UiPath Studio is used to build automation workflows with the aid of which tasks can be automated.
Now that you've understood what UiPath Studio is next in this article on UiPath RPA Architecture, I'm going to tell you about UiPath Robot.
UiPath Robot:
Automation workflows created by the UiPath Studio are executed by the UiPath Robot. So to perform any of your activities, you need to make sure that the
UiPath Robot is in a running state. You may also have a single or multiple robot operating at the same time.
UiPath Orchestrator:
Orchestrator is a product of UiPath that allows you to orchestrate UiPath robots in a continuous repetitive process on different platforms.
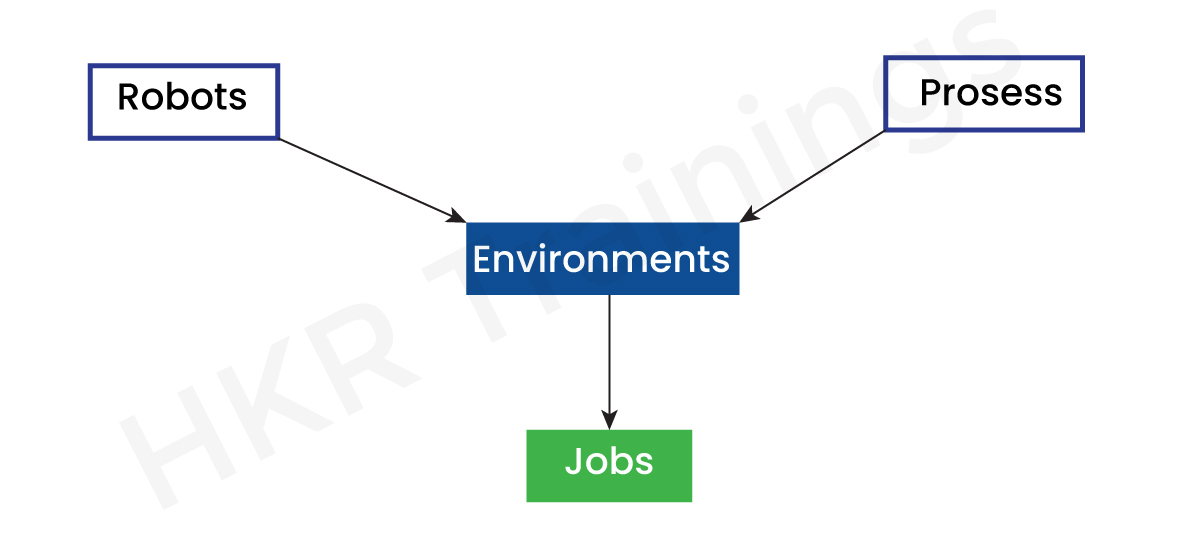
First of all, you need to build robots to perform your mission. Then you need to create a project and publish it so that you can use it as a process. If a process is created, a robot must be assigned to run this process in a specific environment, and this will create a task.
Now that's the simple workflow on how the Orchestrator works. But let me take an example and show you how the UiPath architecture functions.
Scenario:
Consider the scenario where you built an automation workflow in the UiPath Studio. Now once you publish your idea, the NuGet Package will be generated automatically. The NuGet kit is designed for the Microsoft Development Platform and is used to read the.NET files. After that the project is submitted to the Orchestrator Server. Please refer below.
