What exactly is the Code-To-Data Paradigm?
The traditional method is transferring data from a database to a presentation server, performing data-intensive calculations and filtering, and then presenting the filtered data to the user.
The new HANA method is to push our code to the database layer, where all of the data is stored, perform the computations there, and only bring relevant records to the presentation server.

The latency imposed by bringing enormous amounts of data to the display layer is greatly reduced by the C2D paradigm, resulting in high performance even with very big data sets.
To better appreciate this, consider the following scenario, which any ABAP developer can relate to:
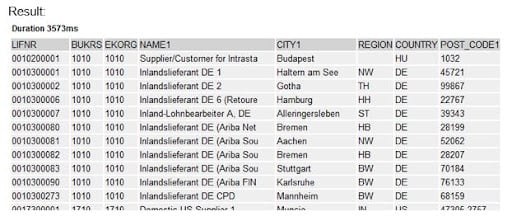
Example Scenario: An ALV report containing the master data and addresses of "ALL" active vendors who have not been marked for central deletion, deletion under "ALL" business code, or deletion under "ALL" purchasing organization.
To gain in-depth knowledge with practical experience in SAP ABAP on HANA, Then explore HKR'S SAP ABAP on HANA Online Course!
As a result of fetching data for all vendors, all business codes, and all Purchasing Organizations, performance will decrease in this case. The resulting report would need to be executed in the background, and in this situation, the typical ABAP report flow will acquire data as follows:
As a result of fetching data for all vendors, all business codes, and all Purchasing Organizations, performance will decrease in this case. The resulting report will need to be executed in the background, and in this situation, the typical ABAP report flow would acquire data as follows:
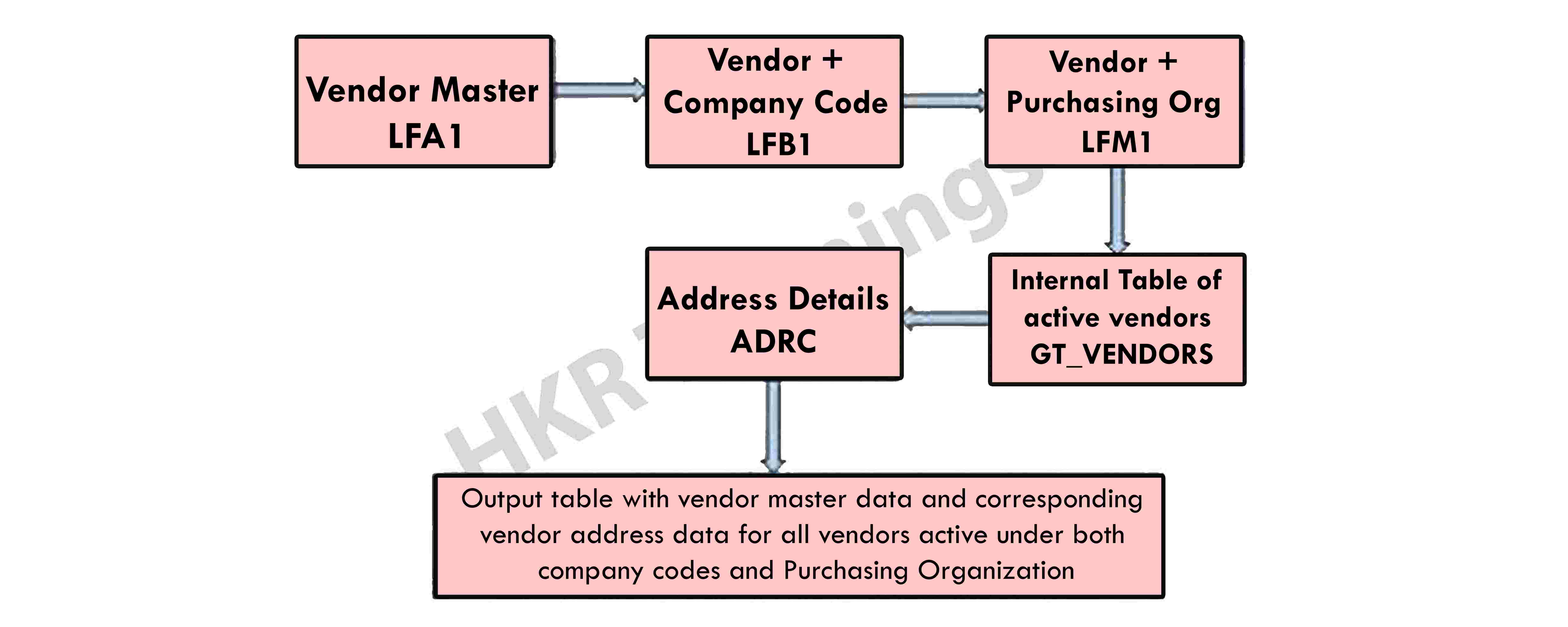
If no joins are utilized in the select statement, the presentation layer will interact with this data a few times. Furthermore, due to the massive volumes of vendor data in the sytem, using joins to fetch data from these databases would be extremely slow. So, what can I do to improve my performance here?