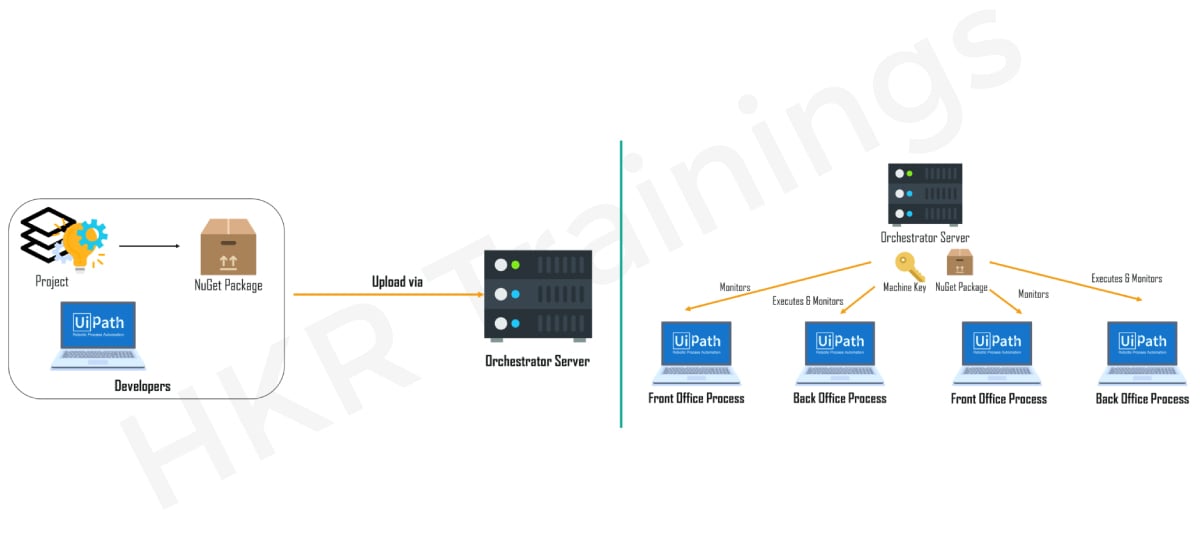
You can now deploy this specific project on any number of computers by mentioning the System Key. Automatically, the Ui.Robots perform and track tasks if they are a back office operation. Similarly, if it is a front-office operation, the user will execute a project or a mission, and the Ui.Robot will only control the task.
So that's how the UiPath Orchestra works. If you would like to know more about the UiPath Orchestrator, please refer to my Orchestrator blog, which talks about how to login to the Orchestrator and deploy the Robot.
Now that you've learned the components of the UiPath Framework, let me show you how these platforms work together and make up the UiPath architecture.
Top 30 frequently asked RPA interview questions & answers for freshers & experienced professionals
UiPath Architecture:
The UiPath architecture consists of three layers. They are:
- Client Layer
- Server layer
- Persistence layer
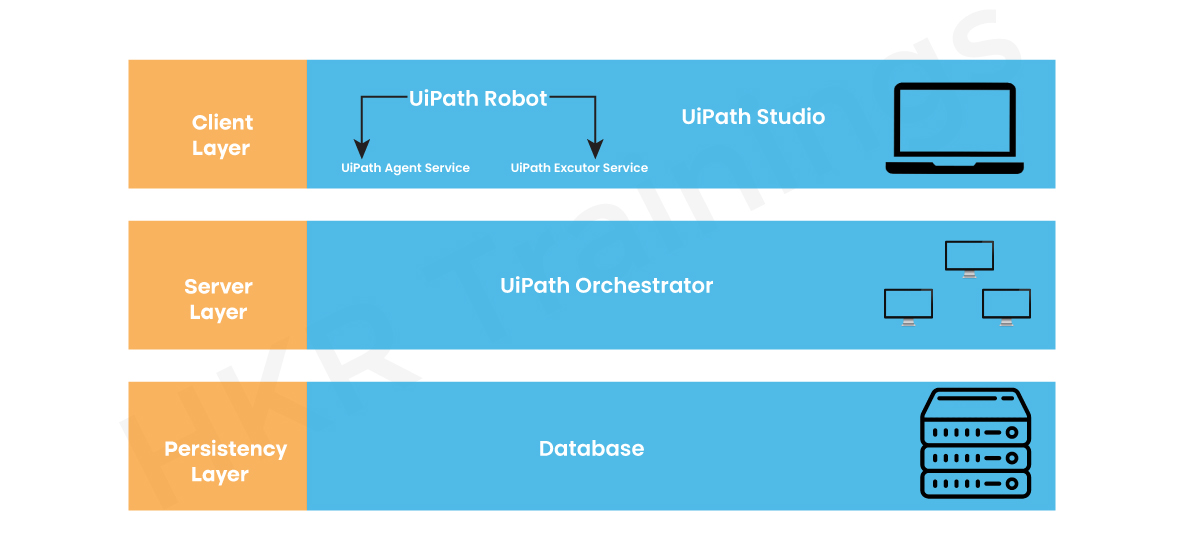
Let's speak one by one about each layer.