SAP ABAP ON HANA Training Online | Certification Course
- Master Your Craft
- Lifetime LMS & Faculty Access
- 24/7 online expert support
- Real-world & Project Based Learning
1) Programming in OpenSQL
You can write OpenSQL syntax in your ABAP code using OpenSQL programming. The fields in the select statement in OpenSQL are comma-separated, all host variables are escaped using the ‘@' sign, concatenation can be done in a single sentence using ‘| |', and so on.
The following is a summary of the above scenario:
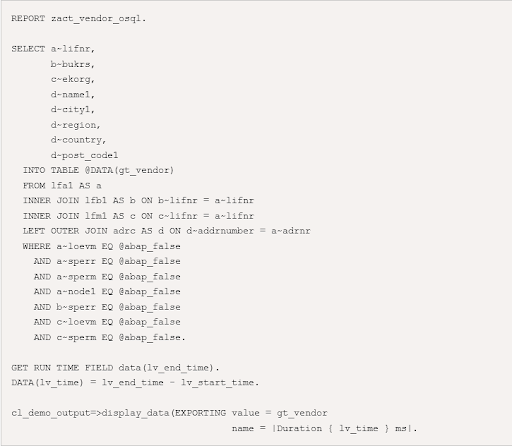
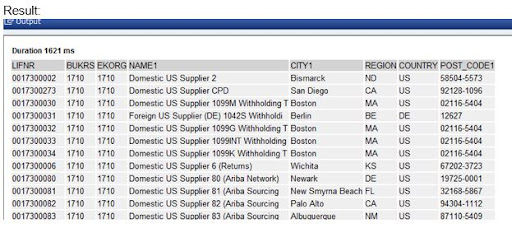
2) Views of CDS (Core Data Services)
SAP released core data services, or CDS, a new data modeling framework. Instead of being defined and consumed on the application server, data models are defined and consumed on the database server using CDS. As a result, a database-level table result view is constructed. CDS are openSQL-compatible and can be developed with ABAP development tools such as Eclipse Oxygen. AMDPs and reports can consume these as well.
In Eclipse, the preceding code would be saved as a data definition and defined as follows:
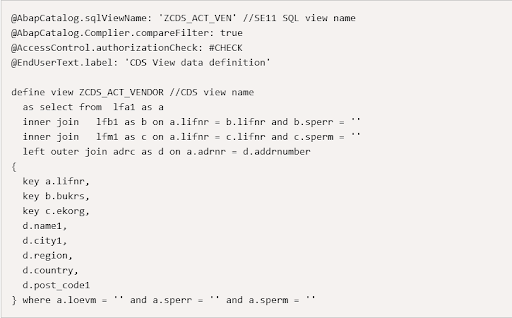
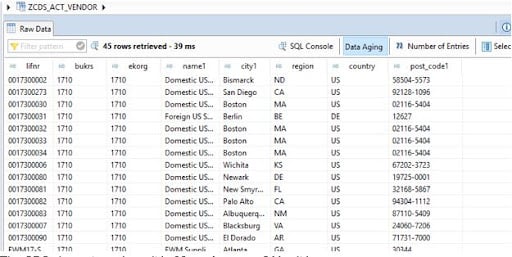
In 39 milliseconds, the CDS view returned a result. Fantastic? Yes, it is correct.

Subscribe to our YouTube channel to get new updates..!
CDS views with parameters and relationships can now be built. If you have a defined result set and some input parameters to pass, you may want to develop a CDS with parameters.
If you have several tables to address in the view and want to keep the result set flexible, you might also design a CDS with the association for a similar scenario.
3) ABAP Managed Database Procedures (AMDP)
AMDPs are database procedures that are written in ABAP and run on the database directly. AMDP classes are used to create AMDPs. The following is an example of how to develop an AMDP class using the scenario described above. An AMDP class is distinguished from other classes by the interface "IF_AMDP_MARKER_HDB."