The Client Layer, beginning with the Client Layer consists of the UiPath Studio and the UiPath Robot. As I stated earlier, UiPath Studio is the place where you create automation workflows, and then UiPath Robot performs those tasks.
Now the UiPath Robot has two components you need to know about:
UiPath Agent Service: This service is used to view the jobs available in the device tray. You may also request to start/stop jobs and modify the settings.
UiPath Executor Service: This service is used to run a given job during a Windows session.
Now, once the Robot is able to perform the mission, the project can be submitted to the Orchestrator Server. You can run the project on different PCs with the aid of the Orchestrator. The Orchestrator controls the deployment, setup, queue management and logging.
The next layer in the image is the Persistence Layer. This layer consists of a database that takes care of queues and queues. It also consists of information on the configuration of robots and their assigned procedures.
Recording and Screen mapping in UiPath:
The UiPath recorder enables users to record mouse movements, keyboard activities to produce automation scripts. Activities are reported and generated as sequences. The record choice can be found on the Design page.
There are two types of recorders: automatic and manual recorder.
Screen Mapping in UiPath:
Screen scraping is a key component of the RPA toolkit, is used to collect bitmap data from the screen and cross-checks it with the information stored to decode it. From the Design menu, press Screen Scrap.
Highlight the region to be scrapped, open the Extracted Data Screen Scraping Window. Works on application components that are not accessible via a code or UI system. Text digitization by Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is possible. It's simple to implement, and always effective.
There are three common methods of screen scraping –
- Full text – all identifiable objects on the UI object are erased
- Native – scrapes text, often captures the text's location, color, font type.
- OCR – virtual desktop scrapping and Citrix software
Workflow and Citrix Manipulation:
How to invoke a workflow?
Workflow is a series of individual processes performed in UiPath for the automation of activities.
Why do we need workflows?
When we're designing a big method, it's hard to follow and validate the process from top to bottom. It is therefore recommended that each process be divided into small processes, checked and invoked in the main workflow. We can switch arguments from one workflow to another. You may simply add UiPath.Core.Activities.InvokeWorkflowFile or press add an Invoke Workflow operation to the first workflow.
We can use three different parameter forms as an argument –
- IN – Arguments passed in, not returned.
- OUT – NULL value, is not of significant importance
- IN/OUT – This indicates meaningful values on input & output values
Become a Kapow Certified professional by learning this HKR Kapow Training !

Subscribe to our YouTube channel to get new updates..!
Data Manipulation:
Data of various kinds can be placed into variables, and there are a few variables you can use in the UiPath Studio. They can be of three types:
- Scalar – Character, Boolean or Number
- Collections – Arrays, Lists, Strings – are a set of characters and dictionaries that are used when separating information from the Orchestra queues.
- Tables – are two-dimensional structures that contain information divided by rows and columns.
In addition, UiPath Studio contains one kind of factor, the Generic Value variable, which is designed to make the use of fundamental activities easy. This variable type can interact with key types of data, including information, numbers and date/time.
Citrix Automation:
The tools and methods used throughout Citrix are for virtual machines, so UiPath cannot interpret them directly. We need to teach the robot about filling, screen scraping, etc. A virtual machine is a kind of computer device emulation. The Citrix recording wizard is an important tool used for automation. We can execute certain mouse clicks, keyboard shortcuts, screen scratches, data inserts, data retrieval, etc. Virtual world, including how we worked on desktop and web surfing.
UiPath Coding and Debugging:
The UiPath operation is like a collection of blocks in the UiPath automation phase. UiPath comes with a number of built-in core tasks. There is a possibility to build such personalized activities to automate processes for ease of use. Two essential steps are required to build a custom operation. They're:
- Writing your personalized activity code
- Adding external assembly (.dll) to UiPath.