Class definition:
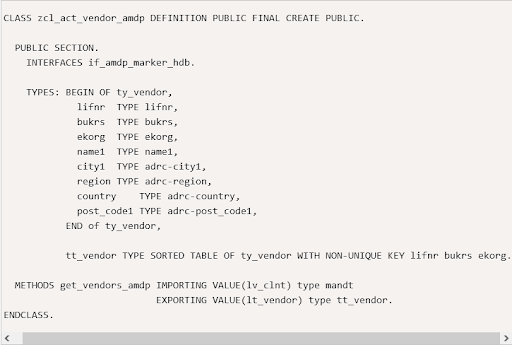
Likewise, methods defined with the notation "BY DATABASE PROCEDURE FOR DATABASE> LANGUAGE LANGUAGE>" will appear in an AMDP class implementation. In our example, the database would be HDB (HANA DB), and the programming language would be SQLSCRIPT.
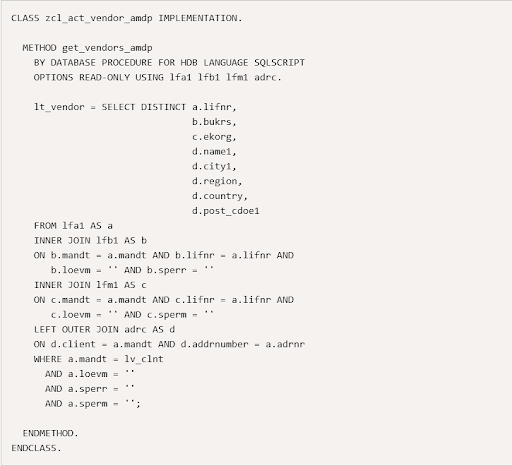
The code push-down feature can then be achieved by using this AMDP class in an ABAP program.
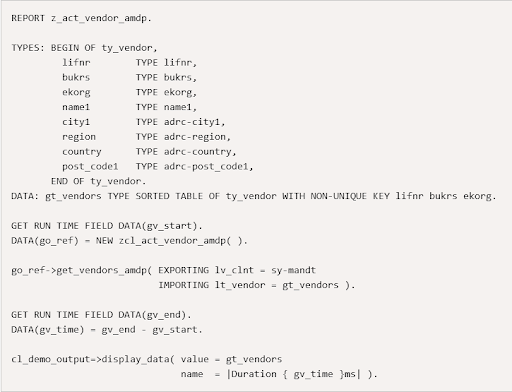
What to select AMDP or CDS or OpenSQL?
How to choose amongst the three programming styles would be a question that any developer would have.
CDS -> OpenSQL -> AMDP was the order of performance in the case above.
Does this imply that the best option in the aforementioned scenario is to construct a CDS? Not at all!
If I don't want to employ the CDS view, OpenSQL could be a good alternative.
CDS views and AMDP can only be produced with ABAP Development Tools such as Eclipse Oxygen. To learn how to install eclipse on your machine, go to the following link:
https://tools.hana.ondemand.com/#abap
When choosing between the three programming styles listed above, there are no hard and fast rules to follow. It is entirely dependent on the necessity as well as the type and manner in which data must be handled. However, the following points can help you figure out how to make the most effective decision.
Select Open SQL when:
- The table selection is unique to the application and will not be used again.
- When you need to construct CDS or AMDP but don't have an ABAP Development Tool. Both can be consumed using a GUI, but not created through one.
- When it comes to data, it doesn't require complex calculations and can be simply maintained with OpenSQL.
- When you have a complicated selection screen with many possibilities, those will be passed as single values as well.
Select CDS views when:
- The view could be reused in other applications or views.
- When there is a significant amount of data from multiple sources.
- When you understand how to write annotations to improve your CDS view.
- Just one result set is necessary.
Select AMDPs When:
- Since your entire code would be written in SQL script and the compiler fails to detect runtime SQL script problems like divide by zero, you are proficient in SQL scripting.
- Since AMDP doesn’t manage client data on its own, you'll need to handle cross-client data.
- When multiple result sets are required.
This article was written to provide you with an overview of HANA and what you can achieve with the new approaches. To any newcomer, my advice is to get your hands on a system and check it out.
Conclusion:
In this tutorial, we have learned and understood the paradigm of code-to-data with an example. The concepts of OpenSQL programming, CDS Views, AMDP, and how to choose between OpenSQL or CDS or AMDP have also been discussed.
About Author
Kavya works for HKR Trainings institute as a technical writer with diverse experience in many kinds of technology-related content development. She holds a graduate education in the Computer science and Engineering stream. She has cultivated strong technical skills from reading tech blogs and also doing a lot of research related to content. She manages to write great content in many fields like Programming & Frameworks, Enterprise Integration, Web Development, SAP, and Business Process Management (BPM). Connect her on LinkedIn and Twitter.
Upcoming SAP ABAP ON HANA Training Online | Certification Course Online classes
| Batch starts on 10th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 14th Mar 2026 |
|
||
| Batch starts on 18th Mar 2026 |
|