UiPath Automation Debugging:
UiPath Automation Debugging is a method that detects and eliminates errors in the programme. It is done to make sure that the applications are error-free. Breakpoints are used to interrupt the execution of the project to verify the state at a given stage.
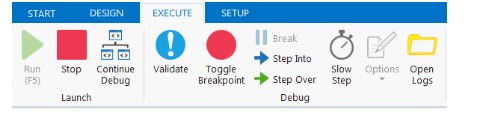
UiPath Studio works with a debug module which is used to quickly spot complex and intricate workflows. There is also an in-time engine to log & check errors in the workflow. The UiPath workflow designer will report these issues to the user. During debugging, the Properties Inspector panel shows the related properties for active action and the current value of all the declared variables. We can also slow down the debugging process with the Slow Phase option.
Conclusion:
I hope this tutorial will help the professionals who want to become an expert in RPA technology. In this tutorial we had covered all the sections required to become proficient such as RPA, Why RPA, various tools in RPA, the life cycle of RPA, how to deploy UiPath, UiPath Components, UI Automation, UiPath Workshop, UiPath coding & debugging, Screen Scraping and Citrix Automation. Moreover RPA Certification Training will make you an expert in dealing with automation problems.
UiPath Tutorial
What is RPA
RPA basically stands for Robotic process Automation. It is a development environment or the software program which is configured with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and (ML) Machine learning capabilities,which would in flip can withstand routine tasks by automated processes. The use of the RPA tool has increased significantly efficiency and enabled low man power.
What is UiPath?
UiPath is a robotic process automation framework for top end automation.UiPath application supports business solutions to streamline repeated office tasks for faster organizational change. It transforms routine tasks into a multi-tool automated system.It was established in 2005 by the Romanian businessman Daniel Dines.
Become a UiPath Certified professional by learning this HKR UiPath Training !
Why UiPath?
More and more firms are embracing Digital on a daily basis.The main benefit with digitization is the efficiency of execution.The hurdle with digitization, however, would be that it involves a variety of tools, and therefore manpower with various expertise is required to manage those tools. But employees with widely different skill sets are rare and expensive.To reduce this issue, the whole IT sector has been looking for an experienced, quick solution and that is achieved by the Uipath automation process tool.
Future scope with UiPath
RPA tools such as Uipath have had a high growth potential, in which most businesses have already shown genuine interest in consumption and enjoy the profits promised by such tools. It has certainly won a wider technology adoption and more advantages are available to consumers, as the use of such tools has reduced significantly operating costs and enhanced higher productivity at the same time.
There is indeed a shortage of RPA resource base in the existing economy, so if you have good RPA experience in this competitive field definitely you can gain a good salary package. Moreover the job opportunities like Uipath Developer, Uipath Tool User, will be able to get between $40,000 and $75,000 based on past experience. The remuneration cited may differ on the basis of distinct factors such as experience, demand, locality of the applicant for the job.
The future of RPA tools has a good aspect to that because many other businesses invest time, effort and manpower to get correct support from RPA tools that will ultimately help everyone to to streamline and improve their business processes
Products of UiPath
Here we are going to discuss the important products that are offered by the Uipath tool and its services to the businesses. They are namely Uipath studio, Uipath robot and Uipath orchestrator.
UiPath Studio:Uipath Studio has an operating system at which customers can conceptually identify the automation process using illustrations. These illustrations will also have or embody a type of tasks to be undertaken.
UiPath Robot:The very first step is to develop the full procedure and then implement the same in the studio. As the function is conducted and implemented, robots will start to pick up the defined steps and implement them without any human interference. These robots are also developed to function in a situation where the system can be triggered by humans/individuals.
UiPath Orchestrator:Uipath orchestrator is an web-based application that is used to deploy, schedule, monitor/manage robots and their respective processes. This is a consolidated system for developing and managing all the robots.
Highlighted features of UiPath
Now we are going to explore the important features of uipath. They are:
- Hosting options: The tool can be organized in all cloud and virtual terminal ecosystems, so web hosts are adaptable when using this widely accepted uipath tool for automating the tasks.
- Application Compatibility: It has a web and desktop application so that customers can use this tool based on availability. It is advantageous to have both web and desktop applications.
- Security: security is considered as an important issue by UiPath, and a number of security measures have been put in place to protect data and users.
- UiPath has enforced the Account Lockout functionality and,using this feature,consumers will be safeguarded from brute force attacks.If the customer is linked to multiple machines with the same login details, the program will actually detect and terminate the login for the first machine. So essentially, the customer will remain active in the unified location at any given point of time.
- Advanced screen scraping solution: mostly with the advent of sophisticated screen scraping solutions,it can operate with any kind of application such as Java, SAP, Flash,.Net, etc. The advantage of using this feature is that the user obtains perfect accuracy.
- This platform is dependable for the prediction of business processes. The Uipath Studio has a lot of advanced features as well.
How to install UiPath?
Now we will learn how to install the uipath step by step.
Step1:Just enter the URL https://www.uipath.com/community in the browser and click on the community edition button, enter all the required fields.
Step2;Click on the community edition button and you will receive an email with download attachment of the community edition button.
Step3: Click on the button and once the download is complete and the essential software is installed you can start using the free trial provided.
Step4: You need to enter the email and the device id through you will be detected automatically and then click on the activate button at the bottom of the screen. Now the uipath is made available on your system.
Types of UiPath Projects
In this section, we will discuss the types of projects and templates that are supported by the uipath.The projects and templates includes:
- Processes
- Library
- Orchestration process
- Background process
- Robotic enterprise framework
- Trigger based attention automation
- Transactional processes
Processes: This type of project is used to design a small blank task to develop various types of automation systems.
Library:This type of project is being used to generate configuration files and then to compile them together like a library. The libraries that have been generated can be introduced as frameworks to the automated processes.
Orchestration process:This type of template is used to perform a method with the help of service orchestration and long transactions.
Background process:The Background Process produces a method which does not involve human input and can operate as a background process. In addition, multiple background methods can run concurrently along the same robot.
Robotic enterprise framework:This type of project is designed with the objective of being used to build a business process appropriate for high deployments.
Trigger based attention automation:As the title implies, this project is used to stimulate automation in reply to a keyboard or mouse user incident.
Transactional processes:This template is used as a flowchart to design the automation workflow.
Top 30 frequently asked UiPath Interview questions !
UiPath Interface
Here we will explore different components and interfaces that are supported by the uipath tool.They are:ribbon, universal search bar, project panel, activities panel, library panel, etc.
- The ribbon panel consists of four tabs such as start, design,execute, and setup. By using the start tab one can easily create a new project.The design provides all the opportunities to customize or run any patterns, flowcharts, or access wizards, and manage variables. Execute will help you to run or stop any projects. Before beginning the debug process, delay down the steps and open the logs. The setup tab is used to compile a project or to generate a shortcut for it, schedule tasks and install extensions
- Universal search bar:The Universal Search bar users can search for everything in the libraries, activities, project and design panels.
- Library panel:The Library program enables the automation to be reused. A search box is also provided to find items faster.
- Project panel:The Project Panel allows the components of the current project to be viewed and the file location to be opened in the Windows Explorer.
- Activities panel:The Activity Panel facilitates fast access to all necessary operations that can be moved to the current project.
Related Article: UiPath vs Blue Prism
Comparison of UiPath over other automation tools:
Mostly in industry, we have a great deal of automation tools that are best practices, such as Selenium, Waite, etc. This automation software works efficiently on web applications but has limits when it comes to desktop applications. So, to satisfy desktop automation, we can certainly use UiPath.
Uipath outperforms some other automation tools commercially available by completing the appropriate features:
- Desktop Automation: Uipath can be used for desktop applications, which is a distinctive characteristic especially in comparison to other automation tools.
- Remote Applications: The Uipath Tool is fully strong and adaptable to remote desktops.
- Uipath's data handling procedures are better than other automation tools available on the market.
- Integrated scraping technique
- Ability to write logic and research methods is much better than other automation tools.
- Pricing: From a price point of view, Uipath is relatively cheap compared to their competitiveness.It's also easy to implement and adopt.
- Automation: Users do not have to perform routine tasks using the Uipath tool.
Building sample script using UiPath:
In this section, you are going to learn on how to build a sample uipath script in a few steps as follows:
Step1: Just click on the blank icon as shown in the below image.
Step2: Enter the details as required and then click create button
Step3:Next click on the recording button and then select the basic which will be taken to a small pop up window where you are asked to clock the record button.
Step4:When this icon is clicked, you will see the cursor starting to turn into a hand icon and the whole screen attempting to turn into blue and outlining all the icons around it as shown below.
Step5:Do the manual tasks you want to automate.UiPath Robotic Process Automation will automatically generate the sequence of your mouse/keyboard actions.Once the recording is finished,click Save and Exit
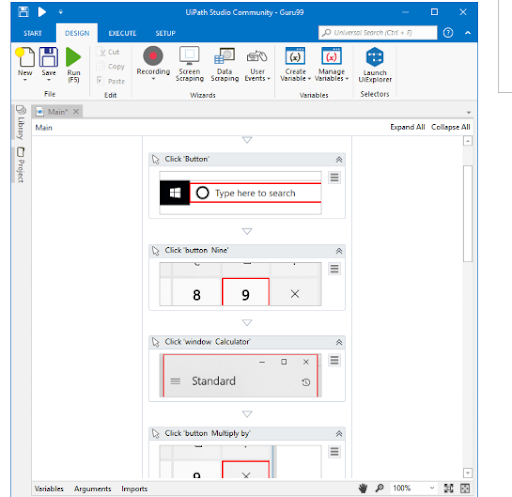
Step6:Here you can see a series of recorded steps as shown in the below image.
Step7:Just click on the run and uipath would repeat the record actions eventually.
In this manner you can easily create the small automation robots.
Related Article: Automatiom Anywhere vs UiPath
Conclusion
In the bove Uipath tutorial all the points are covered in detail related to the Uipath and how it helps the business to improve efficiency and automate the routine task thereby saving manpower and cost constraints. At present each and every sector is digirlaixaing their business operations for effectiveness and interoperability. In that context uipath is the real game and most adopted RPA tool in the current market. Also there will be great demand for the Uipath certified professionals in the industry Still had still confusion in your mind,doubt feel worry just do comments below our expats will clear all your doubts in no time.
Robotic process automation tutorial
Robot Process Automation RPA has emerged as a hot topic in the insurance plan industry. In this instalment of a sequence calculated to demystify RPA, I’ll outline some of the benefits of the technology. RPA software is capable to crunch giant quantities of statistics quickly and effortlessly. Once the commercial enterprise guidelines have been established, the device makes choices constantly and efficaciously – each and every time. There is no employee fatigue, errors or judgement calls and information can be processed 24/7/365.
RPA software automates complex, repetitive, rule-based work that would normally be finished by way of a human sitting at a desktop. This can include human duties like logging in to an application, getting into data, posting transactional facts or even performing complex calculations, however doing it all considerably faster and with greater accuracy than any character could. This functionality can be utilized in a variety of ways to desktop, net or even command line primarily based applications and built-in with ERP systems, BPM Systems and more.
RPA is the present day revolution in productivity enhancement and offers giant financial savings in phrases of time, effort and cost. When utilized to automating core business processes, RPA can lengthen the innovative problem-solving capabilities and productiveness of human beings and deliver most high quality commercial enterprise results.RPA lets in people to work smarter with today's software program to automate business company tasks, which, in turn, generates wealthy approach records that drives meaningful insights, fee and consequences for businesses. Through RPA, humans are accomplishing new levels of approach efficiency, such as prolonged operational cost, speed, accuracy and throughput volume.
About Author
As a content writer at HKR trainings, I deliver content on various technologies. I hold my graduation degree in Information technology. I am passionate about helping people understand technology-related content through my easily digestible content. My writings include Data Science, Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence, Python, Salesforce, Servicenow and etc.
Upcoming Robotic Process Automation Training Online classes
| Batch starts on 28th Feb 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 4th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 8th Mar 2026 |
|

